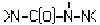 , >N-C(O)-N=N- or
, >N-C(O)-N=N- or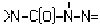 , e.g. carbonohydrazides, carbazones, semicarbazides, semicarbazones; Thioanalogues thereof
, e.g. carbonohydrazides, carbazones, semicarbazides, semicarbazones; Thioanalogues thereofWebCPC CPC COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION
A61K PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL, OR TOILET PURPOSES (devices or methods specially adapted for bringing pharmaceutical products into particular physical or administering forms A61J 3/00; chemical aspects of, or use of materials for deodorisation of air, for disinfection or sterilisation, or for bandages, dressings, absorbent pads or surgical articles A61L; {compounds per se C01, C07, C08, C12N}; soap compositions C11D; {micro-organisms per se C12N})
NOTE - This subclass covers the following subject matter, whether set forth as a composition (mixture), process of preparing the composition or process of treating using the composition:A61K 6/00 Preparations for dentistry (teeth cleaning preparations A61K 8/00, A61Q 11/00; {dental prostheses A61C 13/00; apparatus or methods for oral or dental hygiene A61C})
NOTE - A61K 6/00-A61K 6/0044 and A61K 6/083-A61K 6/10, the use of specific polymers is indicated by addition of classification symbols of the subclass C08L preceded by the sign "+", e.g. compositions for taking dental impressions containing alginates are classified in A61K 6/10+C08L 5/04A61K 6/0002 ・{Compositions characterised by physical properties}
A61K 6/0005 ・・{by refractive index}
A61K 6/0008 ・・{by particle size}
A61K 6/0011 ・・{by retraction, e.g. compositions for widening the sulcus for making dental impressions or removing teeth}
A61K 6/0014 ・・{Self-expanding, e.g. for filling teeth}
A61K 6/0017 ・・{Protective coating for natural or artificial teeth, such as sealing, dye coating, varnish}
A61K 6/002 ・・{Compositions for detecting or measuring, e.g. contact points, irregularities on natural or artificial teeth}
A61K 6/0023 ・{Chemical means for temporarily or permanently fixing teeth, palates or the like}
A61K 6/0026 ・・{Preparations for stabilising dentures in the mouth}
A61K 6/0029 ・{Primers (adhesive primers A61K 6/0023)}
A61K 6/0032 ・{Use of preparations for dental root treatment}
A61K 6/0035 ・・{Cleaning; Disinfecting}
A61K 6/0038 ・・{Filling; Sealing}
A61K 6/0041 ・・{Apical treatment}
A61K 6/0044 ・・{in combination with dental implants}
A61K 6/0047 ・{Preparations for dentistry characterised by the presence of organic or organo-metallic additives}
A61K 6/005 ・・{Cationic, anionic or redox initiators}
A61K 6/0052 ・・{Photochemical radical initiators}
A61K 6/0055 ・・{Thermal radical initiators}
A61K 6/0058 ・・{Dyes}
A61K 6/0061 ・・・{photochromic}
A61K 6/0064 ・・・{thermochromic}
A61K 6/0067 ・・{Medicaments; Drugs}
A61K 6/007 ・{Preparations for dentistry characterized by the presence of inorganic additives}
A61K 6/0073 ・・{Fillers}
A61K 6/0076 ・・・{comprising nitrogen-containing compounds}
A61K 6/0079 ・・・{comprising sulfur-containing compounds}
A61K 6/0082 ・・・{comprising phosphorus-containing compounds}
A61K 6/0085 ・・・・{Apatite}
A61K 6/0088 ・・・{comprising silicon-containing compounds}
A61K 6/0091 ・・・{Glass}
A61K 6/0094 ・・{Pigments}
A61K 6/0097 ・・{Initiators}
A61K 6/02 ・Use of preparations for artificial teeth, for filling or for capping teeth
A61K 6/0205 ・・{Ceramics}
A61K 6/021 ・・・{comprising manganese oxide}
A61K 6/0215 ・・・{comprising magnesium oxide}
A61K 6/022 ・・・{comprising beryllium oxide}
A61K 6/0225 ・・・{comprising chromium oxide}
A61K 6/023 ・・・{comprising iron oxide}
A61K 6/0235 ・・・{comprising titanium oxide}
A61K 6/024 ・・・{comprising zirconium oxide}
A61K 6/0245 ・・・{comprising hafnium oxide}
A61K 6/025 ・・・{comprising rare earth metal oxides}
A61K 6/0255 ・・・{comprising transition metal oxides}
A61K 6/026 ・・・{Leucite}
A61K 6/0265 ・・{Cermet-composites}
A61K 6/027 ・・Use of non-metallic elements or compounds thereof, e.g. carbon {(non-metallic elements per se C01B)}
A61K 6/0273 ・・・{Glass-ceramic-composites}
A61K 6/0276 ・・・{Glasses}
A61K 6/033 ・・・{Phosphorus compounds, e.g. apatite}
A61K 6/04 ・・Use of metals or alloys (alloys per se C22C)
A61K 6/043 ・・・{Rare earth metals}
A61K 6/046 ・・・{Noble metals}
A61K 6/05 ・・・Amalgams
A61K 6/06 ・・Use of inorganic cements (cements per se C04B)
A61K 6/0606 ・・・{Portland cements}
A61K 6/0612 ・・・{Silicates}
A61K 6/0618 ・・・{Pozzolans}
A61K 6/0625 ・・・{Calcium sulfates/gypsum}
A61K 6/0631 ・・・{Al-cements}
A61K 6/0637 ・・・{Ca-Al-sulfate-cements}
A61K 6/0643 ・・・{Phosphate cements (apatite A61K 6/033)}
A61K 6/065 ・・・{Ammonium cements}
A61K 6/0656 ・・・{Zeolite}
A61K 6/0662 ・・・{Quartz or SiO2}
A61K 6/0668 ・・・{Carbonates}
A61K 6/0675 ・・・{Calcium oxide}
A61K 6/0681 ・・・{comprising zirconium oxide}
A61K 6/0687 ・・・{comprising chromium oxide}
A61K 6/0693 ・・・{comprising carbides}
A61K 6/08 ・・Use of natural or synthetic resins (resins per se C08)
A61K 6/083 ・・・Compounds obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds
A61K 6/0835 ・・・・{Polycarboxylate cements or glass ionomer cements}
A61K 6/087 ・・・Compounds obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds
A61K 6/09 ・・・・Polyurethanes
A61K 6/093 ・・・・Polyorganosilicon compounds
A61K 6/097 ・・・Polysaccharides
A61K 6/10 ・Compositions for taking dental impressions (impression methods A61C 9/00)
A61K 8/00 Cosmetic or similar toilet preparations (casings or accessories for storing or handling of solid or pasty toilet or cosmetic substances A45D 40/00)
NOTE - Use of cosmetics or similar toilet preparations is further classified in subclass A61Q.A61K 8/02 ・characterised by special physical form
A61K 8/0204 ・・{Specific forms not provided for by any of groups A61K 8/0208 to A61K 8/14}
A61K 8/0208 ・・{Tissues; Wipes; Patches}
A61K 8/0212 ・・{Face masks}
A61K 8/0216 ・・{Solid or semisolid forms}
A61K 8/022 ・・・{Powders; Compacted Powders}
A61K 8/0225 ・・・・{Granulated powders}
A61K 8/0229 ・・・{Sticks}
A61K 8/0233 ・・・{Distinct layers, e.g. core/shell sticks}
A61K 8/0237 ・・・・{Striped compositions}
A61K 8/0241 ・・{Containing particulates characterized by their shape and/or structure (see also A61K 8/04, A61K 8/11, and A61K 8/14, further aspects are classified in A61K 2800/40 and subcodes)}
A61K 8/0245 ・・・{Specific shapes or structures not provided for by any of the groups of A61K 8/0241}
A61K 8/025 ・・・{Explicitly spheroidal or spherical shape}
A61K 8/0254 ・・・{Platelets; Flakes}
A61K 8/0258 ・・・・{Layered structure}
A61K 8/0262 ・・・・・{Characterized by the central layer}
A61K 8/0266 ・・・・・{Characterized by the sequence of layers}
A61K 8/027 ・・・{Fibers; Fibrils}
A61K 8/0275 ・・・{Containing agglomerated particulates}
A61K 8/0279 ・・・{Porous; Hollow}
A61K 8/0283 ・・・{Matrix particles}
A61K 8/0287 ・・・・{the particulate containing a solid-in-solid dispersion}
A61K 8/0291 ・・{Micelles}
A61K 8/0295 ・・{Liquid crystals}
A61K 8/03 ・・Liquid compositions with two or more distinct layers
A61K 8/04 ・・Dispersions; Emulsions
A61K 8/042 ・・・{Gels}
A61K 8/044 ・・・{Suspensions}
A61K 8/046 ・・・{Aerosols; Foams}
A61K 8/06 ・・・Emulsions
A61K 8/062 ・・・・{Oil-in-water emulsions}
A61K 8/064 ・・・・{Water-in-oil emulsions, e.g. Water-in-silicone emulsions}
A61K 8/066 ・・・・{Multiple emulsions, e.g. water-in-oil-in-water}
A61K 8/068 ・・・・{Microemulsions}
A61K 8/11 ・・Encapsulated compositions
A61K 8/14 ・・Liposomes; Vesicles
A61K 8/18 ・characterised by the composition
A61K 8/19 ・・containing inorganic ingredients
A61K 8/20 ・・・Halogens; Compounds thereof
A61K 8/21 ・・・・Fluorides; Derivatives thereof
A61K 8/22 ・・・Peroxides; Oxygen; Ozone
A61K 8/23 ・・・Sulfur; Selenium; Tellurium; Compounds thereof
A61K 8/24 ・・・Phosphorous; Compounds thereof
A61K 8/25 ・・・Silicon; Compounds thereof
A61K 8/26 ・・・Aluminium; Compounds thereof
A61K 8/27 ・・・Zinc; Compounds thereof
A61K 8/28 ・・・Zirconium; Compounds thereof
A61K 8/29 ・・・Titanium; Compounds thereof
A61K 8/30 ・・containing organic compounds
A61K 8/31 ・・・Hydrocarbons
A61K 8/315 ・・・・{Halogenated hydrocarbons}
A61K 8/33 ・・・containing oxygen
A61K 8/34 ・・・・Alcohols
A61K 8/342 ・・・・・{Alcohols having more than seven atoms in an unbroken chain}
A61K 8/345 ・・・・・{containing more than one hydroxy group}
A61K 8/347 ・・・・・{Phenols}
A61K 8/35 ・・・・Ketones, e.g. benzophenone
A61K 8/355 ・・・・・{Quinones}
A61K 8/36 ・・・・Carboxylic acids; Salts or anhydrides thereof
A61K 8/361 ・・・・・{Carboxylic acids having more than seven carbon atoms in an unbroken chain; Salts or anhydrides thereof}
A61K 8/362 ・・・・・Polycarboxylic acids
A61K 8/365 ・・・・・Hydroxycarboxylic acids; Ketocarboxylic acids
A61K 8/368 ・・・・・with carboxyl groups directly bound to carbon atoms or aromatic rings
A61K 8/37 ・・・・Esters of carboxylic acids
A61K 8/375 ・・・・・{the alcohol moiety containing more than one hydroxy group}
A61K 8/38 ・・・・Percompounds, e.g. peracids
A61K 8/39 ・・・・Alkoxylated derivatives, i.e. derivatives containing from 2 to 10 oxyalkylene groups
A61K 8/40 ・・・containing nitrogen (quinones containing nitrogen A61K 8/35C)
A61K 8/41 ・・・・Amines
A61K 8/411 ・・・・・{Aromatic amines, i.e. where the amino group is directly linked to the aromatic nucleus}
A61K 8/413 ・・・・・{Indoanilines; Indophenol; Indoamines}
A61K 8/415 ・・・・・{Aminophenols}
A61K 8/416 ・・・・・{Quaternary ammonium compounds (A61K 8/35 takes precedence)}
A61K 8/418 ・・・・・{containing nitro groups}
A61K 8/42 ・・・・Amides
A61K 8/43 ・・・・Guanidines
A61K 8/44 ・・・・Aminocarboxylic acids or derivatives thereof, e.g. aminocarboxylic acids containing sulfur; Salts; Esters or N-acylated derivatives thereof
A61K 8/442 ・・・・・{substituted by amido group(s)}
A61K 8/445 ・・・・・{aromatic, i.e. the carboxylic acid directly linked to the aromatic ring}
A61K 8/447 ・・・・・{containing sulfur}
A61K 8/45 ・・・・Alkoxylatedderivatives, i.e. derivatives containing from 2 to 10 oxyalkylene groups
A61K 8/46 ・・・containing sulfur (A61K 8/44 takes precedence)
A61K 8/463 ・・・・{containing sulfuric acid derivatives, e.g. sodium lauryl sulfate}
A61K 8/466 ・・・・{containing sulfonic acid derivatives; Salts}
A61K 8/49 ・・・containing heterocyclic compounds
A61K 8/4906 ・・・・{with one nitrogen as the only hetero atom}
A61K 8/4913 ・・・・・{having five membered rings, e.g. pyrrolidone carboxylic acid}
A61K 8/492 ・・・・・・{having condensed rings, e.g. indol}
A61K 8/4926 ・・・・・{having six membered rings}
A61K 8/4933 ・・・・・{having sulfur as an exocyclic substituent, e.g. pyridinethione}
A61K 8/494 ・・・・{with more than one nitrogen as the only hetero atom}
A61K 8/4946 ・・・・・{Imidazoles or their condensed derivatives, e.g. benzimidazoles}
A61K 8/4953 ・・・・・{containing pyrimidine ring derivatives, e.g. minoxidil}
A61K 8/496 ・・・・・{Triazoles or their condensed derivatives, e.g. benzotriazoles}
A61K 8/4966 ・・・・・{Triazines or their condensed derivatives}
A61K 8/4973 ・・・・{with oxygen as the only hetero atom}
A61K 8/498 ・・・・・{having 6-membered rings or their condensed derivatives, e.g. coumarin}
A61K 8/4986 ・・・・{with sulfur as the only hetero atom}
A61K 8/4993 ・・・・{Alkoxylated derivatives, i.e. derivatives containing from 2 to 10 oxyalkylene groups}
A61K 8/55 ・・・Phosphorus compounds
A61K 8/553 ・・・・{Phospholipids, e.g. lecithin}
A61K 8/556 ・・・・{Alkoxylated derivatives, i.e. derivatives containing from 2 to 10 oxyalkylene groups}
A61K 8/58 ・・・containing atoms other than carbon, hydrogen, halogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur or phosphorus
A61K 8/585 ・・・・{Organosilicon compounds}
A61K 8/60 ・・・Sugars; Derivatives thereof
A61K 8/602 ・・・・{Glycosides, e.g. rutin}
A61K 8/604 ・・・・{Alkylpolyglycosides; Derivatives thereof, e.g. esters}
A61K 8/606 ・・・・{Nucleosides; Nucleotides; Nucleic acids}
A61K 8/608 ・・・・{Alkoxylated derivatives, i.e. derivatives containing from 2 to 10 oxyalkylene groups}
A61K 8/63 ・・・Steroids; Derivatives thereof
NOTE - This group covers steroids, as defined in Note (1) after the title of subclass C07J.A61K 8/64 ・・・Proteins; Peptides; Derivatives or degradation products thereof
A61K 8/645 ・・・・{Proteins of vegetable origin; Derivatives or degradation products thereof}
A61K 8/65 ・・・・Collagen; Gelatin; Keratin; Derivatives or degradation products thereof
A61K 8/66 ・・・・Enzymes
A61K 8/67 ・・・Vitamins
A61K 8/671 ・・・・{Vitamin A; Derivatives thereof, e.g. ester of vitamin A acid, ester of retinol, retinol, retinal}
A61K 8/673 ・・・・{Vitamin B group}
A61K 8/675 ・・・・・{Vitamin B3 or vitamin B3 active, e.g. nicotinamide, nicotinic acid, nicotinyl aldehyde (tocopheryl nicotinate A61K 8/678)}
A61K 8/676 ・・・・{Ascorbic acid, i.e. vitamin C}
A61K 8/678 ・・・・{Tocopherol, i.e. vitamin E}
A61K 8/68 ・・・Sphingolipids, e.g. ceramides, cerebrosides, gangliosides
A61K 8/69 ・・・containing fluorine
A61K 8/70 ・・・・containing perfluoro groups, e.g. perfluoroethers
A61K 8/72 ・・containing organic macromolecular compounds
A61K 8/73 ・・・Polysaccharides
A61K 8/731 ・・・・{Cellulose; Quaternized cellulose derivatives}
A61K 8/732 ・・・・{Starch; Amylose; Amylopectin; Derivatives thereof}
A61K 8/733 ・・・・{Alginic acid; Salts thereof}
A61K 8/735 ・・・・{Mucopolysaccharides, e.g. hyaluronic acid; Derivatives thereof}
A61K 8/736 ・・・・{Chitin; Chitosan; Derivatives thereof}
A61K 8/737 ・・・・{Galactomannans, e.g. guar; Derivatives thereof}
A61K 8/738 ・・・・{Cyclodextrins}
A61K 8/81 ・・・obtained by reactions involving only carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds
A61K 8/8105 ・・・・{Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers}
A61K 8/8111 ・・・・・{Homopolymers or copolymers of aliphatic olefines, e.g. polyethylene, polyisobutene; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers}
A61K 8/8117 ・・・・・{Homopolymers or copolymers of aromatic olefines, e.g. polystyrene; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers}
A61K 8/8123 ・・・・{Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of compounds having one carbon-to-carbon double bond, and at least one being terminated by a halogen; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers, e.g. PVC, PTFE}
A61K 8/8129 ・・・・{Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of compounds having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals, each having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond, and at least one being terminated by an alcohol, ether, aldehydo, ketonic, acetal or ketal radical; Compositions of hydrolysed polymers or esters of unsaturated alcohols with saturated carboxylic acids; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers, e.g. polyvinylmethylether}
A61K 8/8135 ・・・・{Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of compounds having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals, each having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond, and at least one being terminated by an acyloxy radical of a saturated carboxylic acid, of carbonic acid or of a haloformic acid; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers, e.g. vinyl esters (polyvinylacetate)}
A61K 8/8141 ・・・・{Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of compounds having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals, each having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond, and at least one being terminated by only one carboxyl radical, or of salts, anhydrides, esters, amides, imides or nitriles thereof; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers}
A61K 8/8147 ・・・・・{Homopolymers or copolymers of acids; Metal or ammonium salts thereof, e.g. crotonic acid, (meth)acrylic acid; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers}
A61K 8/8152 ・・・・・{Homopolymers or copolymers of esters, e.g. (meth)acrylic acid esters; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers}
A61K 8/8158 ・・・・・{Homopolymers or copolymers of amides or imides, e.g. (meth) acrylamide; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers}
A61K 8/8164 ・・・・{Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of compounds having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals, each having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond, and at least one being terminated by a carboxyl radical, and containing at least one other carboxyl radical in the molecule, or of salts, anhydrides, esters, amides, imides or nitriles thereof; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers, e.g. poly(methyl vinyl ether-co-maleic anhydride)}
A61K 8/817 ・・・・{Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of compounds having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals, each having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond, and at least one being terminated by a single or double bond to nitrogen or by a heterocyclic ring containing nitrogen; Compositions or derivatives of such polymers, e.g. vinylimidazol, vinylcaprolactame, allylamines (Polyquaternium 6)}
A61K 8/8176 ・・・・・{Homopolymers of N-vinyl-pyrrolidones. Compositions of derivatives of such polymers}
A61K 8/8182 ・・・・・{Copolymers of vinyl-pyrrolidones. Compositions of derivatives of such polymers}
A61K 8/8188 ・・・・{Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of compounds having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals, each having only one carbon-to-carbon double bonds, and at least one being terminated by a bond to sulfur or by a hertocyclic ring containing sulfur; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers}
A61K 8/8194 ・・・・{Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of compounds having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals, at least one having two or more carbon-to-carbon double bonds; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers}
A61K 8/84 ・・・obained by reactions otherwise than those involving only carbon-carbon unsaturated bonds
A61K 8/85 ・・・・Polyesters
A61K 8/86 ・・・・Polyethers
A61K 8/87 ・・・・Polyurethanes
A61K 8/88 ・・・・Polyamides
A61K 8/89 ・・・・Polysiloxanes
A61K 8/891 ・・・・・saturated, e.g. dimethicone, phenyl trimethicone, C24-C28 methicone or stearyl dimethicone
A61K 8/892 ・・・・・・modified by a hydroxy group, e.g. dimethiconol
A61K 8/893 ・・・・・・modified by an alkoxy or aryloxy group, e.g. behenoxy dimethicone or stearoxy dimethicone
A61K 8/894 ・・・・・・modified by a polyoxyalkylene group, e.g. cetyl dimethicone copolyol
A61K 8/895 ・・・・・containing silicon bound to unsaturated aliphatic groups, e.g. vinyl dimethicone
A61K 8/896 ・・・・・containing atoms other than silicon, carbon, oxygen and hydrogen, e.g. dimethicone copolyol phosphate
A61K 8/897 ・・・・・・containing halogen, e.g. fluorosilicones
A61K 8/898 ・・・・・・containing nitrogen, e.g. amodimethicone, trimethyl silyl amodimethicone or dimethicone propyl PG-betaine
A61K 8/899 ・・・・・・containing sulfur, e.g. sodium PG-propyldimethicone thiosulfate copolyol
A61K 8/90 ・・・Block copolymers (A61K 8/89 takes precedence)
A61K 8/91 ・・・Graft copolymers (A61K 8/89 takes precedence)
A61K 8/92 ・・Oils, fats or waxes; Derivatives thereof, e.g. hydrogenation products thereof
A61K 8/922 ・・・{of vegetable origin}
A61K 8/925 ・・・{of animal origin}
A61K 8/927 ・・・{of insects, e.g. shellac}
A61K 8/96 ・・containing material, or derivatives thereof of undetermined constitution
A61K 8/965 ・・・{of inanimate origin}
A61K 8/97 ・・・of vegetable origin, e.g. plant extracts
A61K 8/975 ・・・・{Pollen; Algae, Higher fungi}
A61K 8/98 ・・・of animal origin
A61K 8/981 ・・・・{of mammals or bird}
A61K 8/982 ・・・・・{Reproductive organs; Embryos, Eggs}
A61K 8/983 ・・・・・{Blood, e.g. plasma}
A61K 8/985 ・・・・・{Skin or skin outgrowth, e.g. hair, nails}
A61K 8/986 ・・・・・{Milk; Derivatives thereof, e.g. butter}
A61K 8/987 ・・・・{of species other than mammals or birds}
A61K 8/988 ・・・・・{Honey; Royal jelly, Propolis}
A61K 8/99 ・・・from micro-organisms
A61K 9/00 Medicinal preparations characterised by special physical form (nuclear magnetic resonance contrast preparations or magnetic resonance imaging contrast preparataions A61K 49/18; preparations containing radioactive substances A61K 51/12)
NOTE - Among the one-dot groups of A61K 9/00, classification is not made in the last appropriate place.A61K 9/0002 ・{Galenical forms characterised by the drug release technique; Application systems commanded by energy}
A61K 9/0004 ・・{Osmotic delivery systems; Sustained release driven by osmosis, thermal energy or gas}
A61K 9/0007 ・・{Effervescent (A61K 9/0065 takes precedence)}
A61K 9/0009 ・・{involving or responsive to electricity, magnetism or acoustic waves; Galenical aspects of sonophoresis, iontophoresis, electroporation or electroosmosis (microelectromechanical systems A61K 9/0097)}
A61K 9/0012 ・{Galenical forms characterised by the site of application}
A61K 9/0014 ・・{Skin, i.e. galenical aspects of topical compositions (non-active ingredients are additionally classified in A61K 47/00; A61K 9/0009, A61K 9/0021, A61K 9/70D, A61K 9/7023 take precedence; cosmetic preparations A61K 8/00, A61Q; preparations for wound dressings or bandages A61L 26/00)}
A61K 9/0017 ・・・{Non-human animal skin, e.g. pour-on, spot-on}
A61K 9/0019 ・・{Injectable compositions; Intramuscular, intravenous, arterial, subcutaneous administration; Compositions to be administered through the skin in an invasive manner (non-active ingredients are additionally classified in A61K 47/00)}
A61K 9/0021 ・・・{Intradermal administration, e.g. through microneedle arrays, needleless injectors (mechanical aspects A61M)}
A61K 9/0024 ・・・{Solid, semi-solid or solidifying implants, which are implanted or injected in body tissue (compositions for intravenous administration, normal injectable solutions or dispersions for e.g. subcutaneous administration A61K 9/0019; brain implants A61K 9/0085; (coated) prostheses, catheters or stents A61L)}
A61K 9/0026 ・・・{Blood substitute; Oxygen transporting formulations; Plasma extender}
A61K 9/0029 ・・・{Parenteral nutrition; Parenteral nutrition compositions as drug carriers}
A61K 9/0031 ・・{Rectum, anus}
A61K 9/0034 ・・{Urogenital system, e.g. vagina, uterus, cervix, penis, scrotum, urethra, bladder; Personal lubricants}
A61K 9/0036 ・・・{Devices retained in the vagina or cervix for a prolonged period, e.g. intravaginal rings, medicated tampons, medicated diaphragms}
A61K 9/0039 ・・・{Devices retained in the uterus for a prolonged period, e.g. intrauterine devices for contraception}
A61K 9/0041 ・・{Mammary glands, e.g. breasts, udder; Intramammary administration}
A61K 9/0043 ・・{Nose}
A61K 9/0046 ・・{Ear}
A61K 9/0048 ・・{Eye, e.g. artificial tears}
A61K 9/0051 ・・・{Ocular inserts, ocular implants}
A61K 9/0053 ・・{Mouth and digestive tract, i.e. intraoral and peroral administration (rectal administration A61K 9/0031)}
A61K 9/0056 ・・・{Mouth soluble or dispersible forms; Suckable, eatable, chewable coherent forms; Forms rapidly disintegrating in the mouth; Lozenges; Lollipops; Bite capsules; Baked products; Baits or other oral forms for animals}
A61K 9/0058 ・・・・{Chewing gums (non-medicinal aspects, preparing chewing gum A23G 4/00; chewing gum for care of the teeth or oral cavity, e.g. with breath freshener A61Q 11/00)}
A61K 9/006 ・・・{Oral mucosa, e.g. mucoadhesive forms, sublingual droplets; Buccal patches or films; Buccal sprays}
A61K 9/0063 ・・・{Periodont}
A61K 9/0065 ・・・{Forms with gastric retention, e.g. floating on gastric juice, adhering to gastric mucosa, expanding to prevent passage through the pylorus}
A61K 9/0068 ・・・{Rumen, e.g. rumen bolus}
A61K 9/007 ・・{Pulmonary tract; Aromatherapy}
A61K 9/0073 ・・・{Sprays or powders for inhalation; Aerolised or nebulised preparations generated by other means than thermal energy; (nasal sprays A61K 9/0043; inhalation of vapours of volatile or heated drugs, e.g. essential oils or nicotine, A61K 9/007; devices A61M)}
A61K 9/0075 ・・・・{for inhalation via a dry powder inhaler (DPI), e.g. comprising micronized drug mixed with lactose carier particles}
A61K 9/0078 ・・・・{for inhalation via a nebulizer such as a jet nebulizer, ultrasonic nebulizer, e.g. in the form of aqueous drug solutions or dispersions}
A61K 9/008 ・・・・{comprising drug dissolved or suspended in liquid propellant for inhalation via a pressurized metered dose inhaler (MDI)}
A61K 9/0082 ・・・{Lung surfactant, artificial mucus}
A61K 9/0085 ・・{Brain, e.g. brain implants; Spinal cord}
A61K 9/0087 ・{Galenical forms not covered by A61K 9/02 to A61K 9/7023}
A61K 9/009 ・・{Sachets, pouches characterised by the material or function of the envelope (with gastric retention A61K 9/0065; sachets which are not administered but function merely as a container are classified according to the content, e.g. sachets comprising powder for reconstitution of a drink A61K 9/0095)}
A61K 9/0092 ・・{Hollow drug-filled fibres, tubes of the core-shell type, coated fibres, coated rods, microtubules, nanotubes (fibres of the matrix type containing drug A61K 9/70)}
A61K 9/0095 ・・{Drinks; Beverages; Syrups; Compositions for reconstitution thereof, e.g. powders or tablets to be dispersed in a glass of water; Veterinary drenches (A61K 9/0007 takes precedence; eatable gels or foams A61K 9/0056; oral mucosa adhesive forms A61K 9/006)}
A61K 9/0097 ・・{Micromachined devices; Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS); Devices obtained by lithographic treatment of silicon; Devices comprising chips (intradermal microneedle arrays A61K 9/0021; MEMS in general B81B 7/02)}
A61K 9/02 ・Suppositories; Bougies; Bases therefor; {Ovules}({apparatus for making A61J 3/08; devices for introducing into the body A61M 31/00})
A61K 9/025 ・・{characterised by shape or structure, e.g. hollow layered, coated}
A61K 9/06 ・Ointments; Bases therefor; {Other semi-solid forms, e.g. creams, sticks, gels (composition of ointments, creams or gels A61K 47/00)}
WARNING - incomplete, see also A61K 9/00M, A61K 47/00A61K 9/08 ・Solutions; {(composition of solutions A61K 47/00)}
WARNING - incomplete, see also A61K 9/00M, A61K 47/00, A61K 9/0095A61K 9/10 ・Dispersions; Emulsions; {(A61K 9/06 takes precedence; composition of dispersions, emulsions A61K 47/00)}
WARNING - incomplete, see also A61K 9/00M, A61K 47/00, A61K 9/0095A61K 9/107 ・・Emulsions; {Emulsion preconcentrates; Micelles (composition of emulsions A61K 47/00)}
WARNING - incomplete, see also A61K 9/00M, A61K 47/00, A61K 9/0095A61K 9/1075 ・・・{Microemulsions or submicron emulsions; Preconcentrates or solids thereof; Micelles, e.g. made of phospholipids or block copolymers (A61K 9/0026 takes precedence)}
A61K 9/113 ・・・Multiple emulsions, e.g. oil-in-water-in-oil; {(A61K 9/0026 takes precedence)}
A61K 9/12 ・・Aerosols; Foams {(A61K 9/0043, A61K 9/0056, A61K 9/006, A61K 9/0073 take precedence; spray-films A61K 9/7015)}
A61K 9/122 ・・・{Foams; Dry foams (edible foams A61K 9/0056)}
A61K 9/124 ・・・{characterised by the propellant}
A61K 9/127 ・・Liposomes
A61K 9/1271 ・・・{Non-conventional liposomes, e.g. PEGylated liposomes, liposomes coated with polymers (see also A61K 47/48815)}
A61K 9/1272 ・・・・{with substantial amounts of non-phosphatidyl, i.e. non-acylglycerophosphate, surfactants as bilayer-forming substances, e.g. cationic lipids (with cholesterol as the only non-phosphatidyl surfactant A61K 9/127; cationic lipid/DNA complexes see also A61K 47/48046)}
A61K 9/1273 ・・・・{Polymersomes; Liposomes with polymerisable or polymerised bilayer-forming substances (polymers grafted or coated on phosphatidyl liposomes A61K 9/1271, on non-phosphatidyl liposomes A61K 9/1272)}
A61K 9/1274 ・・・{Non-vesicle bilayer structures, e.g. liquid crystals, tubules, cubic phases, cochleates; Sponge phases}
A61K 9/1275 ・・・{Lipoproteins; Chylomicrons; Artificial HDL, LDL, VLDL, protein-free species thereof; Precursors thereof}
A61K 9/1276 ・・・{Globules of milk or constituents thereof}
A61K 9/1277 ・・・{Processes for preparing; Proliposomes}
A61K 9/1278 ・・・・{Post-loading, e.g. by ion or pH gradient}
A61K 9/14 ・Particulate form, e.g. powders, {Processes for size reducing of pure drugs or the resulting products, Pure drug nanoparticles (microspheres A61K 9/16; microcapsules A61K 9/50; nanocapsules, nanoparticles of the matrix type A61K 9/51)}
A61K 9/141 ・・{Intimate drug-carrier mixtures characterised by the carrier, e.g. ordered mixtures, adsorbates, solid solutions, eutectica, co-dried, co-solubilised, co-kneaded, co-milled, co-ground products, co-precipitates, co-evaporates, co-extrudates, co-melts; Drug nanoparticles with adsorbed surface modifiers ((co)spray-dried products A61K 9/16, (co)lyophilised products A61K 9/19; the carrier being chemically bound to the active ingredient A61K 47/48)}
A61K 9/143 ・・・{with inorganic compounds}
A61K 9/145 ・・・{with organic compounds}
A61K 9/146 ・・・{with organic macromolecular compounds}
A61K 9/148 ・・・{with compounds of unknown constitution, e.g. material from plants or animals (with oils, fats, waxes, shellac A61K 9/145)}
A61K 9/16 ・・Agglomerates; Granulates; Microbeadlets; {Microspheres; Pellets; Solid products obtained by spray drying, spray freeze drying, spray congealing, (multiple) emulsion solvent evaporation or extraction (A61K 9/20 takes precedence if the final form is a tablet; microspheres with drug-free outer coating, microcapsules A61K 9/50; mixture of different granules, microcapsules, (coated) microparticles A61K 9/50M; nanoparticles A61K 9/51)}
A61K 9/1605 ・・・{Excipients; Inactive ingredients}
A61K 9/1611 ・・・・{Inorganic compounds}
A61K 9/1617 ・・・・{Organic compounds, e.g. phospholipids, fats}
A61K 9/1623 ・・・・・{Sugars or sugar alcohols, e.g. lactose; Derivatives thereof; Homeopathic globules}
A61K 9/1629 ・・・・{Organic macromolecular compounds}
A61K 9/1635 ・・・・・{obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyvinyl pyrrolidone, poly(meth)acrylates}
A61K 9/1641 ・・・・・{obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyethylene glycol, poloxamers}
A61K 9/1647 ・・・・・・{Polyesters, e.g. poly(lactide-co-glycolide)}
A61K 9/1652 ・・・・・{Polysaccharides, e.g. alginate, cellulose derivatives; Cyclodextrin (homeopathic globules A61K 9/1623)}
A61K 9/1658 ・・・・・{Proteins, e.g. albumin, gelatin}
A61K 9/1664 ・・・・{Compounds of unknown constitution, e.g. material from plants or animals (oils, fats, waxes, shellac A61K 9/1617)}
A61K 9/167 ・・・{with an outer layer or coating comprising drug; with chemically bound drugs or non-active substances on their surface (with further drug-free outer coating A61K 9/50K)}
A61K 9/1676 ・・・・{having a drug-free core with discrete complete coating layer containing drug (adsorbates of liquid drug formulations on inert powders without simultaneous granulation step A61K 9/14H; with further drug-free outer coating A61K 9/5078; drug conjugated to non-active particles A61K 47/48853)}
A61K 9/1682 ・・・{Processes}
A61K 9/1688 ・・・・{resulting in pure drug agglomerate optionally containing up to 5% of excipient}
A61K 9/1694 ・・・・{resulting in granules or microspheres of the matrix type containing more than 5% of excipient}
A61K 9/19 ・・lyophilised, {i.e. freeze-dried, solutions or dispersions (lyophilised products with subsequent particle size reduction A61K 9/14; granules or pellets made by lyphilisation A61K 9/16P; solid oral dosage forms made by lyophilisation A61K 9/20P; lyophilisation additives A61K 47/00)}
A61K 9/20 ・Pills, tablets, {discs, rods (A61K 9/0004, A61K 9/0007, A61K 9/0056, A61K 9/0065 take precedence; for reconstitution of a drink A61K 9/0095)}
A61K 9/2004 ・・{Excipients; Inactive ingredients}
A61K 9/2009 ・・・{Inorganic compounds}
A61K 9/2013 ・・・{Organic compounds, e.g. phospholipids, fats}
A61K 9/2018 ・・・・{Sugars, or sugar alcohols, e.g. lactose, mannitol; Derivatives thereof, e.g. polysorbates}
A61K 9/2022 ・・・{Organic macromolecular compounds}
A61K 9/2027 ・・・・{obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyvinyl pyrrolidone, poly(meth)acrylates}
A61K 9/2031 ・・・・{obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyethylene glycol, polyethylene oxide, poloxamers}
A61K 9/2036 ・・・・・{Silicones; Polysiloxanes}
A61K 9/204 ・・・・・{Polyesters, e.g. poly(lactide-co-glycolide)}
A61K 9/2045 ・・・・・{Polyamides; Polyaminoacids, e.g. polylysine}
A61K 9/205 ・・・・{Polysaccharides, e.g. alginate, gums; Cyclodextrin}
A61K 9/2054 ・・・・・{Cellulose; Cellulose derivatives, e.g. hydroxypropyl methylcellulose}
A61K 9/2059 ・・・・・{Starch, including chemically or physically modified derivatives; Amylose; Amylopectin; Dextrin}
A61K 9/2063 ・・・・{Proteins, e.g. gelatin}
A61K 9/2068 ・・・{Compounds of unknown constitution, e.g. material from plants or animals (oils, fats, waxes, shellac A61K 9/2013)}
A61K 9/2072 ・・{characterised by shape, structure or size; Tablets with holes, special break lines or identification marks; Partially coated tablets; Disintegrating flat shaped forms (A61K 9/0004, A61K 9/0056, A61K 9/0065 take precedence)}
A61K 9/2077 ・・・{Tablets comprising drug-containing microparticles in a substantial amount of supporting matrix; Multiparticulate tablets}
A61K 9/2081 ・・・・{with microcapsules or coated microparticles according to A61K 9/50}
A61K 9/2086 ・・・{Layered tablets, e.g. bilayer tablets; Tablets of the type inert core-active coat (active cores with a complete drug-free outer coat A61K 9/28)}
A61K 9/209 ・・・・{containing drug in at least two layers or in the core and in at least one outer layer}
A61K 9/2095 ・・{Tabletting processes; Dosage units made by direct compression of powders or specially processed granules, by eliminating solvents, by melt-extrusion, by injection molding, by 3D printing (mechanical aspects A61J 3/00)}
A61K 9/28 ・・Dragees; Coated pills or tablets {e.g. with film or compression coating (A61K 9/2072 takes precedence, e.g. partially coated tablets A61K 9/2072, coated multilayer tablets A61K 9/2086, tablets with drug-coated core A61K 9/209)}
A61K 9/2806 ・・・{Coating materials}
A61K 9/2813 ・・・・{Inorganic compounds}
A61K 9/282 ・・・・{Organic compounds, e.g. fats}
A61K 9/2826 ・・・・・{Sugars or sugar alcohols, e.g. sucrose; Derivatives thereof}
A61K 9/2833 ・・・・{Organic macromolecular compounds}
A61K 9/284 ・・・・・{obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyvinyl pyrrolidone}
A61K 9/2846 ・・・・・・{Poly(meth)acrylates}
A61K 9/2853 ・・・・・{obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyethylene glycol, polyethylene oxide, poloxamers, poly(lactide-co-glycolide)}
A61K 9/286 ・・・・・{Polysaccharides, e.g. gums; Cyclodextrin}
A61K 9/2866 ・・・・・・{Cellulose; Cellulose derivatives, e.g. hydroxypropyl methylcellulose}
A61K 9/2873 ・・・・・{Proteins, e.g. gelatin}
A61K 9/288 ・・・・{Compounds of unknown constitution, e.g. material from plants or animals (oils, fats, waxes, shellac A61K 9/282)}
A61K 9/2886 ・・・{having two or more different drug-free coatings; Tablets of the type inert core-drug layer-inactive layer (of the type active core-drug layer-inactive layer A61K 9/209)}
A61K 9/2893 ・・・{Tablet coating processes (mechanical aspects A61J 3/06)}
A61K 9/48 ・Preparations in capsules, e.g. of gelatin, of chocolate; {(A61K 9/0004 takes precedence; bite capsules A61K 9/0056)}
A61K 9/4808 ・・{characterised by the form of the capsule or the structure of the filling; Capsules containing small tablets; Capsules with outer layer for immediate drug release (capsules filled with granules or microparticles A61K 9/16; filled with microcapsules or coated microparticles A61K 9/50; with mixture of different granules, microcapsules, (coated) microparticles A61K 9/50M)}
A61K 9/4816 ・・{Wall or shell material}
A61K 9/4825 ・・・{Proteins, e.g. gelatin (gelatin capsule shells with substantial amounts of other macromolecular substances A61K 9/48B)}
A61K 9/4833 ・・{Encapsulating processes; Filling of capsules (mechanical aspects A61J 3/07)}
A61K 9/4841 ・・{Filling excipients; Inactive ingredients}
A61K 9/485 ・・・{Inorganic compounds}
A61K 9/4858 ・・・{Organic compounds}
A61K 9/4866 ・・・{Organic macromolecular compounds}
A61K 9/4875 ・・・{Compounds of unknown constitution, e.g. material from plants or animals (oils, fats, waxes, shellac A61K 9/4858)}
A61K 9/4883 ・・{Capsule finishing, e.g. dyeing, aromatising, polishing}
A61K 9/4891 ・・{Coated capsules; Multilayered drug free capsule shells (with drug coating for immediate release A61K 9/48A; osmotic devices A61K 9/0004)}
A61K 9/50 ・・Microcapsules {having a gas, liquid or semi-solid filling; Solid microparticles or pellets surrounded by a distinct coating layer, e.g. coated microspheres, coated drug crystals (A61K 9/2081 takes precedence; particles with a single coating comprising drug A61K 9/16K)}
A61K 9/5005 ・・・{Wall or coating material}
A61K 9/501 ・・・・{Inorganic compounds}
A61K 9/5015 ・・・・{Organic compounds, e.g. fats, sugars}
A61K 9/5021 ・・・・{Organic macromolecular compounds}
A61K 9/5026 ・・・・・{obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyvinyl pyrrolidone, poly(meth)acrylates}
A61K 9/5031 ・・・・・{obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyethylene glycol, poly(lactide-co-glycolide)}
A61K 9/5036 ・・・・・{Polysaccharides, e.g. gums, alginate; Cyclodextrin}
A61K 9/5042 ・・・・・・{Cellulose; Cellulose derivatives, e.g. phthalate or acetate succinate esters of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose}
A61K 9/5047 ・・・・・・・{Cellulose ethers containing no ester groups, e.g. hydroxypropyl methylcellulose}
A61K 9/5052 ・・・・・{Proteins, e.g. albumin}
A61K 9/5057 ・・・・・・{Gelatin}
A61K 9/5063 ・・・・{Compounds of unknown constitution, e.g. material from plants or animals (oils, fats, waxes, shellac A61K 9/5015)}
A61K 9/5068 ・・・・・{Cell membranes or bacterial membranes enclosing drugs (with additional exogenous lipids A61K 9/127; virus envelopes A61K 9/5184)}
A61K 9/5073 ・・・{having two or more different coatings optionally including drug-containing subcoatings}
A61K 9/5078 ・・・・{with drug-free core}
A61K 9/5084 ・・・{Mixtures of one or more drugs in different galenical forms, at least one of which being granules, microcapsules or (coated) microparticles according to A61K 9/16 or A61K 9/50, e.g. for obtaining a specific release pattern or for combining different drugs (tablets containing such a mixture A61K 9/2077)}
A61K 9/5089 ・・・{Processes}
A61K 9/5094 ・・・{Microcapsules containing magnetic carrier material, e.g. ferrite for drug targetting}
A61K 9/51 ・・・Nanocapsules; {Nanoparticles;(nanotubes A61K 9/0092; polymeric micelles A61K 9/1075; polymersomes A61K 9/1273; pure drug nanoparticles A61K 9/14; drug nanoparticles with adsorbed surface modifiers A61K 9/141; conjugates, e.g. between drug and non-active nanoparticles, A61K 47/48; preparations for in vivo diagnosis A61K 49/00; with radioactive substances A61K 51/00)}
A61K 9/5107 ・・・・{Excipients; Inactive ingredients}
A61K 9/5115 ・・・・・{Inorganic compounds}
A61K 9/5123 ・・・・・{Organic compounds, e.g. fats, sugars}
A61K 9/513 ・・・・・{Organic macromolecular compounds; Dendrimers}
A61K 9/5138 ・・・・・・{obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyvinyl pyrrolidone, poly(meth)acrylates}
A61K 9/5146 ・・・・・・{obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyethylene glycol, polyamines, polyanhydrides}
A61K 9/5153 ・・・・・・・{Polyesters, e.g. poly(lactide-co-glycolide)}
A61K 9/5161 ・・・・・・{Polysaccharides, e.g. alginate, chitosan, cellulose derivatives; Cyclodextrin}
A61K 9/5169 ・・・・・・{Proteins, e.g. albumin, gelatin}
A61K 9/5176 ・・・・・{Compounds of unknown constitution, e.g. material from plants or animals (oils, fats, waxes, shellac A61K 9/5123)}
A61K 9/5184 ・・・・・・{Virus capsids or envelopes enclosing drugs (with additional exogenous lipids A61K 9/127; bacterial membranes A61K 9/5068)}
A61K 9/5192 ・・・・{Processes}
A61K 9/70 ・Web, sheet or filament bases; {Films; Fibres of the matrix type containing drug; (hollow drug-filled fibres A61K 9/0092; bandages, dressings or absorbent pads A61F 13/00, chemical aspects thereof A61L 15/00)}
A61K 9/7007 ・・{Drug-containing films, membranes or sheets(A61K 9/0041 ,A61K 9/0043
,A61K 9/006 ,A61K 9/0063 take precedence)}A61K 9/7015 ・・{Drug-containing film-forming compositions, e.g. spray-on}
A61K 9/7023 ・・{Transdermal patches and similar drug-containing composite devices, e.g. cataplasms (galenical aspects of iontophoretic devices A61K 9/0009; microneedle arrays A61K 9/0021; buccal patches A61K 9/006)}
A61K 9/703 ・・・{characterised by shape or structure; Details concerning release liner or backing; Refillable patches; User-activated patches}
A61K 9/7038 ・・・・{Transdermal patches of the drug-in-adhesive type, i.e. comprising drug in the skin-adhesive layer}
A61K 9/7046 ・・・・・{the adhesive comprising macromolecular compounds}
A61K 9/7053 ・・・・・・{obtained by reactions only involving carbon to carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyvinyl, polyisobutylene, polystyrene}
A61K 9/7061 ・・・・・・・{Polyacrylates}
A61K 9/7069 ・・・・・・{obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon to carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polysiloxane, polyesters, polyurethane, polyethylene oxide}
A61K 9/7076 ・・・・・{the adhesive comprising ingredients of undetermined constitution or reaction products thereof, e.g. rosin or other plant resins}
A61K 9/7084 ・・・・{Transdermal patches having a drug layer or reservoir, and one or more separate drug-free skin-adhesive layers, e.g. between drug reservoir and skin, or surrounding the drug reservoir; Liquid-filled reservoir patches}
A61K 9/7092 ・・・・{Transdermal patches having multiple drug layers or reservoirs, e.g. for obtaining a specific release pattern, or for combining different drugs}
A61K 31/00 Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
NOTE - When classifying in groups A61K 31/00 to A61K 41/00 the symbol A61K 2300/00 may be added, using Combination Sets, to indicate a mixture of activeingredients.A61K 31/01 ・Hydrocarbons
A61K 31/015 ・・carbocyclic
A61K 31/02 ・Halogenated hydrocarbons
A61K 31/025 ・・carbocyclic
A61K 31/03 ・・・aromatic
A61K 31/035 ・・having aliphatic unsaturation
A61K 31/04 ・Nitro compounds
A61K 31/045 ・Hydroxy compounds, e.g. alcohols; Salts thereof, e.g. alcoholates
A61K 31/047 ・・having two or more hydroxy groups, e.g. sorbitol
A61K 31/05 ・・Phenols
A61K 31/055 ・・・the aromatic ring being substituted by halogen
A61K 31/06 ・・・the aromatic ring being substituted by nitro groups
A61K 31/065 ・・Diphenyl-substituted acyclic alcohols
A61K 31/07 ・・Retinol compounds, e.g. vitamin A (retinoic acids A61K 31/203)
A61K 31/075 ・Ethers or acetals
A61K 31/08 ・・acyclic, e.g. paraformaldehyde
A61K 31/085 ・・having an ether linkage to aromatic ring nuclear carbon
A61K 31/09 ・・・having two or more such linkages
A61K 31/095 ・Sulfur, selenium, or tellurium compounds, e.g. thiols
A61K 31/10 ・・Sulfides; Sulfoxides ; Sulfones
A61K 31/105 ・・Persulfides (thiuram disulfides A61K 31/145; thiosulfonic acids A61K 31/185)
A61K 31/11 ・Aldehydes
A61K 31/115 ・・Formaldehyde
A61K 31/12 ・Ketones
A61K 31/121 ・・acyclic
A61K 31/122 ・・having the oxygen directly attached to a ring, e.g. quinones, vitamin K1, anthralin
A61K 31/125 ・・・Camphor; Nuclear substituted derivatives thereof
A61K 31/13 ・Amines {(A61K 31/04 takes precedence)}
A61K 31/131 ・・acylic
A61K 31/132 ・・having two or more amino groups, e.g. spermidine, putrescine
A61K 31/133 ・・having hydroxy groups, e.g. sphingosine
A61K 31/135 ・・having aromatic rings {e.g. ketamine, nortriptyline (methadone A61K 31/137)}
A61K 31/136 ・・・having the amino group directly attached to the aromatic ring, e.g. benzeneamine
A61K 31/137 ・・・Arylalkylamines, e.g. amphetamine, epihephrine, salbutamol, ephedrine {or methadone}
A61K 31/138 ・・・Aryloxyalkylamines, e.g. propanolol, tamoxifen, phenoxybenzamine (atenolol A61K 31/165; pindolol A61K 31/404; timolol A61K 31/5377)
A61K 31/14 ・・Quaternary ammonium compounds, e.g. edrophonium, choline (betaines A61K 31/205)
A61K 31/145 ・・having sulfur, e.g. thiurams (>N-C(S)-S-C(S)-N< and >N-C(S)-S-S-C(S)-N<), Sulfinylamines (-N=SO), Sulfonylamines (-N=SO2) (isothiourea A61K 31/155)
A61K 31/15 ・・Oximes (>C=N-O); Hydrazines (>N-N<); Hydrazones (>N-N=) {Imines (C-N=C)}
A61K 31/155 ・・Amidines (-N=C-N-), e.g. guanidine (H2N-C(=NH)-NH2), isourea (N=C(OH)-NH2), isothiourea (-N=C(SH)-NH2)
A61K 31/16 ・Amides, e.g. hydroxamic acids
A61K 31/164 ・・of a carboxlic acid with an aminoalcohol, e.g. ceramides
A61K 31/165 ・・having aromatic rings, e.g. colchicine, atenolol, progabide
A61K 31/166 ・・・having the carbon of a carboxamide group directly attached to the aromatic ring, e.g. procainamide, procarbazine, metoclopramide, labetalol
A61K 31/167 ・・・having the nitrogen of a carboxamide group directly attached to the aromatic ring, e.g. lidocaine, paracetamol
A61K 31/17 ・・having the group >N-C(O)-N< or >N-C(S)-N<, e.g. urea, thiourea, carmustine (isoureas, isothioureas A61K 31/155; sulfonylureas A61K 31/64)
A61K 31/175 ・・・having the group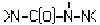 , >N-C(O)-N=N- or
, >N-C(O)-N=N- or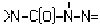 , e.g. carbonohydrazides, carbazones, semicarbazides, semicarbazones; Thioanalogues thereof
, e.g. carbonohydrazides, carbazones, semicarbazides, semicarbazones; Thioanalogues thereof
A61K 31/18 ・・Sulfonamides (compounds containing a para-N-benzene-sulfonyl-N- group A61K 31/63)
A61K 31/185 ・Acids; Anhydrides, halides or salts thereof, e.g. sulfur acids, imidic, hydrazonic, hydroximic acids (hydroxamic acids A61K 31/16; peroxy acids A61K 31/327)
NOTE - Cyclic anhydrides are considered to be heterocyclic ringsA61K 31/19 ・・Carboxylic acids, e.g. valproic acid (Salicylic acid A61K 31/60)
A61K 31/191 ・・・having two or more hydroxy groups, e.g. gluconic acid
A61K 31/192 ・・・having aromatic groups, e.g. sulindac, 2-arylpropionic acids, ethacrynic acid
A61K 31/194 ・・・having two or more carboxyl groups, e.g. succinic, maleic or phthalic acid
A61K 31/195 ・・・having an amino group
A61K 31/196 ・・・・the amino group being directly attached to a ring, e.g. anthranilic acid, mefenamic acid, diclofenac, chlorambucil
A61K 31/197 ・・・・the amino and the carboxyl group being attached to the same acyclic carbon chain, e.g. gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), beta-alanine, epsilon-aminocaproic acid, pantothenic acid (carnitine A61K 31/205)
A61K 31/198 ・・・・・Alpha-aminoacids, e.g. alanine, edetic acids (EDTA), (betaine A61K 31/205; proline A61K 31/401; tryptophan A61K 31/405; histidine A61K 31/4172; peptides not degraded to individual aminoacids A61K 38/00)
A61K 31/20 ・・・having a carboxyl group bound to a chain of seven or more carbon atoms, e.g. stearic, palmitic, arachidic acids
A61K 31/201 ・・・・having one or two double bonds, e.g. oleic, linoleic acids
A61K 31/202 ・・・・having three or more double bonds, e.g. linolenic (eicosanoids, e.g. leukotrienes A61K 31/557)
A61K 31/203 ・・・・Retinoic acids {Salts thereof}
A61K 31/205 ・・Amine addition salts of organic acids; Inner quaternary ammonium salts, e.g. betaine, carnitine
A61K 31/21 ・Esters, e.g. nitroglycerine, selenocyanates
A61K 31/215 ・・of carboxylic acids
A61K 31/216 ・・・of acids having aromatic rings, e.g. benactizyne, clofibrate
A61K 31/22 ・・・of acyclic acids, e.g. pravastatin
A61K 31/221 ・・・・with compounds having an amino group, e.g. acetylcholine, acetylcarnitine
A61K 31/222 ・・・・with compounds having aromatic groups, e.g. dipivefrine, ibopamine
A61K 31/223 ・・・・of alpha-aminoacids
A61K 31/225 ・・・・Polycarboxylic acids
A61K 31/23 ・・・・of acids having a carboxyl group bound to a chain of seven or more carbon atoms
A61K 31/231 ・・・・・having one or two double bonds
A61K 31/232 ・・・・・having three or more double bonds, e.g. etretinate
A61K 31/235 ・・・having an aromatic ring attached to a carboxyl group
A61K 31/24 ・・・・having an amino or nitro group
A61K 31/245 ・・・・・Amino benzoic acid types, e.g. procaine, novocaine (salicylic acid esters A61K 31/60)
A61K 31/25 ・・・with polyoxyalkylated alcohols, e.g. esters of polyethylene glycol
A61K 31/255 ・・of sulfoxy acids or sulfur analogues thereof
A61K 31/26 ・・Cyanate or isoyanate esters; Thiocyanate or isothiocyanate esters
A61K 31/265 ・・of carbonic, thiocarbonic, or thiocarboxylic acids, e.g. thioacetic acid, xanthogenic acid, trithiocarbonic acid
A61K 31/27 ・・of carbamic or thiocarbamic acids, meprobamate, carbachol, neostigmine
A61K 31/275 ・Nitriles; Isonitriles
A61K 31/277 ・・having a ring, e.g. verapamil
A61K 31/28 ・Compounds containing heavy metals
A61K 31/282 ・・Platinum compounds
A61K 31/285 ・・Arsenic compounds
A61K 31/29 ・・Antimony or bismuth compounds
A61K 31/295 ・・Iron group metal compounds
A61K 31/30 ・・Copper compounds
A61K 31/305 ・・Mercury compounds
A61K 31/31 ・・・containing nitrogen
A61K 31/315 ・・Zinc compounds
A61K 31/32 ・・Tin compounds
A61K 31/325 ・Carbamic acids; Thiocarbamic acids; Anhydrides or salts thereof (thiurams A61K 31/145)
A61K 31/327 ・Peroxy compounds, e.g. hydroperoxides, peroxides, peroxyacids
A61K 31/33 ・Heterocyclic compounds
A61K 31/335 ・・having oxygen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. fungichromin
A61K 31/336 ・・・having three-membered rings, e.g. oxirane, fumagillin
A61K 31/337 ・・・having four-membered rings, e.g. taxol
A61K 31/34 ・・・having five-membered rings with one oxygen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. isosorbide
A61K 31/341 ・・・・not condensed with another ring, e.g. ranitidine, furosemide, bufetolol, muscarine
A61K 31/343 ・・・・condensed with a carbocyclic ring, e.g. coumaran, bufuralol, befunolol, clobenfurol, amiodarone
A61K 31/345 ・・・・Nitrofurans (nitrofurantoin A61K 31/4178)
A61K 31/35 ・・・having six-membered rings with one oxygen as the only ring hetero atom
A61K 31/351 ・・・・not condensed with another ring
A61K 31/352 ・・・・condensed with carbocyclic rings, e.g. cannabinols, methantheline
A61K 31/353 ・・・・・3,4-Dihydrobenzopyrans, e.g. chroman, catechin
A61K 31/355 ・・・・・・Tocopherols, e.g. vitamin E
A61K 31/357 ・・・having two or more oxygen atoms in the same ring, e.g. crown ethers, guanadrel
A61K 31/36 ・・・Compounds containing methylenedioxyphenyl groups, e.g. sesamin
A61K 31/365 ・・・Lactones
A61K 31/366 ・・・・having six-membered rings, e.g. delta-lactones
A61K 31/37 ・・・・・Coumarins, e.g. psoralen
A61K 31/375 ・・・・Ascorbic acid, i.e. vitamin C; Salts thereof
A61K 31/38 ・・having sulfur as a ring hetero atom
A61K 31/381 ・・・having five-membered rings
A61K 31/382 ・・・having six-membered rings, e.g. thioxanthenes (thiotixene A61K 31/496)
A61K 31/385 ・・・having two or more sulfur atoms in the same ring
A61K 31/39 ・・・having oxygen in the same ring
A61K 31/395 ・・having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine, rifamycins (rifampin A61K 31/496)
A61K 31/396 ・・・having thre-membered rings, e.g. aziridine
A61K 31/397 ・・・having four-membered rings, e.g. azetidine
A61K 31/40 ・・・having five-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. sulpiride, succinimide, tolmetin, buflomedil
A61K 31/401 ・・・・Proline; Derivatives thereof, e.g. captopril
A61K 31/4015 ・・・・having oxo groups directly attached to the heterocyclic ring, e.g. piracetam, ethosuximide
A61K 31/402 ・・・・1-aryl substituted, e.g. piretanide
A61K 31/4025 ・・・・not condensed and containing further heterocyclic rings, e.g. cromakalim
A61K 31/403 ・・・・condensed with carbocyclic rings, e.g. carbazole
A61K 31/4035 ・・・・・Isoindoles, e.g. phthalimide
A61K 31/404 ・・・・・Indoles, e.g. pindolol
A61K 31/4045 ・・・・・・Indole-alkylamines; Amides thereof, e.g. serotonin, melatonin
A61K 31/405 ・・・・・・Indole-alkanecarboxylic acids; Derivatives thereof, e.g. tryptophan, indomethacin
A61K 31/407 ・・・・condensed with other heterocyclic ring systems, e.g. ketorolac, physostigmine
A61K 31/409 ・・・・having four such rings, e.g. phorphine derivatives, bilirubin, biliverdine (hemin, hematin A61K 31/555)
A61K 31/41 ・・・having five-membered rings with two or more ring hetero atoms, at least one of which being nitrogen, e.g. tetrazole
A61K 31/415 ・・・・1,2-Diazoles
A61K 31/4152 ・・・・・having oxo groups directly attached to the heterocyclic ring, e.g. antipyrine, phenylbutazone, sulfinpyrazone
A61K 31/4155 ・・・・・non condensed and containing further heterocyclic rings
A61K 31/416 ・・・・・condensed with carbocyclic ring systems, e.g. indazole
A61K 31/4162 ・・・・・condensed with heterocyclic ring systems
A61K 31/4164 ・・・・1,3-Diazoles
A61K 31/4166 ・・・・・having oxo groups directly attached to the heterocyclic ring, e.g. phenytoin
A61K 31/4168 ・・・・・having a nitrogen attached in position 2, e.g. clonidine
A61K 31/417 ・・・・・Imidazole-alkylamines, e.g. histamine, phentolamine
A61K 31/4172 ・・・・・Imidazole-alkanecarboxylic acids, e.g. histidine
A61K 31/4174 ・・・・・Arylalkylimidazoles, e.g. oxymetazolin, naphazoline, miconazole
A61K 31/4178 ・・・・・not condensed 1,3-diazoles and containing further heterocyclic rings, e.g. pilocarpine, nitrofurantoin
A61K 31/4184 ・・・・・condensed with carbocyclic rings, e.g. benzimidazoles
A61K 31/4188 ・・・・・condensed with other heterocyclic ring systems, e.g. biotin, sorbinil
A61K 31/4192 ・・・・1,2,3-Triazoles
A61K 31/4196 ・・・・1,2,4-Triazoles
A61K 31/42 ・・・・Oxazoles
A61K 31/421 ・・・・・1,3-Oxazoles, e.g. pemoline, trimethadione
A61K 31/422 ・・・・・not condensed and containing further heterocyclic rings
A61K 31/423 ・・・・・condensed with carbocyclic rings
A61K 31/424 ・・・・・condensed with heterocyclic ring systems, e.g. clavulanic acid
A61K 31/4245 ・・・・Oxadiazoles
A61K 31/425 ・・・・Thiazoles
A61K 31/426 ・・・・・1,3-Thiazoles
A61K 31/427 ・・・・・not condensed and containing further heterocyclic rings
A61K 31/428 ・・・・・condensed with carbocyclic rings
A61K 31/429 ・・・・・condensed with heterocyclic ring systems
A61K 31/43 ・・・・・・Compounds containing 4-thia-1-azabicyclo [3.2.0] heptane ring systems,i.e. compounds containing a ring system of the formula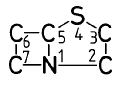 e.g. penicillins, penems
e.g. penicillins, penems
A61K 31/431 ・・・・・・・containing further heterocyclic rings, e.g. ticarcillin, azlocillin, oxacillin
A61K 31/433 ・・・・Thidiazoles
A61K 31/435 ・・・having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
A61K 31/4353 ・・・・ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems
A61K 31/4355 ・・・・・the heterocyclic ring system containing a five-membered ring having oxygen as a ring hetero atom
A61K 31/436 ・・・・・the heterocyclic ring system containing a six-membered ring having oxygen as a ring hetero atom, e..g. rapamycin
A61K 31/4365 ・・・・・the heterocyclic ring system having sulfur as a ring hetero atom, e.g. ticlopidine
A61K 31/437 ・・・・・the heterocyclic ring system containing a five-membered ring having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. indolizine, beta-carboline
A61K 31/4375 ・・・・・the heterocyclic ring system containing a six-membered ring having nitrogen as a ring heteroatom, e.g. quinolizines, naphthyridines, berberine, vincamine
A61K 31/438 ・・・・the ring being spiro-condensed with carbocyclic ring systems
A61K 31/439 ・・・・the ring forming part of a bridged ring system, e.g. quinuclidine (8-azabicyclo [3.2.1] octanes A61K 31/46)
A61K 31/44 ・・・・Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof
A61K 31/4402 ・・・・・only substituted in position 2, e.g. pheniramine, bisacodyl
A61K 31/4406 ・・・・・only substituted in position 3, e.g. zimeldine (nicotinic acid A61K 31/455)
A61K 31/4409 ・・・・・only substituted in position 4, e.g. isoniazid, iproniazid
A61K 31/4412 ・・・・・having oxo groups directly attached to the heterocyclic ring
A61K 31/4415 ・・・・・Pyridoxine, i.e. Vitamin B6 (pyridoxal phosphate A61K 31/675)
A61K 31/4418 ・・・・・having a carbocyclic group directly attached to the heterocyclic ring, e.g. cyproheptadine
A61K 31/4422 ・・・・・1,4-Dihydropyridines, e.g. nifedipine, nicardipine
A61K 31/4425 ・・・・・Pyridinium derivatives, e.g. pralidoxime, pyridostigmine
A61K 31/4427 ・・・・・containing further heterocyclic ring systems
A61K 31/443 ・・・・・・containing a five-membered ring with oxygen as a ring hetero atom
A61K 31/4433 ・・・・・・containing a six-membered ring with oxygen as a ring hetero atom
A61K 31/4436 ・・・・・・containing a heterocyclic ring having sulfur as a ring hetero atom
A61K 31/4439 ・・・・・・containing a five-membered ring with nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. omeprazole (nicotine A61K 31/465)
A61K 31/444 ・・・・・・containing a six-membered ring with nitrogen as a ring heteroatom, e.g. amrinone
A61K 31/445 ・・・・・Non condensed piperidines, e.g. piperocaine
A61K 31/4453 ・・・・・・only substituted in position 1, e.g. propipocaine, diperodon
A61K 31/4458 ・・・・・・only substituted in position 2, e.g. methylphenidate
A61K 31/4462 ・・・・・・only substituted in position 3
A61K 31/4465 ・・・・・・only substituted in position 4
A61K 31/4468 ・・・・・・having a nitrogen directly attached in position 4, e.g. clebopride, fentanyl
A61K 31/45 ・・・・・・having oxo groups directly attached to the heterocyclic ring, e.g. cycloheximide
A61K 31/451 ・・・・・・having a carbocyclic group directly attached to the heterocyclic ring, e.g. glutethimide, meperidine, loperamide, phencyclidine, piminodine
A61K 31/4515 ・・・・・・having a butyrophenone group in position 1, e.g. haloperidol (pipamperone A61K 31/4545)
A61K 31/452 ・・・・・・Piperidinium derivatives (pancuronium A61K 31/58)
A61K 31/4523 ・・・・・・containing further heterocyclic ring systems
A61K 31/4525 ・・・・・・・containing a five-membered ring with oxygen as a ring hetero atom
A61K 31/453 ・・・・・・・containing a six-membered ring with oxygen as a ring hetero atom
A61K 31/4535 ・・・・・・・containing a heterocyclic ring having sulfur as a ring hetero atom, e.g. pizotifen
A61K 31/454 ・・・・・・・containing a five-membered ring with nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. pimozide, domperidone
A61K 31/4545 ・・・・・・・containing a six-membered ring with nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. pipamperone, anabasine
A61K 31/455 ・・・・・Nicotinic acids, e.g. niacin; Derivatives thereof, e.g. esters, amides
A61K 31/46 ・・・・8-Azabicyclo [3.2.1] octane; Derivatives thereof, e.g. atropine, cocaine
A61K 31/465 ・・・・Nicotine; Derivatives thereof
A61K 31/47 ・・・・Quinolines; Isoquinolines
A61K 31/4704 ・・・・・2-Quinolinones, e.g. carbostyril
A61K 31/4706 ・・・・・4-Aminoquinolines; 8-Aminoquinolines, e.g. chloroquine, primaquine
A61K 31/4709 ・・・・・Non-condensed quinolines and containing further heterocyclic rings
A61K 31/472 ・・・・・Non-condensed isoquinolines, e.g. papaverine
A61K 31/4725 ・・・・・・containing further heterocyclic rings
A61K 31/473 ・・・・・ortho- or peri-condensed with carbocyclic ring systems, e.g. acridines, phenanthridines
A61K 31/4738 ・・・・・ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems
A61K 31/4741 ・・・・・・condensed with ring systems having oxygen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. tubocuraran derivatives, noscapine, bicuculline
A61K 31/4743 ・・・・・・condensed with ring systems having sulfur as a ring hetero atom
A61K 31/4745 ・・・・・・condensed with ring systems having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. phenantrolines (yohimbine derivatives, vinblastine A61K 31/475; ergoline derivatives A61K 31/48)
A61K 31/4747 ・・・・・Spiro-condensed
A61K 31/4748 ・・・・・forming part of bridged ring systems (strychnine A61K 31/475; morphinan derivatives A61K 31/485)
A61K 31/475 ・・・・・having an indole ring, e.g. yohimbine, reserpine, strychnine, vinblastine (vincamine A61K 31/4375)
A61K 31/48 ・・・・・Ergoline derivatives, e.g. lysergic acid, ergotamine
A61K 31/485 ・・・・・Morphinan derivatives, e.g. morphine, codeine
A61K 31/49 ・・・・・Cinchonan derivatives, e.g. quinine
A61K 31/495 ・・・having six-membered rings with two {or more} nitrogen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms, e.g. piperazine {or tetrazines}(A61K 31/48 takes precedence){(with three nitrogen atoms A61K 31/53)}
A61K 31/496 ・・・・Non-condensed piperazines containing further heterocyclic rings, e.g. rifampin, thiothixene
A61K 31/4965 ・・・・Non-condensed pyrazines
A61K 31/497 ・・・・・containing further heterocyclic rings
A61K 31/498 ・・・・Pyrazines or piperazines ortho- and peri-condensed with carbocyclic ring systems, e.g. quinoxaline, phenazine
A61K 31/4985 ・・・・Pyrazines or piperazines ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems
A61K 31/499 ・・・・Spiro-condensed pyrazines or piperazines
A61K 31/4995 ・・・・Pyrazines or piperazines forming part of bridged ring systems
A61K 31/50 ・・・・Pyridazines; Hydrogenated pyridazines
A61K 31/501 ・・・・・not condensed and containing further heterocyclic rings
A61K 31/502 ・・・・・ortho- or peri-condensed with carbocyclic ring systems, e.g. cinnoline, phthalazine
A61K 31/5025 ・・・・・ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems
A61K 31/503 ・・・・・spiro-condensed
A61K 31/504 ・・・・・forming part of bridged ring systems
A61K 31/505 ・・・・Pyrimidines; Hydrogenated pyrimidines, e.g. trimethoprim
A61K 31/506 ・・・・・not condensed and containing further heterocyclic rings
A61K 31/51 ・・・・・・Thiamines, e.g. vitamin B1
A61K 31/513 ・・・・・having oxo groups directly attached to the heterocyclic ring, e.g. cytosine
A61K 31/515 ・・・・・Barbituric acids; Derivatives thereof, e.g. sodium pentobarbital
A61K 31/517 ・・・・・ortho- or peri-condensed with carbocyclic ring systems, e.g. quinazoline, perimidine
A61K 31/519 ・・・・・ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic rings
A61K 31/52 ・・・・・・Purines, e.g. adenine
A61K 31/522 ・・・・・・・having oxo groups directly attached to the heterocyclic ring, e.g. hypoxanthine, guanine, acyclovir
A61K 31/525 ・・・・・・Isoalloxazines, e.g. riboflavins, vitamin B2
A61K 31/527 ・・・・・spiro-condensed
A61K 31/529 ・・・・・forming part of bridged ring systems
A61K 31/53 ・・・having six-membered rings with three nitrogens as the only ring hetero atoms, e.g. chlorazanil, melamine, (melarsoprol A61K 31/555){(with four nitrogen atoms A61K 31/495)}
A61K 31/535 ・・・having six-membered rings with at least one nitrogen and one oxygen as the ring hetero atoms, e.g. 1,2-oxazines
A61K 31/5355 ・・・・non-condensed oxazines and containing further heterocyclic rings
A61K 31/536 ・・・・ortho- or peri-condensed with carbocyclic ring systems
A61K 31/5365 ・・・・ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems
A61K 31/537 ・・・・spiro-condensed or forming part of bridged ring systems
A61K 31/5375 ・・・・1,4-Oxazines, e.g. morpholine
A61K 31/5377 ・・・・・not condensed and containing further heterocyclic rings, e.g. timolol
A61K 31/538 ・・・・・ortho- or peri-condensed with carbocyclic ring systems
A61K 31/5383 ・・・・・ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems
A61K 31/5386 ・・・・・Spiro-condensed or forming part of bridged ring systems
A61K 31/539 ・・・・having two or more oxygen atoms in the same ring, e.g. dioxazines
A61K 31/5395 ・・・・having two or more nitrogen atoms in the same ring, e.g. oxadiazines
A61K 31/54 ・・・having six-membered rings with at least one nitrogen and one sulfur as the ring hetero atoms, e.g. sulthiame
A61K 31/541 ・・・・non-condensed thiazines containing further heterocyclic rings
A61K 31/5415 ・・・・ortho- or peri-condensed with carbocyclic ring systems, e.g. phenothiazine, chlorpromazine, piroxicam
A61K 31/542 ・・・・ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems
A61K 31/545 ・・・・・Compounds containing 5-thia-1-azabicyclo [4.2.0] octane ring systems, i.e. compounds containing a ring system of the formula: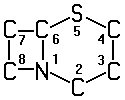 , e.g. cephalosporins, {cefaclor, or cephalexine}
, e.g. cephalosporins, {cefaclor, or cephalexine}
A61K 31/546 ・・・・・・containing further heterocyclic rings, e.g. cephalothin
A61K 31/547 ・・・・spiro-condensed or forming part of bridged ring systems
A61K 31/548 ・・・・having two or more sulfur atoms in the same ring
A61K 31/549 ・・・・having two or more nitrogen atoms in the same ring, e.g. hydrochlorothiazide
A61K 31/55 ・・・having seven-membered rings, e.g. azelastine, pentylenetetrazole
A61K 31/551 ・・・・having two nitrogen atoms, e.g. dilazep
A61K 31/5513 ・・・・・1,4-Benzodiazepines, e.g. diazepam {or clozapine}
A61K 31/5517 ・・・・・・condensed with five-membered rings having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. imidazobenzodiazepines, triazolam
A61K 31/553 ・・・・having at least one nitrogen and one oxygen as ring hetero atoms, e.g. loxapine, staurosporine
A61K 31/554 ・・・・having at least one nitrogen and one sulfur as ring hetero atoms, e.g. chlothiapine, diltiazem
A61K 31/555 ・・containing heavy metals, e.g. hemin, hematin, melarsoprol
A61K 31/557 ・Eicosanoids, e.g. leukotrienes {or prostaglandins}
A61K 31/5575 ・・having a cyclopentane, e.g. Prostaglandin E2, Prostaglandin F2-alpha
A61K 31/5578 ・・having a pentalene ring system, e.g. carbacyclin, iloprost
A61K 31/558 ・・having heterocyclic rings containing oxygen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. thromboxanes
A61K 31/5585 ・・・having five-membered rings containing oxygen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. prostacyclin
A61K 31/559 ・・having heterocyclic rings containing hetero atoms other than oxygen
A61K 31/56 ・Compounds containing cyclopenta[a]hydrophenanthrene ring systems; Derivatives, e.g. steroids
NOTE - Attention is drawn to Note (1) following the title of subclass C07J which explains what is covered by the term "steroids"A61K 31/565 ・・not substituted in position 17 beta by a carbon atom, e.g. estrane, estradiol
A61K 31/566 ・・・having an oxo group in position 17, e.g. estrone
A61K 31/567 ・・・substituted in position 17 alpha, e.g. mestranol, norethandrolone
A61K 31/568 ・・・substituted in positions 10 and 13 by a chain having at least one carbon atom, e.g. androstanes, e.g. testosterone
A61K 31/5685 ・・・・having an oxo group in position 17, e.g. androsterone
A61K 31/569 ・・・・substituted in position 17 alpha, e.g. ethisterone
A61K 31/57 ・・substituted in position 17 beta by a chain of two carbon atoms, e.g. pregnane, progesterone
A61K 31/573 ・・・substituted in position 21, e.g. cortisone, dexamethasone, prednisone {or aldosterone}
A61K 31/575 ・・substituted in position 17 beta by a chain of three or more carbon atoms, e.g. cholane, cholestane, ergosterol, sitosterol
A61K 31/58 ・・containing heterocyclic rings, e.g. danazol, stanozolol, pancuronium or digitogenin {(digitoxin A61K 31/7048)}
A61K 31/585 ・・・containing lactone rings, e.g. oxandrolone, bufalin
A61K 31/59 ・Compounds containing 9, 10- seco- cyclopenta[a]hydrophenanthrene ring systems
A61K 31/592 ・・9,10-Secoergostane derivatives, e.g. ergocalciferol, i.e. vitamin D2
A61K 31/593 ・・9,10-Secocholestane derivatives, e.g. cholecalciferol, i.e. vitamin D3
A61K 31/60 ・Salicylic acid; Derivatives thereof
A61K 31/603 ・・having further aromatic rings, e.g. diflunisal
A61K 31/606 ・・having amino groups
A61K 31/609 ・・Amides, e.g. salicylamide {(labetalol, metoclopramide A61K 31/166)}
A61K 31/612 ・・having the hydroxy group in position 2 esterified, e.g. salicylsulfuric acid (fosfosal A61K 31/661)
A61K 31/616 ・・・by carboxylic acids, e.g. acetylsalicyclic acid
A61K 31/618 ・・having the carboxyl group in position 1 esterified, e.g. salsalate
A61K 31/621 ・・・having the hydroxy group in position 2 esterified, e.g. benorylate
A61K 31/625 ・・having heterocyclic substituents, e.g. 4-salicycloylmorpholine, (sulfasalazine A61K 31/635)
A61K 31/63 ・Compounds containing para-N-benzenesulfonyl-N-groups, e.g. sulfanilamide, p-nitrobenzenesulfonyl hydrazide
A61K 31/635 ・・having a heterocyclic ring, e.g. sulfasalazine
A61K 31/64 ・Sulfonylureas, e.g. glibenclamide, tolbutamide, chlorpropamide
A61K 31/65 ・Tetracyclines
A61K 31/655 ・Azo (-N=N-){(sulfasalazine A61K 31/635)}, diazo (=N2), azoxy (>N-O-N< or N(=O)-N<), azido (-N3) or diazoamino (-N=N-N<) compounds
A61K 31/66 ・Phosphorus compounds
A61K 31/661 ・・Phosphorus acids or esters thereof not having P-C bonds, e.g. fosfosal, dichlorvos, malathion {or mevinphos}
A61K 31/6615 ・・・Compounds having two or more esterified phosphorus acid groups, e.g. inositol triphosphate, phytic acid
A61K 31/662 ・・Phosphorus acids or esters thereof having P-C bonds, e.g. foscarnet, trichlorfon
A61K 31/663 ・・・Compounds having two or more phosphorus acid groups or esters thereof, e.g. clodronic acid, pamidronic acid
A61K 31/664 ・・Amides of phosphorus acids
A61K 31/665 ・・having oxygen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. fosfomycin
A61K 31/67 ・・having sulfur as a ring hetero atom
A61K 31/675 ・・having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. pyridoxal phosphate
A61K 31/683 ・・Diesters of a phosphorus acid with two hydroxy compounds, e.g. phosphatidylinositols
A61K 31/685 ・・・one of the hydroxy compounds having nitrogen atoms, e.g. phosphatidylserine, lecithin
A61K 31/688 ・・・both hydroxy compounds having nitrogen atoms, e.g. sphingomyelin
A61K 31/69 ・Boron compounds
A61K 31/695 ・Silicon compounds
A61K 31/70 ・Carbohydrates; Sugars; Derivatives thereof (sorbitol A61K 31/047)
NOTE - In this group, the expressions are used with the meanings indicated in Note (3) following the title of the subclass C07HA61K 31/7004 ・・Monosaccharide having only carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms
A61K 31/7008 ・・Compounds having an amino group directly attached to a carbon atom of the saccharide radical, e.g. D-galactosamine, ranimustine
A61K 31/7012 ・・Compounds having a free or esterified carboxyl group attached, directly or through a carbon chain, to a carbon atom of the saccharide radical, e.g. glucuronic acid, neuraminic acid (gluconic acid A61K 31/191; ascorbic acid A61K 31/375)
A61K 31/7016 ・・Disaccharides, e.g. lactose, lactulose (lactobionic acid A61K 31/7032)
A61K 31/702 ・・Oligosaccharides, i.e. having three to five saccharide radicals attached to each other by glycosidic linkages
A61K 31/7024 ・・Esters of saccharides
A61K 31/7028 ・・Compounds having saccharide radicals attached to non-saccharide compounds by glycosidic linkages
A61K 31/7032 ・・・attached to a polyol, i.e. compound having two or more free or esterified hydroxy groups, including the hydroxy group involved in the glycosidic linkage, e.g. monoglucosyldiacylglycerides, lactobionic acid, gangliosides
A61K 31/7034 ・・・attached to a carbocyclic compound, e.g. phloridzin
A61K 31/7036 ・・・・having at least one amino group directly attached to the carbocyclic ring, e.g. streptomycin, gentamycin, amikacin, validamycin, fortimicins
A61K 31/704 ・・・・attached to a condensed carbocyclic ring system, e.g. sennosides, thiocolchicosides, escin, daunorubicin {(digitoxin A61K 31/7048)}
A61K 31/7042 ・・Compounds having saccharide radicals and heterocyclic rings
A61K 31/7048 ・・・having oxygen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. leucoglucosan, hesperidin, erythromycin, nystatin {digitoxin or digoxin}
A61K 31/7052 ・・・having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. nucleosides, nucleotides
A61K 31/7056 ・・・・containing five-membered rings with nitrogen as a ring hetero atom
A61K 31/706 ・・・・containing six-membered rings with nitrogen as a ring hetero atom
A61K 31/7064 ・・・・・containing condensed or non-condensed pyrimidines
A61K 31/7068 ・・・・・・having oxo groups directly attached to the pyrimidine ring, e.g. cytidine, cytidylic acid
A61K 31/7072 ・・・・・・・having two oxo groups directly attached to the pyrimidine ring, e.g. uridine, uridylic acid, thymidine, zidovudine
A61K 31/7076 ・・・・・・containing purines, e.g. adenosine, adenylic acid
A61K 31/708 ・・・・・・・having oxo groups directly attached to the purine ring system, e.g. guanosine, guanylic acid
A61K 31/7084 ・・Compounds having two nucleosides or nucleotides, e.g. nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide, flavine-adenine dinucleotide
A61K 31/7088 ・・Compounds having three or more nucleosides or nucleotides
A61K 31/7105 ・・・Natural ribonucleic acids, i.e. containing only riboses attached to adenine, guanine, cytosine or uracil and having 3'-5' phosphodiester links
A61K 31/711 ・・・Natural deoxyribonucleic acids, i.e. containing only 2'-deoxyriboses attached to adenine, guanine, cytosine or thymine and having 3'-5' phosphodiester links
A61K 31/7115 ・・・Nucleic acids or oligonucleotides having modified bases, i.e. other than adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil or thymine
A61K 31/712 ・・・Nucleic acids or oligonucleotides having modified sugars, i.e. other than ribose or 2'-deoxyribose
A61K 31/7125 ・・・Nucleic acids or oligonucleotides having modified internucleoside linkage, i.e. other than 3'-5' phosphodiesters
A61K 31/713 ・・・Double-stranded nucleic acids or oligonucleotides
A61K 31/7135 ・・Compounds containing heavy metals
A61K 31/714 ・・・Cobalamins, e.g. cyanocobalamin, i.e. vitamin B12
A61K 31/715 ・・Polysaccharides, i.e. having more than five saccharide radicals attached to each other by glycosidic linkages; Derivatives thereof, e.g. ethers, esters
A61K 31/716 ・・・Glucans
A61K 31/717 ・・・・Celluloses
A61K 31/718 ・・・・Starch or degraded starch, e.g. amylose, amylopectin
A61K 31/719 ・・・・Pullulans
A61K 31/721 ・・・・Dextrans
A61K 31/722 ・・・・Chitin, chitosan
A61K 31/723 ・・・・Xanthans
A61K 31/724 ・・・・Cyclodextrins
A61K 31/726 ・・・Glycosaminoglycans, i.e. mucopolysaccharides (chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate A61K 31/737)
A61K 31/727 ・・・・Heparin; Heparan
A61K 31/728 ・・・・Hyaluronic acid
A61K 31/729 ・・・Agar; Agarose; Agaropectin
A61K 31/731 ・・・Carrageenans
A61K 31/732 ・・・Pectin
A61K 31/733 ・・・Fructosans, e.g. inulin
A61K 31/734 ・・・Alginic acid
A61K 31/736 ・・・Glucomannans or galactomannans, e.g. locust bean gum, guar gum
A61K 31/737 ・・・Sulfated polysaccharides, e.g. chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate (A61K 31/727 takes precedence)
A61K 31/738 ・・・Cross-linked polysaccharides
A61K 31/739 ・・・Lipopolysaccharides
A61K 31/74 ・Synthetic polymeric materials
A61K 31/745 ・・Polymers of hydrocarbons
A61K 31/75 ・・・of ethene
A61K 31/755 ・・Polymers containing halogen
A61K 31/76 ・・・of vinyl chloride
A61K 31/765 ・・Polymers containing oxygen
A61K 31/77 ・・・of oxiranes
A61K 31/775 ・・・Phenolic resins
A61K 31/78 ・・・of acrylic acid or derivatives thereof
A61K 31/785 ・・Polymers containing nitrogen
A61K 31/787 ・・・containing heterocyclic rings having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom
A61K 31/79 ・・・・Polymers of vinyl pyrrolidone
A61K 31/795 ・・Polymers containing sulfur
A61K 31/80 ・・Polymers containing hetero atoms not provided for in groups A61K 31/755 to A61K 31/795
A61K 33/00 Medicinal preparations containing inorganic active ingredients
A61K 33/02 ・Ammonia; Compounds thereof
A61K 33/04 ・Sulfur, selenium or tellurium; Compounds thereof
A61K 33/06 ・Aluminium, calcium or magnesium; Compounds thereof, {e.g. clay}
A61K 33/08 ・・Oxides; Hydroxides
A61K 33/10 ・・Carbonates; Bicarbonates
A61K 33/12 ・・Magnesium silicate
A61K 33/14 ・Alkali metal chlorides; Alkaline earth metal chlorides
A61K 33/16 ・Fluorine compounds
A61K 33/18 ・Iodine; Compounds thereof
A61K 33/20 ・Elemental chlorine; Inorganic compounds releasing chlorine
A61K 33/22 ・Boron compounds
A61K 33/24 ・Heavy metals; Compounds thereof
A61K 33/245 ・・{Bismuth; Derivatives thereof}
A61K 33/26 ・・Iron; Compounds thereof
A61K 33/28 ・・Mercury; Compounds thereof
A61K 33/30 ・・Zinc; Compounds thereof
A61K 33/32 ・・Manganese; Compounds thereof
A61K 33/34 ・・Copper; Compounds thereof
A61K 33/36 ・・Arsenic; Compounds thereof
A61K 33/38 ・・Silver; Compounds thereof
A61K 33/40 ・Peroxides
A61K 33/42 ・Phosphorus; Compounds thereof
A61K 33/44 ・Elemental carbon, e.g. charcoal, carbon black
A61K 35/00 Medicinal preparations containing materials or reaction products thereof with undetermined constitution
NOTE - When classifying in this group, the last place rule (applied throughout A61K) does not apply. Namely, classification is made for each active component or material.A61K 35/02 ・from inanimate materials
A61K 35/04 ・・Tars; Bitumens; Mineral oils; Ammonium bituminisulfonates, e.g. ichthyol (carbon A61K 33/00)
A61K 35/06 ・・・Mineral oils, {e.g. paraffinic oils, aromatic oils based on aromatic hydrocarbons (essential oils derived from plants A61K 36/00)}
A61K 35/08 ・・Mineral waters; {Sea water}
A61K 35/10 ・・Peat; Amber; {Turf; Humus (wood tar, sap or resin A61K 36/00)}
A61K 35/12 ・Materials from mammals; {compositions comprising non-specified tissues or cells; Compositions comprising non-embryonic stem cells (uncharacterized stem cells A61K 35/545); Genetically modified cells (gene therapy C12N 5/10; vaccines or medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies A61K 39/00)}{Note: If the cells are characterized, classify under the corresponding tissue or tissue of origin}
NOTE - When the cells are characterized, classification is given under the corresponding tissue or tissue of originA61K 35/13 ・・{Tumor cells, irrespective of tissue of origin (tumor vaccines A61K 39/00)}
A61K 35/14 ・・Blood {(haemoglobin A61K 38/42; umbilical cord blood A61K 35/51)}; Artificial blood (perfluorocarbons A61K 31/02)]
A61K 35/15 ・・・{Cells of the myeloid line, e.g. granulocytes, basophils, eosinophils, neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages or mast cells; Myeloid precursor cells; Antigen presenting cells, e.g. dendritic cells (presenting a specific antigen A61K 39/00; therapeutic combinations of antibodies, or fragments thereof, and blood-derived cells A61K 35/15, A61K 39/00 or C07K 16/00)}
A61K 35/16 ・・・{Blood plasma; Blood serum (umbilical cord blood A61K 35/51)}
A61K 35/17 ・・・{Lymphocytes; B-cells; T-cells; Natural killer cells; Interferon- and cytokine-activated lymphocytes (when activated by a specific antigen A61K 39/00)}
A61K 35/18 ・・・Erythrocytes {(hemoglobin A61K 38/42)}
A61K 35/19 ・・・{Platelets; Megacaryocytes}
A61K 35/20 ・・Milk; Colostrum; {Whey}
A61K 35/22 ・・{Urinary tract, e.g. kidney or bladder; Intraglomerular mesangial cells; Renal mesenchymal cells; Adrenal gland}; Urine
A61K 35/24 ・・Mucus; Mucous glands; Bursa; {Synovial fluid}; Arthral fluid; Excreta; Spinal fluid {(saliva A61K 35/38)}
A61K 35/26 ・・Lymph; {Lymph nodes;} Thymus; {Spleen; Splenocytes; Thymocytes}
A61K 35/28 ・・{Bone} marrow; {Hematopoietic stem cells; Mesenchymal stem cells of any origin, e.g. adipose-derived stem cells}
A61K 35/30 ・・Nerves; Brain; {Eyes; Corneal cells; Cerebrospinal fluid; Neuronal stem cells; Neuronal precursor cells; Glial cells; Oligodendrocytes; Schwann cells; Astroglia, astrocytes; Choroid plexus; Spinal cord tissue}
A61K 35/32 ・・Bones; {Osteocytes; Osteoblasts;} Tendons; {Tenocytes;} Teeth; {Odontoblasts;} Cartilage; {Chondrocytes; Synovial membrane}
A61K 35/33 ・・{Fibroblasts}
A61K 35/34 ・・Muscles; {Smooth muscle cells} Heart; {Cardiac stem cells; Myoblasts; Myocytes; Cardiomyocytes (vascular smooth muscle A61K 35/44)}
A61K 35/35 ・・{Fat tissue; Adipocytes; Stromal cells; Connective tissues of general nature (adipose-derived stem cells A61K 35/28, collagen A61K 38/39)}
A61K 35/36 ・・Skin; Hair; Nails; Sebacious glands; Cerumen; {Epidermis; Epithelial cells; Keratinocytes; Langerhans cells; Ecdodermal cells (islets of Langerhans A61K 35/39)}
NOTE - Epithelial cells of specific tissues, e.g. lung epithelium, are classified under the respective tissueA61K 35/37 ・・Digestive system
A61K 35/38 ・・・Stomach; Intestine; {Goblet cells; Oral mucosa; Saliva}
A61K 35/39 ・・・Pancreas; Islets of Langerhans {(Langerhans cells of epidermis A61K 35/36)}
A61K 35/407 ・・・Liver; {Hepatocytes}
A61K 35/413 ・・・{Gallbladder;} Bile
A61K 35/42 ・・{Respiratory System:} e.g. Lungs; {Bronchi; Lung cells}
A61K 35/44 ・・Vessels {e.g. blood vessels or lymphatic vessels; Vascular smooth muscle cells; Endothelial cells; Endothelial progenitor cells}
A61K 35/48 ・・Reproductive organs
A61K 35/50 ・・・Placenta; Amniotic fluid; {Amnion, Amniotic stem cells; Placental stem cells}
A61K 35/51 ・・・{Umbilical cord; Umbilical cord blood; Umbilical stem cells}
A61K 35/52 ・・・Sperm {Prostate, Seminal fluid; Leydig cells of testes}
A61K 35/54 ・・・Ovary; Embryos; {Fetal cells; Germ cells}
A61K 35/545 ・・・・{Embryonic stem cells; Pluripotent stem cells; Induced pluripotent stem cells; Uncharacterized stem cells}
A61K 35/55 ・・Glands not provided for in any of the preceding subgroups of this main group {e.g. thyroid, parathyroid, pineal gland}
A61K 35/56 ・Materials from animals other than mammals
A61K 35/57 ・・{Birds; Materials from birds, e.g. eggs or feathers}
A61K 35/58 ・・{Reptiles}
A61K 35/583 ・・・{Snakes [N: Lizards; Chameleons (therapeutic use of a snake venom protein A61K38)}
A61K 35/586 ・・・{Turtles, Tortoises}
A61K 35/60 ・・Fish; {Seahorses; Fish eggs}
A61K 35/61 ・・{Sea animals other than those covered by group A61K 35/60}
A61K 35/612 ・・・{Crustaceans, e.g. crabs, lobsters, shrimps, krill or crayfish; Barnacles}
A61K 35/614 ・・・{Cnidaria, e.g. sea anemones, corals, coral animals, jellyfish}
A61K 35/616 ・・・{Echinodermata, e.g. star fish, sea cucumbers, sea urchins}
A61K 35/618 ・・・{Molluscs, e.g. fresh-water molluscs, oysters, clams, squids, octopus, cuttlefish, snails or slugs}
A61K 35/62 ・・Leeches; {Worms, e.g. cestodes or tapeworms, nematodes, roundworms, earth worms, ascarids, filarias, hookworms, trichinella or taenia}
A61K 35/64 ・・{Arthropods}
A61K 35/642 ・・・{Insects, e.g. bees, wasps or fleas}
A61K 35/644 ・・・・{Beeswax; Propolis; Royal jelly; Honey}
A61K 35/646 ・・・{arachnids, e.g. spiders, scorpions, ticks or mites}
A61K 35/648 ・・・{Myriapods, e.g. centipedes or millipedes}
A61K 35/65 ・・{Amphibians, e.g. toads, frogs, salamanders, newts}
A61K 35/66 ・Micro-organisms or materials thereof (mutated microorganisms or microorganisms per se C12R 1/00; microorganisms in food, for nutritional purposes A23L 1/3014; fungi, yeast or candida A61K 36/06)]
NOTE - Classification is given in this group only the micro-organism is the active ingredientA61K 35/68 ・・Protozoa {e.g. flagella, amoebas, sporozoans, plasmodium or toxoplasma}
A61K 35/74 ・・Bacteria {(therapeutic use of a bacterial protein A61K 38/00; bacteria per se or mutant bacteria C12R 1/00; bacteria in food, for nutritional purposes A23L 1/3014)}
A61K 35/741 ・・・{Probiotics (as part of food or functional food A23L 1/3014; probiotic yeast, i.e. saccharomyces A61K 36/06)}
A61K 35/742 ・・・・{Spore-forming bacteria, e.g. Bacillus coagulans or Lactobacillus sporogenes}
A61K 35/744 ・・・・{Lactic acid bacteria, e.g. enterococci, pediococci, lactococci, streptococci, leuconostoc}
A61K 35/745 ・・・・・{Bifidobacteria}
A61K 35/747 ・・・・・{Lactobacilli, e.g. L. acidophilus, L. brevis}
A61K 35/748 ・・・{Cyanobacteria; Spirulina; Blue-green algae; Blue-green bacteria (algae, microalgae or microphytes A61K 36/00)}
A61K 35/76 ・・Viruses, {Bacteriophages; (viruses per se C12N 7/00; viral proteins per se C07K 14/005; use of virus as a vector C12N 15/86; use of virus or part thereof as vaccine A61K 39/12; therapeutic use of a viral protein A61K 38/16)}
A61K 35/761 ・・・{Adenovirus}
A61K 35/763 ・・・{Herpes virus}
A61K 35/765 ・・・{Reovirus; Rotavirus}
A61K 35/766 ・・・{Rhabdovirus, e.g. vesicular stomatitis virus}
A61K 35/768 ・・・{Other oncolytic viruses}
A61K 36/00 Medicinal preparations of undetermined constitution containing material from algae, lichens, fungi or plants, or derivatives thereof, e.g. traditional herbal medicines {(antigens from pollen A61K 39/36)}
NOTE - In this group, common names of plants, where given, are presented in brackets following their corresponding Latin names.A61K 36/02 ・Algae
A61K 36/03 ・・Phaeophycota or phaeophyta (brown algae), e.g. Fucus
A61K 36/04 ・・Rhodophycota or rhodophya (red algae), e.g. Porphyra
A61K 36/05 ・・Chlorophycota or chlorophyta (green algae), e.g. Chlorella
A61K 36/06 ・Fungi, e.g. yeasts
A61K 36/062 ・・Ascomycota
A61K 36/064 ・・・Saccharomycetales, e.g. baker's yeast
A61K 36/066 ・・・Clavicipitaceae
A61K 36/068 ・・・・Cordyceps
A61K 36/07 ・・Basidiomycota, e.g. Cryptococcus
A61K 36/074 ・・・Ganoderma
A61K 36/076 ・・・Poria
A61K 36/09 ・Lichens
A61K 36/10 ・Bryophyta
A61K 36/11 ・Pteridophyta or Filicophyta (ferns)
A61K 36/12 ・・Filicopsida or Pteridopsida
A61K 36/126 ・・・Drynaria
A61K 36/13 ・Coniferophyta (gymnosperms)
A61K 36/14 ・・Cupressaceae (Cypress family), e.g. juniper or cypress
A61K 36/15 ・・Pinaceae (Pine family), e.g. pine or cedar
A61K 36/16 ・Ginkgophyta, e.g. Ginkgoaceae (Ginkgo family)
A61K 36/17 ・Gnetophyta, e.g. Ephedraceae (Mormon-tea tamily)
A61K 36/18 ・Magnoliophyta (angiosperms)
A61K 36/185 ・・Magnoliopsida (dicotyledons)
A61K 36/19 ・・・Acanthaceae (Acanthus family)
A61K 36/195 ・・・・Strobilanthes
A61K 36/20 ・・・Aceraceae (Maple family)
A61K 36/21 ・・・Amaranthaceae (Amaranth family), e.g. pigweed, rockwort or globe amaranth
A61K 36/22 ・・・Anacardiaceae (Sumac family), e.g. smoketree, sumac or poison oak
A61K 36/23 ・・・Apiaceae or Umbelliferae (Carrot family), e.g. dill, chervil, coriander or cumin
A61K 36/232 ・・・・Angelica
A61K 36/233 ・・・・Bupleurum
A61K 36/234 ・・・・Cnidium (snowparsley)
A61K 36/235 ・・・・Foeniculum (fennel)
A61K 36/236 ・・・・Ligusticum (licorice-root)
A61K 36/237 ・・・・Notopterygium
A61K 36/238 ・・・・Saposhnikovia
A61K 36/24 ・・・Apocynaceae (Dogbane family), e.g. plumeria or periwinkle
A61K 36/25 ・・・Araliaceae (Ginseng family), e.g. ivy, aralia, schefflera or tetrapanax
A61K 36/254 ・・・・Acanthopanax or Eleutherococcus
A61K 36/258 ・・・・Panax (ginseng)
A61K 36/26 ・・・Aristolochiaceae (Birthwort family), e.g. heartleaf
A61K 36/264 ・・・・Aristolochia (Dutchman's pipe)
A61K 36/268 ・・・・Asarum (wild ginger)
A61K 36/27 ・・・Asclepiadaceae (Milkweed family), e.g. hoya
A61K 36/28 ・・・Asteraceae or Compositae (Aster or Sunflower family), e.g. chamomile, feverfew, yarrow or echinacea
A61K 36/282 ・・・・Artemisia, e.g. wormwood or sagebrush
A61K 36/284 ・・・・Atractylodes
A61K 36/285 ・・・・Aucklandia
A61K 36/286 ・・・・Carthamus (distaff thistle)
A61K 36/287 ・・・・Chrysanthemum, e.g. daisy
A61K 36/288 ・・・・Taraxacum (dandelion)
A61K 36/289 ・・・・Vladimiria
A61K 36/29 ・・・Berberidaceae (Barberry family), e.g. barberry, cohosh or mayapple
A61K 36/296 ・・・・Epimedium
A61K 36/30 ・・・Boraginaceae (Borage family), e.g. comfrey, lungwort or forget-me-not
A61K 36/31 ・・・Brassicaceae or Cruciferae (Mustard family), e.g. broccoli, cabbage or kohlrabi
A61K 36/315 ・・・・Isatis, e.g. Dyer's woad
A61K 36/32 ・・・Burseraceae (Frankincense family)
A61K 36/324 ・・・・Boswellia, e.g. frankincense
A61K 36/328 ・・・・Commiphora, e.g. mecca myrrh or balm of Gilead
A61K 36/33 ・・・Cactaceae (Cactus family), e.g. pricklypear or Cereus
A61K 36/34 ・・・Campanulaceae (Bellflower family)
A61K 36/342 ・・・・Adenophora
A61K 36/344 ・・・・Codonopsis
A61K 36/346 ・・・・Platycodon
A61K 36/35 ・・・Caprifoliaceae (Honeysuckle family)
A61K 36/355 ・・・・Lonicera (honeysuckle)
A61K 36/36 ・・・Caryophyllaceae (Pink family), e.g. babysbreath or soapwort
A61K 36/37 ・・・Celastraceae (Staff-tree or Bittersweet family), e.g. tripterygium or spindletree
A61K 36/38 ・・・Clusiaceae, Hypericaceae or Guttiferae (Hypericum or Mangosteen family), e.g. common St. Johnswort
A61K 36/39 ・・・Convolvulaceae (Morning-glory family), e.g. bindweed
A61K 36/40 ・・・Cornaceae (Dogwood family)
A61K 36/41 ・・・Crassulaceae (Stonecrop family)
A61K 36/42 ・・・Cucurbitaceae (Cucumber family)
A61K 36/424 ・・・・Gynostemma
A61K 36/428 ・・・・Trichosanthes
A61K 36/43 ・・・Cuscutaceae (Dodder family), e.g. Cuscuta epithymum or greater dodder
A61K 36/44 ・・・Ebenaceae (Ebony family), e.g. persimmon
A61K 36/45 ・・・Ericaceae or Vacciniaceae (Heath or Blueberry family), e.g. blueberry, cranberry or bilberry
A61K 36/46 ・・・Eucommiaceae (Eucommia family), e.g. hardy rubber tree
A61K 36/47 ・・・Euphorbiaceae (Spurge family), e.g. Ricinus (castorbean)
A61K 36/48 ・・・Fabaceae or Leguminosae (Pea or Legume family); Caesalpiniaceae; Mimosaceae; Papilionaceae
A61K 36/481 ・・・・Astragalus (milkvetch)
A61K 36/482 ・・・・Cassia, e.g. golden shower tree
A61K 36/483 ・・・・Gleditsia (locust)
A61K 36/484 ・・・・Glycyrrhiza (licorice)
A61K 36/485 ・・・・Gueldenstaedtia
A61K 36/486 ・・・・Millettia
A61K 36/487 ・・・・Psoralea
A61K 36/488 ・・・・Pueraria (kudzu)
A61K 36/489 ・・・・Sophora, e.g. necklacepod or mamani
A61K 36/49 ・・・Fagaceae (Beech family), e.g. oak or chestnut
A61K 36/50 ・・・Fumariaceae (Fumitory family), e.g. bleeding heart
A61K 36/505 ・・・・Corydalis
A61K 36/51 ・・・Gentianaceae (Gentian family)
A61K 36/515 ・・・・Gentiana
A61K 36/52 ・・・Juglandaceae (Walnut family)
A61K 36/53 ・・・Lamiaceae or Labiatae (Mint family), e.g. thyme, rosemary or lavender
A61K 36/532 ・・・・Agastache, e.g. giant hyssop
A61K 36/533 ・・・・Leonurus (motherwort)
A61K 36/534 ・・・・Mentha (mint)
A61K 36/535 ・・・・Perilla (beefsteak plant)
A61K 36/536 ・・・・Prunella or Brunella (selfheal)
A61K 36/537 ・・・・Salvia (sage)
A61K 36/538 ・・・・Schizonepeta
A61K 36/539 ・・・・Scutellaria (skullcap)
A61K 36/54 ・・・Lauraceae (Laurel family), e.g. cinnamon or sassafras
A61K 36/55 ・・・Linaceae (Flax family), e.g. Linum
A61K 36/56 ・・・Loganiaceae (Logania family), e.g. trumpetflower or pinkroot
A61K 36/57 ・・・Magnoliaceae (Magnolia family)
A61K 36/575 ・・・・Magnolia
A61K 36/58 ・・・Meliaceae (Chinaberry or Mahogany family), e.g. Azadirachta (neem)
A61K 36/59 ・・・Menispermaceae (Moonseed family), e.g. hyperbaena or coralbead
A61K 36/60 ・・・Moraceae (Mulberry family), e.g. breadfruit or fig
A61K 36/605 ・・・・Morus (mulberry)
A61K 36/61 ・・・Myrtaceae (Myrtle family), e.g. teatree or eucalyptus
A61K 36/62 ・・・Nymphaeaceae (Water-lily family)
A61K 36/63 ・・・Oleaceae (Olive family), e.g. jasmine, lilac or ash tree
A61K 36/634 ・・・・Forsythia
A61K 36/638 ・・・・Ligustrum, e.g. Chinese privet
A61K 36/64 ・・・Orobanchaceae (Broom-rape family)
A61K 36/65 ・・・Paeoniaceae (Peony family), e.g. Chinese peony
A61K 36/66 ・・・Papaveraceae (Poppy family), e.g. bloodroot
A61K 36/67 ・・・Piperaceae (Pepper family), e.g. Jamaican pepper or kava
A61K 36/68 ・・・Plantaginaceae (Plantain Family)
A61K 36/69 ・・・Polygalaceae (Milkwort family)
A61K 36/70 ・・・Polygonaceae (Buckwheat family), e.g. spineflower or dock
A61K 36/704 ・・・・Polygonum, e.g. knotweed
A61K 36/708 ・・・・Rheum (rhubarb)
A61K 36/71 ・・・Ranunculaceae (Buttercup family), e.g. larkspur, hepatica, hydrastis, columbine or goldenseal
A61K 36/714 ・・・・Aconitum (monkshood)
A61K 36/716 ・・・・Clematis (leather flower)
A61K 36/718 ・・・・Coptis (goldthread)
A61K 36/72 ・・・Rhamnaceae (Buckthorn family), e.g. buckthorn, chewstick or umbrella-tree
A61K 36/725 ・・・・Ziziphus, e.g. jujube
A61K 36/73 ・・・Rosaceae (Rose family), e.g. strawberry, chokeberry, blackberry, pear or firethorn
A61K 36/732 ・・・・Chaenomeles, e.g. flowering quince
A61K 36/734 ・・・・Crataegus (hawthorn)
A61K 36/736 ・・・・Prunus, e.g. plum, cherry, peach, apricot or almond
A61K 36/738 ・・・・Rosa (rose)
A61K 36/739 ・・・・Sanguisorba (burnet)
A61K 36/74 ・・・Rubiaceae (Madder family)
A61K 36/744 ・・・・Gardenia
A61K 36/746 ・・・・Morinda
A61K 36/748 ・・・・Oldenlandia or Hedyotis
A61K 36/75 ・・・Rutaceae (Rue family)
A61K 36/752 ・・・・Citrus, e.g. lime, orange or lemon
A61K 36/754 ・・・・Evodia
A61K 36/756 ・・・・Phellodendron, e.g. corktree
A61K 36/758 ・・・・Zanthoxylum, e.g. pricklyash
A61K 36/76 ・・・Salicaceae (Willow family), e.g. poplar
A61K 36/77 ・・・Sapindaceae (Soapberry family), e.g. lychee or soapberry
A61K 36/78 ・・・Saururaceae (Lizard's-tail family)
A61K 36/79 ・・・Schisandraceae (Schisandra family)
A61K 36/80 ・・・Scrophulariaceae (Figwort family)
A61K 36/804 ・・・・Rehmannia
A61K 36/808 ・・・・Scrophularia (figwort)
A61K 36/81 ・・・Solanaceae (Potato family), e.g. tobacco, nightshade, tomato, belladonna, capsicum or jimsonweed
A61K 36/815 ・・・・Lycium (desert-thorn)
A61K 36/82 ・・・Theaceae (Tea family), e.g. camellia
A61K 36/83 ・・・Thymelaeaceae (Mezereum family), e.g. leatherwood or false ohelo
A61K 36/835 ・・・・Aquilaria
A61K 36/84 ・・・Valerianaceae (Valerian family), e.g. valerian
A61K 36/85 ・・・Verbenaceae (Verbena family)
A61K 36/855 ・・・・Clerodendrum, e.g. glorybower
A61K 36/86 ・・・Violaceae (Violet family)
A61K 36/87 ・・・Vitaceae or Ampelidaceae (Vine or Grape family), e.g. wine grapes, muscadine or peppervine
A61K 36/88 ・・Liliopsida (monocotyledons)
A61K 36/882 ・・・Acoraceae (Calamus family), e.g. sweetflag or Acorus calamus
A61K 36/884 ・・・Alismataceae (Water-plantain family)
A61K 36/886 ・・・Aloeaceae (Aloe family), e.g. aloe vera
A61K 36/888 ・・・Araceae (Arum family), e.g. caladium, calla lily or skunk cabbage
A61K 36/8884 ・・・・Arisaema, e.g. Jack in the pulpit
A61K 36/8888 ・・・・Pinellia
A61K 36/889 ・・・Arecaceae, Palmae or Palmaceae (Palm family), e.g. date or coconut palm or palmetto
A61K 36/8895 ・・・・Calamus, e.g. rattan
A61K 36/89 ・・・Cyperaceae (Sedge family)
A61K 36/8905 ・・・・Cyperus (flatsedge)
A61K 36/894 ・・・Dioscoreaceae (Yam family)
A61K 36/8945 ・・・・Dioscorea, e.g. yam, Chinese yam or water yam
A61K 36/896 ・・・Liliaceae (Lily family), e.g. daylily, plantain lily, Hyacinth or narcissus
A61K 36/8962 ・・・・Allium, e.g. garden onion, leek, garlic or chives
A61K 36/8964 ・・・・Anemarrhena
A61K 36/8965 ・・・・Asparagus, e.g. garden asparagus or asparagus fern
A61K 36/8966 ・・・・Fritillaria, e.g. checker lily or mission bells
A61K 36/8967 ・・・・Lilium, e.g. tiger lily or Easter lily
A61K 36/8968 ・・・・Ophiopogon (Lilyturf)
A61K 36/8969 ・・・・Polygonatum (Solomon's seal)
A61K 36/898 ・・・Orchidaceae (Orchid family)
A61K 36/8984 ・・・・Dendrobium
A61K 36/8988 ・・・・Gastrodia
A61K 36/899 ・・・Poaceae or Gramineae (Grass family), e.g. bamboo, corn or sugar cane
A61K 36/8994 ・・・・Coix (Job's tears)
A61K 36/8998 ・・・・Hordeum (barley)
A61K 36/90 ・・・Smilacaceae (Catbrier family), e.g. greenbrier or sarsaparilla
A61K 36/902 ・・・Sparganiaceae (Bur-reed family)
A61K 36/904 ・・・Stemonaceae (Stemona family), e.g. croomia
A61K 36/906 ・・・Zingiberaceae (Ginger family)
A61K 36/9062 ・・・・Alpinia, e.g. red ginger or galangal
A61K 36/9064 ・・・・Amomum, e.g. round cardamom
A61K 36/9066 ・・・・Curcuma, e.g. common turmeric, East Indian arrowroot or mango ginger
A61K 36/9068 ・・・・Zingiber, e.g. garden ginger
A61K 38/00 Medicinal preparations containing peptides (peptides containing beta-lactam rings A61K 31/00; cyclic dipeptides not having in their molecule any other peptide link than those which form their ring, e.g. piperazine-2,5-diones, A61K 31/00; ergot alkaloids of the cyclic peptide type A61K 31/48; containing macromolecular compounds having statistically distributed amino acid units A61K 31/74; medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies A61K 39/00; medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients, e.g. peptides as drug carriers, A61K 47/00)
NOTE - The terms or expressions used in this group follow exactly the definitions given inA61K 38/005 ・{Enzyme inhibitors (protease inhibitors A61K 38/55)}
A61K 38/01 ・Hydrolysed proteins; Derivatives thereof
A61K 38/011 ・・{from plants}
A61K 38/012 ・・{from animals}
A61K 38/014 ・・・{from connective tissue peptides, e.g. gelatin, collagen}
A61K 38/015 ・・・・{from keratin}
A61K 38/017 ・・・{from blood}
A61K 38/018 ・・・{from milk}
A61K 38/02 ・Peptides of undefined number of amino acids; Derivatives thereof
A61K 38/03 ・Peptides having up to 20 amino acids in an undefined or only partially defined sequence; Derivatives thereof
A61K 38/04 ・Peptides having up to 20 amino acids in a fully defined sequence; Derivatives thereof ({enzyme inhibitors A61K 38/005}; gastrins {A61K 38/2207} somatostatins A61K 38/31, melanotropins A61K 38/34; {protease inhibitors A61K 38/55})
A61K 38/043 ・・{Kallidins; Bradykinins; Related peptides}
A61K 38/046 ・・{Tachykinins, e.g. eledoisins, substance P; Related peptides}
A61K 38/05 ・・Dipeptides
A61K 38/06 ・・Tripeptides
A61K 38/063 ・・・{Glutathione}
A61K 38/066 ・・・{TRH, thyroliberin, thyrotropin releasing hormone}
A61K 38/07 ・・Tetrapeptides
A61K 38/08 ・・Peptides having 5 to 11 amino acids {(A61K 38/043 to A61K 38/046 take precedence)}
A61K 38/085 ・・・{Angiotensins}
A61K 38/09 ・・・Luteinising hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) {i.e. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)}; Related peptides
A61K 38/10 ・・Peptides having 12 to 20 amino acids {(A61K 38/043 to A61K 38/046 take precedence)}
A61K 38/105 ・・・{Bombesin; Related peptides}
A61K 38/11 ・・・Oxytocins; Vasopressins; Related peptides
A61K 38/12 ・・Cyclic peptides {, e.g. bacitracins; Polymyxins; Gramicidins S, C; Tyrocidins A, B or C (A61K 38/043 to A61K 38/046 take precedence)}
A61K 38/13 ・・・Cyclosporins
A61K 38/14 ・・Peptides containing saccharide radicals; Derivatives thereof {e.g. bleomycin, phleomycin, muramylpeptides or vancomycin}
A61K 38/15 ・・Depsipeptides; Derivatives thereof
A61K 38/16 ・Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof {(enzyme inhibitors A61K 38/005)}
A61K 38/162 ・・{from virus}
A61K 38/164 ・・{from bacteria}
A61K 38/166 ・・・{Streptokinase}
A61K 38/168 ・・{from plants}
A61K 38/17 ・・from animals; from humans {(enzyme inhibitors A61K 38/005)}
A61K 38/1703 ・・・{from vertebrates (A61K 38/1767 takes precedence)}
A61K 38/1706 ・・・・{from fish}
A61K 38/1709 ・・・・{from mammals}
A61K 38/1712 ・・・・・{Not used, see subgroup}
A61K 38/1716 ・・・・・・{Amyloid plaque core protein}
A61K 38/1719 ・・・・・・{Muscle proteins, e.g. myosin, actin}
A61K 38/1722 ・・・・・・{Plasma globulins, lactoglobulin}
A61K 38/1725 ・・・・・・{Complement proteins, e.g. anaphylatoxin, C3a, C5a}
A61K 38/1729 ・・・・・・{Cationic antimicrobial peptides, e.g. defensins}
A61K 38/1732 ・・・・・・{Lectins}
A61K 38/1735 ・・・・・・{Mucins, e.g. human intestinal mucin}
A61K 38/1738 ・・・・・・{Calcium binding proteins, e.g. calmodulin}
A61K 38/1741 ・・・・・・{alpha-Glycoproteins}
A61K 38/1745 ・・・・・・{C-reactive protein}
A61K 38/1748 ・・・・・・{Keratin; Cytokeratin}
A61K 38/1751 ・・・・・・{Bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein (BPI)}
A61K 38/1754 ・・・・・・{Insulin-like growth factor binding protein}
A61K 38/1758 ・・・・・・{p53}
A61K 38/1761 ・・・・・・{Apoptosis related proteins, e.g. Apoptotic protease-activating factor-1 (APAF-1), Bax, Bax-inhibitory protein(s) (BI; bax-I), Myeloid cell leukemia associated protein (MCL-1), Inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP), Bcl-2}
A61K 38/1764 ・・・・・・{Tumor specific antigens; Tumor rejection antigen precursors (TRAP), e.g. MAGE}
A61K 38/1767 ・・・{from invertebrates}
A61K 38/177 ・・・{Receptors; Cell surface antigens; Cell surface determinants}
A61K 38/1774 ・・・・{Immunoglobulin superfamily (e.g. CD2, CD4, CD8, ICAM molecules, B7 molecules, Fc-receptors, MHC-molecules)}
A61K 38/1777 ・・・・{Integrin superfamily}
A61K 38/178 ・・・・{Lectin superfamily, e.g. selectins}
A61K 38/1783 ・・・・{Nuclear receptors, e.g. retinoic acid receptor (RAR), RXR, nuclear orphan receptors}
A61K 38/1787 ・・・・{for neuromediators, e.g. serotonin receptor, dopamine receptor}
A61K 38/179 ・・・・{for growth factors; for growth regulators}
A61K 38/1793 ・・・・{for cytokines; for lymphokines; for interferons}
A61K 38/1796 ・・・・{for hormones (for neuromediators A61K 38/1787)}
A61K 38/18 ・・・Growth factors; Growth regulators
A61K 38/1808 ・・・・{Epidermal growth factor (EGF) urogastrone}
A61K 38/1816 ・・・・{Erythropoietin (EPO)}
A61K 38/1825 ・・・・{Fibroblast growth factor (FGF)}
A61K 38/1833 ・・・・{Hepatocyte growth factor; Scatter factor; Tumor cytotoxic factor II}
A61K 38/1841 ・・・・{Transforming growth factor (TGF)}
A61K 38/185 ・・・・{Nerve growth factor (NGF); Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF); Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF); Glial derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF); Neurotrophins, e.g. NT-3}
A61K 38/1858 ・・・・{Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)}
A61K 38/1866 ・・・・・{Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)}
A61K 38/1875 ・・・・{Bone morphogenic factor; Osteogenins; Osteogenic factor; Bone-inducing factor}
A61K 38/1883 ・・・・{Neuregulins, e.g.. p185erbB2 ligands, glial growth factor, heregulin, ARIA, neu differentiation factor}
A61K 38/1891 ・・・・[Angiogenesic factors; Angiogenin]
A61K 38/19 ・・・Cytokines; Lymphokines; Interferons
A61K 38/191 ・・・・{Tumor necrosis factors [TNF}, e.g. lymphotoxin [LT] i.e. TNF-beta]
A61K 38/193 ・・・・{Colony stimulating factors [CSF}]
A61K 38/195 ・・・・{Chemokines, e.g. RANTES}
A61K 38/196 ・・・・{Thrombopoietin}
A61K 38/20 ・・・・Interleukins [IL]
A61K 38/2006 ・・・・・{IL-1}
A61K 38/2013 ・・・・・{IL-2}
A61K 38/202 ・・・・・{IL-3}
A61K 38/2026 ・・・・・{IL-4}
A61K 38/2033 ・・・・・{IL-5}
A61K 38/204 ・・・・・{IL-6}
A61K 38/2046 ・・・・・{IL-7}
A61K 38/2053 ・・・・・{IL-8}
A61K 38/206 ・・・・・{IL-9}
A61K 38/2066 ・・・・・{IL-10}
A61K 38/2073 ・・・・・{IL-11}
A61K 38/208 ・・・・・{IL-12}
A61K 38/2086 ・・・・・{IL-13 to IL-16}
A61K 38/2093 ・・・・・{Leukaemia inhibitory factor (LIF)}
A61K 38/21 ・・・・Interferons {(IFN)}
A61K 38/212 ・・・・・{IFN-alpha}
A61K 38/215 ・・・・・{IFN-beta}
A61K 38/217 ・・・・・{IFN-gamma}
A61K 38/22 ・・・Hormones (derived from pro-opiomelanocortin, pro-enkephalin or pro-dynorphin A61K 38/33, e.g. corticotropin A61K 38/35)
A61K 38/2207 ・・・・{Gastrins; Cholecystokinins [CCK}]
A61K 38/2214 ・・・・{Motilins}
A61K 38/2221 ・・・・{Relaxins}
A61K 38/2228 ・・・・{Corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) (Urotensin) }
A61K 38/2235 ・・・・{Secretins}
A61K 38/2242 ・・・・{Atrial natriuretic factor complex: Atriopeptins, atrial natriuretic protein (ANP); Cardionatrin, Cardiodilatin}
A61K 38/225 ・・・・{Calcitonin gene related peptide}
A61K 38/2257 ・・・・{Prolactin}
A61K 38/2264 ・・・・{Obesity-gene products, e.g. leptin}
A61K 38/2271 ・・・・{Neuropeptide Y}
A61K 38/2278 ・・・・{Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP); Related peptides (e.g. Exendin)}
A61K 38/2285 ・・・・{Endothelin, vasoactive intestinal contractor (VIC)}
A61K 38/2292 ・・・・{Thymosin; Related peptides}
A61K 38/23 ・・・・Calcitonins
A61K 38/24 ・・・・Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH); Chorionic gonadotropins, e.g. HCG; Luteinising hormone (LH); Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
A61K 38/25 ・・・・Growth hormone-releasing factor (GH-RF) (Somatoliberin)
A61K 38/26 ・・・・Glucagons
A61K 38/27 ・・・・Growth hormone (GH) (Somatotropin)
A61K 38/28 ・・・・Insulins
A61K 38/29 ・・・・Parathyroid hormone (parathormone); Parathyroid hormone-related peptides
A61K 38/30 ・・・・Insulin-like growth factors (somatomedins), e.g. IGF-1, IGF-2 {insulin-like growth factor binding protein A61K 38/1754}
A61K 38/31 ・・・・Somatostatins
A61K 38/32 ・・・・Thymopoietins
A61K 38/33 ・・・derived from pro-opiomelanocortin, pro-enkephalin or pro-dynorphin
A61K 38/34 ・・・・Melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH), e.g. alpha- or beta-melanotropin
A61K 38/35 ・・・・Corticotropin (ACTH)
A61K 38/36 ・・・Blood coagulation or fibrinolysis factors
A61K 38/363 ・・・・{Fibrinogen}
A61K 38/366 ・・・・{Thrombomodulin}
A61K 38/37 ・・・・Factors VIII
A61K 38/38 ・・・Albumins
A61K 38/385 ・・・・{Serum albumin}
A61K 38/39 ・・・Connective tissue peptides, e.g. collagen, elastin, laminin, fibronectin, vitronectin, cold insoluble globulin (CIG)
A61K 38/395 ・・・{Alveolar surfactant peptides; Pulmonary surfactant peptides}
A61K 38/40 ・・・Transferrins, e.g. lactoferrins, ovotransferrins
A61K 38/41 ・・Porphyrin- or corrin-ring-containing peptides
A61K 38/415 ・・・{Cytochromes}
A61K 38/42 ・・・Haemoglobins; Myoglobins
A61K 38/43 ・・Enzymes; Proenzymes; Derivatives thereof
NOTE - In this group, 1. proenzymes are classified with the corresponding enzymes; 2. enzymes are generally categorised according to the "Nomenclature and Classification of Enzymes" of the International Commission of Enzymes.A61K 38/44 ・・・Oxidoreductases (1)
A61K 38/443 ・・・・{acting on CH-OH groups as donors, e.g. glucose oxidase, lactate dehydrogenase (1.1)}
A61K 38/446 ・・・・{Superoxide dismutase (1.15)}
A61K 38/45 ・・・Transferases (2)
A61K 38/46 ・・・Hydrolases (3)
A61K 38/465 ・・・・{acting on ester bonds (3.1), e.g. lipases, ribonucleases}
A61K 38/47 ・・・・acting on glycosyl compounds (3.2), e.g. cellulases, lactases
A61K 38/48 ・・・・acting on peptide bonds (3.4)
A61K 38/4806 ・・・・・{from animals other than mammals, e.g. snakes}
A61K 38/4813 ・・・・・{Exopeptidases (3.4.11. to 3.4.19)}
A61K 38/482 ・・・・・{Serine endopeptidases (3.4.21)}
A61K 38/4826 ・・・・・・{Trypsin (3.4.21.4) Chymotrypsin (3.4.21.1)}
A61K 38/4833 ・・・・・・{Thrombin (3.4.21.5)}
A61K 38/484 ・・・・・・{Plasmin (3.4.21.7)}
A61K 38/4846 ・・・・・・{Factor VII (3.4.21.21); Factor IX (3.4.21.22); Factor Xa (3.4.21.6); Factor XI (3.4.21.27); Factor XII (3.4.21.38)}
A61K 38/4853 ・・・・・・{Kallikrein (3.4.21.34 or 3.4.21.35)}
A61K 38/486 ・・・・・・{Elastase (3.4.21.36 or 3.4.21.37)}
A61K 38/4866 ・・・・・・{Protein C (3.4.21.69)}
A61K 38/4873 ・・・・・{Cysteine endopeptidases (3.4.22), e.g. stem bromelain, papain, ficin, cathepsin H}
A61K 38/488 ・・・・・{Aspartic endopeptidases (3.4.23), e.g. pepsin, chymosin, renin, cathepsin E}
A61K 38/4886 ・・・・・{Metalloendopeptidases (3.4.24), e.g. collagenase}
A61K 38/4893 ・・・・・・{Botulinum neurotoxin (3.4.24.69)}
A61K 38/49 ・・・・・Urokinase; Tissue plasminogen activator
A61K 38/50 ・・・・acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds, other than peptide bonds (3.5), e.g. asparaginase
A61K 38/51 ・・・Lyases (4)
A61K 38/52 ・・・Isomerases (5)
A61K 38/53 ・・・Ligases (6)
A61K 38/54 ・・・Mixtures of enzymes or proenzymes covered by more than a single one of groups A61K 38/44 to A61K 38/46 or A61K 38/51 to A61K 38/53
A61K 38/55 ・・Protease inhibitors
A61K 38/553 ・・・{Renin inhibitors}
A61K 38/556 ・・・{Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors}
A61K 38/56 ・・・from plants
A61K 38/57 ・・・from animals; from humans {(A61K 38/553, A61K 38/556 take precedence)}
A61K 38/58 ・・・・from leeches, e.g. hirudin, eglin
A61K 39/00 Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies (materials for immunoassay G01N 33/53)
NOTE - Groups A61K 39/002 to A61K 39/295 cover preparations containing protozoa, bacteria, viruses, or subunits thereof, e.g. membrane parts.A61K 39/0001 ・{Archaeal antigens}
A61K 39/0002 ・{Fungal antigens, e.g. Trichophyton, Aspergillus, Candida}
A61K 39/0003 ・{Invertebrate antigens}
A61K 39/0005 ・{Vertebrate antigens (from snakes A61K 39/38)}
A61K 39/0006 ・・{Contraceptive vaccins; Vaccines against sex hormones}
A61K 39/0007 ・・{Nervous system antigens; Prions}
A61K 39/0008 ・・{Antigens related to auto-immune diseases; Preparations to induce self-tolerance}
A61K 39/001 ・・{Preparations to induce tolerance to non-self, e.g. prior to transplantation}
A61K 39/0011 ・・{Cancer antigens}
A61K 39/0012 ・・{Lipids; Lipoproteins}
A61K 39/0013 ・{Therapeutic immunisation against small organic molecules, e.g. cocaine, nicotine}
A61K 39/0015 ・{Combination vaccines based on measles-mumps-rubella }
A61K 39/0016 ・{Combination vaccines based on diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis }
A61K 39/0017 ・・{Combination vaccines based on whole cell diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis }
A61K 39/0018 ・・{Combination vaccines based on acellular diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis }
A61K 39/002 ・Protozoa antigens
A61K 39/005 ・・Trypanosoma antigens
A61K 39/008 ・・Leishmania antigens
A61K 39/012 ・・Coccidia antigens
A61K 39/015 ・・Hemosporidia antigens, e.g. Plasmodium antigens
A61K 39/018 ・・・Babesia antigens, e.g. Theileria antigens
A61K 39/02 ・Bacterial antigens
A61K 39/0208 ・・{Specific bacteria not otherwise provided for}
A61K 39/0216 ・・{Bacteriodetes, e.g. Bacteroides, Ornithobacter, Porphyromonas}
A61K 39/0225 ・・{Spirochetes, e.g. Treponema, Leptospira, Borrelia}
A61K 39/0233 ・・{Rickettsiales, e.g. Anaplasma}
A61K 39/0241 ・・{Mollicutes, e.g. Mycoplasma, Erysipelothrix}
A61K 39/025 ・・{Enterobacteriales, e.g. Enterobacter}
A61K 39/0258 ・・・{Escherichia}
A61K 39/0266 ・・・{Klebsiella}
A61K 39/0275 ・・・{Salmonella}
A61K 39/0283 ・・・{Shigella}
A61K 39/0291 ・・・{Yersinia}
A61K 39/04 ・・Mycobacterium, e.g. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
A61K 39/05 ・・{Actinobacteria, e.g. Actinomyces, Streptomyces, Nocardia, Bifidobacterium, Gardnerella}, Corynebacterium; Propionibacterium {(Mycobacterium A61K 39/04)}
A61K 39/07 ・・Bacillus
A61K 39/08 ・・Clostridium, e.g. Clostridium tetani
A61K 39/085 ・・Staphylococcus
A61K 39/09 ・・{Lactobacillales, e.g. aerococcus, enterococcus, lactobacillus, lactococcus}, streptococcus
A61K 39/092 ・・・{Streptococcus}
A61K 39/095 ・・Neisseria
A61K 39/098 ・・{Brucella}
A61K 39/099 ・・{Bordetella}
A61K 39/102 ・・{Pasteurellales, e.g. Actinobacillus}, Pasteurella; Haemophilus
A61K 39/104 ・・{Pseudomonadales, e.g.} Pseudomonas
A61K 39/1045 ・・・{Moraxella}
A61K 39/105 ・・{Delta proteobacteriales, e.g. Lawsonia; Epsilon proteobacteriales, e.g. campylobacter, helicobacter}
A61K 39/107 ・・{Vibrio}
A61K 39/114 ・・Fusobacterium
A61K 39/116 ・・Polyvalent bacterial antigens
WARNING - A61K 39/0016 and of A61K 39/02A61K 39/118 ・・Chlamydiaceae, e.g. Chlamydia trachomatis or Chlamydia psittaci
A61K 39/12 ・Viral antigens
A61K 39/125 ・・Picornaviridae, e.g. calicivirus
A61K 39/13 ・・・Poliovirus
A61K 39/135 ・・・Foot- and mouth-disease virus
A61K 39/145 ・・Orthomyxoviridae, e.g. influenza virus
A61K 39/15 ・・Reoviridae, e.g. calf diarrhea virus
A61K 39/155 ・・Paramyxoviridae, e.g. parainfluenza virus
A61K 39/165 ・・・Mumps or measles virus
A61K 39/17 ・・・Newcastle disease virus
A61K 39/175 ・・・Canine distemper virus
A61K 39/187 ・・Hog cholera virus
A61K 39/193 ・・Equine encephalomyelitis virus
A61K 39/20 ・・Rubella virus
A61K 39/205 ・・Rhabdoviridae, e.g. rabies virus
A61K 39/21 ・・Retroviridae, e.g. equine infectious anemia virus
A61K 39/215 ・・Coronaviradae, e.g. avian infectious bronchitis virus
A61K 39/225 ・・・Porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus
A61K 39/23 ・・Parvoviridae, e.g. feline panleukopenia virus
A61K 39/235 ・・Adenoviridae
A61K 39/245 ・・Herpetoviridae, e.g. herpes simplex virus
A61K 39/25 ・・・Varicella-zoster virus
A61K 39/255 ・・・Marek`s disease virus
A61K 39/265 ・・・Infectious rhinotracheitis virus
A61K 39/27 ・・・Equine rhinopneumonitis virus
A61K 39/275 ・・Poxviridae, e.g. avipoxvirus
A61K 39/285 ・・・Vaccinia virus or variola virus
A61K 39/29 ・・Hepatitis virus
A61K 39/292 ・・・{Serum hepatitis virus, hepatitis B virus, e.g. Australia antigen}
A61K 39/295 ・・Polyvalent viral antigens (vaccinia virus or variola virus A61K 39/285); Mixtures of viral and bacterial antigens
WARNING - A61K 39/00M, to subgroups of A61K 39/0016 and of A61K 39/12A61K 39/35 ・Allergens
A61K 39/36 ・・from pollen
A61K 39/38 ・Antigens from snakes
A61K 39/385 ・Haptens or antigens, bound to carriers
A61K 39/39 ・characterised by the immunostimulating additives, e.g. chemical adjuvants
A61K 39/395 ・Antibodies (agglutinins A61K 38/36; {as drug carriers A61K 47/48}); Immunoglobulins; Immune serum, e.g. antilymphocytic serum
A61K 39/39508 ・・{from milk, i.e. lactoglobulins}
A61K 39/39516 ・・{from serum, plasma}
A61K 39/39525 ・・・{Purification}
A61K 39/39533 ・・{against materials from animals}
A61K 39/39541 ・・・{against normal tissues, cells}
A61K 39/3955 ・・・{against proteinaceous materials, e.g. enzymes, hormones, lymphokines}
A61K 39/39558 ・・・{against tumor tissues, cells, antigens}
A61K 39/39566 ・・・{against immunoglobulins, e.g. anti-idiotypic antibodies}
A61K 39/39575 ・・{against materials from other living beings excluding bacteria and viruses, e.g. protozoa, fungi, plants}
A61K 39/39583 ・・{against materials not provided for elsewhere, e.g. haptens, coenzymes}
A61K 39/39591 ・・{Stabilisation, fragmentation}
A61K 39/40 ・・bacterial
A61K 39/42 ・・viral
A61K 39/44 ・・Antibodies bound to carriers
A61K 41/00 Medicinal preparations obtained by treating materials with wave energy or particle radiation; {Therapies using these preparations}(A61K 31/59 takes precedence; generation of ultrasonic waves B06B; electric discharge tubes H01J)
A61K 41/0004 ・{Homeopathy; Vitalisation; Resonance; Dynamisation, e.g. esoteric applications; Oxygenation of blood}
A61K 41/0009 ・{Inactivation or decontamination of a medicinal preparation prior to administration to the animal or human, e.g. : inactivation of viruses or bacteria for vaccines, sterilisation by electromagnetic radiation}
NOTE - See A61K 41/0019 for the specific method; see A61L 2/0029 if the invention lies in the method of sterilization of the medicinal preparation rather than the sterilized medicinal preparationA61K 41/0014 ・・{by ultrasonic waves}
A61K 41/0019 ・・{by UV, IR, Rx or gamma rays}
A61K 41/0023 ・{Agression treatment or altering}
NOTE - This groups covers aggression treatment or altering- of a medicinal preparation prior to administration to the human/animal, e.g. altering a binding specificity of a monoclonal antibody used in a medicinal agent with an oxidizing agent or an electric potential;- of a tissue/organ prior to graft, e.g. destroying immunodominant epitopes; - the permeability of cell membranes or biological barriers in vivo, e.g. by ultrasound, prior to the administration of a medicinal preparation to the animal/human; - for inducing the production of stress response proteins or heat shock proteins in order to reduce subsequent response to injuriesA61K 41/0028 ・{Disruption, e.g. by heat or ultrasounds, sonophysical or sonochemical activation; e.g. thermosensitive or heat-sensitive liposomes, disruption of calculi with a medicinal preparation and ultrasounds}
A61K 41/0033 ・・{Sonodynamic cancer therapy with sonochemically active agents or sonosensitizers, having their cytotoxic effects enhanced through application of ultrasounds (ultrasound therapy per se A61N 7/00)}
A61K 41/0038 ・{Radiosensitizing, i.e. administration of pharmaceutical agents that enhance the effect of radiotherapy (radiotherapy per se A61N 5/10)}
A61K 41/0042 ・{Photocleavage of drugs in vivo, e.g. cleavage of photolabile linkers in vivo by UV radiation for releasing the pharmacologically-active agent from the administered agent; photothrombosis or photoocclusion}
A61K 41/0047 ・{Sonopheresis, i.e. ultrasonically-enhanced transdermal delivery, electroporation of a pharmacologically active agent}
NOTE - To be classified in A61K 9/0009 when it is in relation to the galenic form]A61K 41/0052 ・{Thermotherapy; Hyperthermia; Magnetic induction; Induction heating therapy}
NOTE - simple magnetic guidance of drugs in vivo is to be classified in A61K 41/00, and in A61K 47/4893A61K 41/0057 ・{Photodynamic therapy with a photosensitizer, i.e. agent able to produce reactive oxygen species upon exposure to light or radiation, e.g. UV or visible light; photocleavage of nucleic acids with an agent}
A61K 41/0061 ・・{5-aminolevulinic acid-based PDT: 5-ALA-PDT involving porphyrins or precursors of protoporphyrins generated in vivo from 5-ALA}
A61K 41/0066 ・・{Psoralene-activated UV-A photochemotherapy (PUVA-therapy), e.g. for treatment of psoriasis or eczema, extracorporeal photopheresis with psoralens or fucocoumarins}
A61K 41/0071 ・・{PDT with porphyrins having exactly 20 ring atoms, i.e. based on the non-expanded tetrapyrrolic ring system, e.g. bacteriochlorin, chlorin-e6, or phthalocyanines}
A61K 41/0076 ・・{PDT with expanded (metallo)porphyrins, i.e. having more than 20 ring atoms, e.g. texaphyrins, sapphyrins, hexaphyrins, pentaphyrins, porphocyanines}
A61K 41/008 ・・{Two-Photon or Multi-Photon PDT, e.g. with upconverting dyes or photosensitisers}
A61K 41/0085 ・{Mossbauer effect therapy based on mossbauer effect of a material, i.e. re-emission of gamma rays after absorption of gamma rays by the material; selective radiation therapy, i.e. involving re-emission of ionizing radiation upon exposure to a first ionizing radiation}
A61K 41/009 ・{Neutron capture therapy, e.g. using uranium or non-boron material}
A61K 41/0095 ・・{Boron neutron capture therapy, i.e. BNCT, e.g. using boronated porphyrins}
A61K 45/00 Medicinal preparations containing active ingredients not provided for in groups A61K 31/00 to A61K 41/00
A61K 45/05 ・Immunological preparations stimulating the reticulo-endothelial system, e.g. against cancer
A61K 45/06 ・Mixtures of active ingredients without chemical characterisation, e.g. antiphlogistics and cardiaca
A61K 47/00 Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers, inert additives
A61K 47/02 ・Inorganic compounds
A61K 47/06 ・Organic compounds, {e.g. mineral oil, petrolatum, synthetic polyolefins}
A61K 47/08 ・・containing oxygen, {e.g. ethers, acetals, ketones, quinones, aldehydes, peroxides}
A61K 47/10 ・・・Alcohols; Phenols; Salts thereof, {e.g. glycerol; Polyethylene glycol (PEG); Poloxamers; PEG/POE alkyl ethers (sugar alcohols A61K 47/26; copolymers containing polyalkylene glycol or poloxamer A61K 47/34)}
A61K 47/12 ・・・Carboxylic acids; Salts or anhydrides thereof
A61K 47/14 ・・・Esters of carboxylic acids {e.g. fatty acid monoglycerides, medium-chain triglycerides, parabens}
A61K 47/16 ・・containing nitrogen, {e.g. nitro-, nitroso-, azo-compounds, nitriles, cyanates}
A61K 47/18 ・・・Amines; Quaternary ammonium compounds, {e.g. amides, ureas}
A61K 47/183 ・・・・{Amino acids or aminosulphonic acids, e.g. glycine, EDTA, aspartame}
A61K 47/186 ・・・・{Quaternary ammonium compounds, e.g. benzalkonium chloride, cetrimide}
A61K 47/20 ・・containing sulfur, {e.g. DMSO, docusate, sodium lauryl sulfate (A61K 47/183, A61K 47/186 take precedence)}
A61K 47/22 ・・Heterocyclic compounds, {e.g. ascorbic acid, tocopherol, pyrrolidones (A61K 47/183, A61K 47/186 take precedence)}
A61K 47/24 ・・containing atoms other than carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, halogen, nitrogen or sulfur, {e.g. cyclomethicone, phospholipids}
A61K 47/26 ・・Carbohydrates, {e.g. mono-, di-, oligosaccharides, nucleic acids, sugar alcohols, amino sugars; Derivatives thereof, e.g. polysorbates, sorbitan fatty acid esters, glycyrrhizin (A61K 47/183, A61K 47/186 take precedence)}
A61K 47/28 ・・Steroids, {e.g. cholesterol, bile acids, glycyrrhetinic acid (A61K 47/183, A61K 47/186 take precedence)}
A61K 47/30 ・Macromolecular compounds
A61K 47/32 ・・Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, {e.g. carbomers, poly(meth)acrylates, polyvinyl pyrrolidone}
A61K 47/34 ・・Macromolecular compounds obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, {e.g. polyesters, polyamino acids, polysiloxanes, copolymers of polyalkylene glycol or poloxamer (PEG or poloxamers A61K 47/10)}
NOTE - This group does not cover polyalkoxylated compounds, which are classified according to the derivatized compounds. The following list provides examples of such polyalkoxylated compounds together with their relevant group:A61K 47/36 ・・Polysaccharides; Derivatives thereof, {e.g. gums, starch, alginate, dextrin, hyaluronic acid, chitosan, inulin, agar, pectin}
A61K 47/38 ・・・Cellulose; Derivatives thereof
A61K 47/40 ・・・Cyclodextrins; Derivatives thereof {(cyclodextrin inclusion compounds A61K 47/48969)}
A61K 47/42 ・・Proteins; Polypeptides; Degradation products thereof; Derivatives thereof {e.g. albumin, gelatin, zein (oligopeptides having up to 5 amino acids A61K 47/183; polyamino acids A61K 47/34)}
A61K 47/44 ・Oils, fats or waxes according to more than one of groups A61K 47/02 to A61K 47/42; {Natural or modified natural oils, fats or waxes, e.g. (polyethoxylated) castor oil, montan wax, ozokerite, lignite, shellac, rosin, beeswax, lanolin (synthetic glycerides, e.g. medium-chain triglycerides A61K 47/14)}
A61K 47/46 ・Ingredients of undetermined constitution or reaction products thereof, {e.g. skin, bone, milk, cotton fiber, eggshell, oxgall, plant extracts}
A61K 47/48 ・the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer drug conjugates
A61K 47/48007 ・・{the pharmacologically- or therapeutically-active agent being covalently bound or complexed to a modifying agent}
NOTE - The modifying agent being a macromolecular compound A61K 47/48K, a peptide, protein or polyamino acid A61K 47/48R, an antibody or immunoglobulin A61K 47/48TA61K 47/48015 ・・・{the modifying agent being an inorganic compound; e.g. inorganic ion that being chemically complexed with the pharmacologically- or therapeutically-active agent (A61K 47/48161 takes precedence)}
NOTE - Classic ion pairs of medicinal agents are not classified in A61K 47/48 but in A61K 31/00A61K 47/48023 ・・・{the modifying agent being an organic compound (A61K 47/48161 takes precedence)}
A61K 47/4803 ・・・・{the modifying agent being an organic ion that forms an ion pair complex with the pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent.}
A61K 47/48038 ・・・・{the modifying agent being a carboxylic acid, e.g. a fatty acid or an amino acid}
NOTE - When covalently linked to the pharmacologically or therapeutically-active agent, it can be via its carboxylic function or via another chemical function leaving the carboxylic function freeA61K 47/48046 ・・・・{the modifying agent being a lipid, e.g. a triglyceride; the modifying agent being a polyamine, e.g. spermine or spermidine}
NOTE - Fatty acid conjugates are classified in A61K 47/48038;cholesterol conjugates are classified in A61K 47/48123A61K 47/48053 ・・・・・{the modifying agent being a phospholipid.}
A61K 47/48061 ・・・・{the modifying agent being a heterocyclic compound (A61K 47/48153 takes precedence)}
A61K 47/48069 ・・・・・{the modifying agent being a heterocyclic compound which being a porphyrine or a porphyrine with an expanded ring system, e.g. texaphyrine}
NOTE - Porphyrins used as photosensitizers in photodynamic therapy: seeA61K 47/48076 ・・・・{the modifying agent being a chelate, i.e. single central atom/ion sequestered by a polydentate ligand, e.g. Gd-DOTA or Zinc-amino acid chelate, or a chelate-forming compound, i.e. chelating group, e.g. DOTA or ethylenediamine, that being covalently/complexed to the pharmacologicallyor therapeutically-active agent}
NOTE - Paramagnetic chelates used in MRI and not linked to by further compound, e.g. polymer, peptide, protein, antibody, small molecules like sugars, are only classified in A61K 49/101 and subgroupes.A61K 47/48084 ・・・・{the modifying agent being a phosphate or phosphonate not being a phospholipid, e.g. bone-seeking}
NOTE - nucleic acid carriers to be classified in A61K 47/48092A61K 47/48092 ・・・・{the modifying agent linked to the pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent being a sugar, nucleoside, nucleotide, nucleic acid}{Note nucleic acids can be coding, non-coding, nucleic acid which being therapeutically-active or not, e.g.: oligonucleotides, DNA, RNA, siRNA, nucleic acid aptamers}
A61K 47/481 ・・・・{the modifying agent being also a pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent, i.e. the entire conjugate being a codrug, i.e. a dimer, oligomer or polymer of pharmacologically or therapeutically active compounds, e.g. a polymer of aspirin}{Note a sugar, nucleoside, nucleotide, nucleic acid is classified in A61K 47/48092; a polymer of an active agent is not classified in A6K47/48K6}
A61K 47/48107 ・・・・・{one of the codrug's components being a vitamin, e.g. niacinamide (vitamin B3), cobalamin (vitamin B12), folate, vitamin A, retinoic acid}
A61K 47/48115 ・・・・・{one of the codrug's components being an antibiotic}
A61K 47/48123 ・・・・{the modifying agent being a steroid plant sterol, glycyrrhetic acid, enoxolone, bile acid}
NOTE - - Cholesterol only classified here and not in A61K 47/48046- Codrugs of pharmacologically active/therapeutically-active steroids are classified in this group and also in A61K 47/481A61K 47/4813 ・・・・{pretargeting systems involving an organic compound, not being a peptide, protein or antibody, for targeting specific cells}
NOTE - The concept of "pre-targeting" covers the administration of the modifying agent (which being an agent able to target specific cells in the body), and of the pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent (drug D) in several steps, their "binding" occurring at the in vivo targeted site. It involves administration in at least two steps, for example:(i) a conjugate T-A corresponding to a targeting agent able to target specific cells or receptors in the body (T) linked to a compound A, and (ii) a conjugate D-M corresponding to the drug linked to a modifying agent M able to target the compound A. The sequence involves e.g. the administration of T-A and then D-M. Between step (i) and step (ii), a further compound able to bind to A and M may also be administered, e.g. during a clearing step. Classification being made according to the nature of T in the subgroupes of A61K 47/4813, A61K 47/48346 and A61K 47/48723. In A61K 47/4813 and its subgroupes, T being an organic compound, not being a peptide, protein or antibody. Classification being also made according to the nature of organic compound T in the appropriate A61K 47/48023 subgroup. If T being a peptide, protein or antibody, classification being made in the corresponding A61K 47/48346 or A61K 47/48723 pretargeting class]A61K 47/48138 ・・・・・{ECTA, enzyme catalyzed therapeutic agent}
NOTE - In the definition of A61K 47/4813, an enzyme being used as groupA61K 47/48146 ・・・・・{the modifying agent being biotin}
NOTE - In the definition of A61K 47/4813, M and A form a pair of biotin and (strept)avidin, or derivatives of biotin and (strept)avidinA61K 47/48153 ・・・・{the modifying agent being a chemiluminescent acceptor}
NOTE - A chemical reaction induces the cleavage of the pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent from the carrier while at the same time producing light. If the conjugate if cleaved through activation by light in vivo in order to release the drug, then the classification symbol beingA61K 47/48161 ・・・・{Redox delivery systems, e.g. dihydropyridine pyridinium salt redox systems}
A61K 47/48169 ・・{the modifying agent being an organic macromolecular compound, i.e. an oligomeric, polymeric, dendrimeric molecule}
NOTE - a peptide, protein, polyamino acid being classified in A61K 47/48238 and subgroupes; an antibody in A61K 47/48369 and subgroupes.In case of block copolymers, the different (large) blocks are classified in the appropriateA61K 47/48176 ・・・{the organic macromolecular compound has been obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. poly(meth)acrylate, polyacrylamide, polystyrene, polyvinylpyrrolidone, polyvinylalcohol}
A61K 47/48184 ・・・・{the macromolecular compound obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds being an ion exchange resin, e.g. polystyrene sulfonic acid resin}
A61K 47/48192 ・・・{the organic macromolecular compound has been obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyureas, polyurethanes}
A61K 47/482 ・・・・{the macromolecule is/contains a polyester, e.g. PLGA, polylactide-co-glycolide}
A61K 47/48207 ・・・・{the macromolecule is/contains a polyamide, e.g. nylon (polyamino acids A61K 47/48238)}
A61K 47/48215 ・・・・{the organic macromolecular compound being a polyoxyalkylene oligomer, polymer, dendrimer, e.g. PEG, PPG, PEO, polyglycerol}
A61K 47/48223 ・・・・{the macromolecule contains phosphorus in the main chain, e.g. poly-phosphazene}
A61K 47/4823 ・・・{the organic macromolecular compound being a polysaccharide or a derivative, e.g. starch, chitosan, chitin, cellulose, pectin, cyclodextrin with the pharmacologically active agent being covalently linked to the external surface of the ring structure, a bacterial polysaccharide or oligosaccharide antigen, a glycosaminoglycan}
NOTE - if cyclodextrin being used to complex the drug, then the appropriate classification being A61K 47/48969;proteoglycans as modifying agents attached to the pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent are classified in the appropriate A61K 47/48238 subgroupA61K 47/48238 ・・{the modifying agent being a protein, peptide, polyamino acid}
NOTE - antibodies or immunoglobulins are classified in A61K 47/48369 subgroupesSpecial physical or galenic forms modified by covalent attachment or complexation of a protein, peptide or polyamino acid, are given theA61K 47/48246 ・・・[N: drug-peptide, protein or polyamino acid conjugates, i.e. the modifying agent being a protein, peptide, polyamino acid which being linked/complexed to a molecule that being the pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent (peptidic linker are classified in A61K 47/48338)
NOTE - The connection of the drug to the peptide, protein or polyamino acid can be by a direct covalent linkage or through a linker Fusion/chimeric proteins genetically produced, e.g. by recombinant DNA technology, are classified in C07K 2319/00 and subgroups, not in A61K 47/48246 and subgroups.A61K 47/48253 ・・・・{the peptide, protein or polyamino acid in the drug conjugate being a branched, dendritic or hypercomb peptide}
A61K 47/48261 ・・・・{the peptide or protein in the drug conjugate being a toxin or a lectin, e.g. clostridial toxins or Pseudomonas exotoxin}
A61K 47/48269 ・・・・{the peptide or protein in the drug conjugate being a cytokine, e.g. IL2, chemokine, growth factors, interferons being the inactive part of the conjugate}
NOTE - ligands of growth factors are not classified hereA61K 47/48276 ・・・・{the peptide or protein in the drug conjugate being a receptor as such, e.g. CD4; a cell surface antigen (therefore not a peptide ligand targeting the antigen); a cell surface determinant, i.e. a part of the surface of a cell}
NOTE - a peptide targeting a receptor being not classified here
A61K 47/48284 ・・・・{the peptide or protein in the drug conjugate being an albumin, e.g. HSA, BSA, ovalbumin, or a Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin (KHL)}
A61K 47/48292 ・・・・{the peptide or protein in the drug conjugate being a connective tissue peptide, e.g. collagen, fibronectin, gelatin}
A61K 47/483 ・・・・{the peptide or protein in the drug conjugate being a transferrin, e.g. a lactoferrin or ovotransferrin}
A61K 47/48307 ・・・・{the peptide or protein in the drug conjugate being a haemoglobin}
A61K 47/48315 ・・・・{the peptide or protein in the drug conjugate being a polycationic or polyanionic oligopeptide, polypeptide or polyamino acid, e.g. polylysine, polyarginine, polyglutamic acid, peptide TAT}
A61K 47/48323 ・・・・・{polyanionic oligopeptide, polypeptide or polyamino acid, used to complex nucleic acids being the therapeutic agent}
A61K 47/4833 ・・・・{the entire peptide or protein drug conjugate elicits an immune response, e.g. conjugate vaccines}
NOTE - Haptens, e.g. conjugate of morphine or nicotine and KLH inducing an immune response being classified in A61K 47/4833 and A61K 47/48284A61K 47/48338 ・・・{peptidic linker, binder, spacer, e.g. peptidic enzyme-labile linker}
A61K 47/48346 ・・・{pretargeting systems involving a peptide or protein (not an antibody A61K 47/48723) for targeting specific cells}
NOTE - The concept of "pre-targeting" covers the administration of the modifying agent (which being an agent able to target specific cells in the body), and of the pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent (drug D) in several steps, their "binding" occurring at the in vivo targeted site. It involves administration in at least two steps, for example:(i) a conjugate T-A corresponding to a targeting agent T able to target specific cells or receptors in the body (T) linked to a compound A, and (ii) a conjugate D-M corresponding to the drug D linked to a modifying agent M, able to target the compound A. The sequence involves e.g. the administration of T-A and then D-M. Between step (i) and step (ii), a further compound able to bind to both A and M may also be administered (e.g. during a clearing step).Classification being made according to the nature of T in the subgroupes of A61K 47/4813, A61K 47/48346 and A61K 47/48723. In A61K 47/48346 and its subgroupes, T being a peptide or protein, not being a antibody. If M being biotin and A being a (strept)avidin or a derivative thereof, then A61K 47/48353 being used as classification symbolA61K 47/48353 ・・・・[pretargeting system, clearing therapy or rescue therapy involving biotin-(strept)avidin systems]
NOTE - In this group, M and A in the definition of A61K 47/48346 can form a biotin/(strept)avidin systemA61K 47/48361 ・・・・{Enzyme prodrug therapy, e.g. gene directed enzyme drug therapy (GDEPT), VDEPT}
NOTE - An enzyme being used as group A in the definition of A61K 47/4813, and being first targeted to specific cells via administration of the conjugate T-A. Then, the conjugate M-D which being a substrate for A being administered. The enzyme A being able to cleave the conjugateA61K 47/48369 ・・{the modifying part being an antibody, an immunoglobulin, or a fragment thereof, e.g. a Fc-fragment}
A61K 47/48376 ・・・{drug-antibody or immunoglobulin conjugates defined by the pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent}
NOTE - The modifying part being an antibody or immunoglobulin bearing antigen-binding sitesA61K 47/48384 ・・・・{drug conjugated to an antibody or immunoglobulin, e.g. cisplatin-antibody conjugates}
NOTE - The modifying part being an antibody or immunoglobulin bearing at least one antigen-binding site.In A61K 47/48384 and its subgroupes, classification being made according to the nature of the drug, i.e. the pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent in the antibody conjugate. If the nature of the antibody in a specific conjugate being known, it being indicated with the corresponding A61K 47/48507 subgroup, in addition to the subgroup A61K 47/48384 characterizing the drug. If the conjugate comprises also a polymer or a polyamino acid, then the class A61K 47/48692 or A61K 47/487 being also givenA61K 47/48392 ・・・・・{the drug being a vinca alkaloid}
A61K 47/484 ・・・・・{the drug or compound being a sugar, nucleoside, nucleotide, nucleic acid, e.g. RNA antisense}
A61K 47/48407 ・・・・・・{the drug being an antibiotic, e.g. one of the antitumor antibiotics:
A61K 47/48415 ・・・・・{the drug being a protein or peptide, e.g. transferrin or bleomycin}
A61K 47/48423 ・・・・・・{the drug being a peptidic cytokine, e.g. an interleukin or interferon}
A61K 47/4843 ・・・・・・{the drug being an enzyme}
A61K 47/48438 ・・・・・・{the drug being a toxin}
A61K 47/48446 ・・・・・・・{the drug being a plant toxin}
A61K 47/48453 ・・・・・・・・{the drug being a plant heterodimeric toxin; chains A or B containing toxins, e.g. abrin, modeccin}
A61K 47/48461 ・・・・・・・・・{the drug being ricin (double chain)}
A61K 47/48469 ・・・・・・・・{the drug being a ribosomal inhibitory protein, (RIP-i or RIP-II), e.g. Pap, gelonin, dianthin}
A61K 47/48476 ・・・・・・・・・{the drug being ricin A}
A61K 47/48484 ・・・・・・・{the drug being a bacterial toxin, e.g. diphteria toxin, Pseudomonas exotoxin A}
A61K 47/48492 ・・・・・・・{the drug being a fungal toxin, e.g. alpha sarcine, mitogillin, zinniol, restrictocin}
A61K 47/485 ・・・・・・・{the drug being a viral toxin}
A61K 47/48507 ・・・{the modifying agent being a well defined antibody or immunoglobulin bearing at least one antigen-binding site}
NOTE - According to the nature of the antibody, the appropriate A61K 47/48515 subgroup being given. If the pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent in the antibody conjugate being known, the appropriateA61K 47/48515 ・・・・{not used; see subgroups}
A61K 47/48523 ・・・・・{the antibody being against material from viruses}
A61K 47/4853 ・・・・・・{the antibody being targeting a RNA virus}
A61K 47/48538 ・・・・・{the antibody being targeting a material from animals or humans.}
A61K 47/48546 ・・・・・{the antibody being targeting a cytokine, e.g. growth factors, VEGF, TNF, a lymphokine or an interferon}
A61K 47/48553 ・・・・・{the antibody being targeting an hormone, or an hormone-releasing or -inhibiting factor}
A61K 47/48561 ・・・・・{the antibody being targeting a receptor, a cell surface antigen, a cell surface determinant}
A61K 47/48569 ・・・・・{the antibody being targeting a determinant of a tumour cell}
A61K 47/48576 ・・・・・・{the tumour determinant being carcino-embryonic antigen}
A61K 47/48584 ・・・・・・{the tumour determinant being from breast cancer cell}
A61K 47/48592 ・・・・・・{the tumour determinant being from lung cancer cell}
A61K 47/486 ・・・・・・{the tumour determinant being from liver or pancreas cancer cell}
A61K 47/48607 ・・・・・・{the tumour determinant being from kidney or bladder cancer cell}
A61K 47/48615 ・・・・・・{the tumour determinant being from stomach or intestines cancer cell}
A61K 47/48623 ・・・・・・{the tumour determinant being from skin, nerves or brain cancer cell}
A61K 47/4863 ・・・・・・{the tumour determinant being from a cell of a blood cancer}
A61K 47/48638 ・・・・・・{the tumour determinant being from a cell of the reproductive system:
A61K 47/48646 ・・・・・{the antibody being targeting an enzyme}
A61K 47/48653 ・・・・・{the antibody being targeting an immunoglobulin, being an anti-idiotypic antibody}
A61K 47/48661 ・・・・・{the antibody being a hybrid immunoglobulin}
A61K 47/48669 ・・・・・・{the antibody being an immunoglobulin containing regions, domains, residues from different species}
A61K 47/48676 ・・・・・・{the immunoglobulin has two or more different antigen-binding sites, e.g. bispecific or multispecific immunoglobulin}
A61K 47/48684 ・・・・{cluster-antibody conjugates, i.e. the modifying agent consists of a plurality of antibodies that are covalently linked to each other, or of different antigen-binding fragments fragments that are covalently linked to each other}
A61K 47/48692 ・・・・{polymer-drug antibody conjugates, e.g. mitomycin-dextran-Ab; DNA-polylysine-antibody complex or conjugate, used for therapy}
A61K 47/487 ・・・・・{the conjugate or the polymer being a starburst, a dendrimer, a cascade}
A61K 47/48707 ・・・・{antibody-chelate conjugate wherein the chelate being used for therapeutic purposes (when radioabeled and used in radiodiagnosis or radiotherapy A61K 51/1093 and the corresponding A61K 51/1003 subgroup; antibody-chelate used for MRI A61K 49/14)}
A61K 47/48715 ・・・{conjugates wherein the antibody being the modifying agent and wherein the linker, binder, spacer confers particular properties to the conjugate, e.g. peptidic enzyme-labile linker or acid-labile linker giving rise to an acid-labile immunoconjugate wherein the drug may be released from its antibody conjugated part in an acidic, e.g. tumoural, environment}
A61K 47/48723 ・・・{pretargeting systems involving an antibody for targeting specific cells}
NOTE - The concept of "pre-targeting" covers the administration of the modifying agent (which being an agent able to target specific cells in the body), and of the pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent (drug D) in several steps, their "binding" occurring at the in vivo targeted site. It involves administration in at least two steps, for example: (i) a conjugate T-A corresponding to a targeting agent able to target specific cells or receptors in the body (T) linked to a compound A, and (ii) a conjugate D-M corresponding to the drug linked to a modifying agent M, able to target the compound A. The sequence involves e.g. the administration of T-A and then D-M. Between step (i) and step (ii), a further compound able to bind to A and M may also be administered (e.g. during a clearing step).A61K 47/4873 ・・・・{clearing therapy or enhanced clearance, i.e. wherein an antibody clearing agent being used in addition to T-A and D-M according to the definitions in A61K 47/48723}
A61K 47/48738 ・・・・{rescue therapy; agonist-antagonist; antidote; targeted rescue or protection e.g. folic acid-folinic acid, conjugated to antibodies both or only one}
A61K 47/48746 ・・・・{two or three steps pretargeting systems, wherein an antibody conjugate being used in at least one of the steps; ligand-antiligand therapy}
A61K 47/48753 ・・・・・{avidin-biotin system wherein at least one avidin- or biotin-conjugated antibody being used in a two- or three-steps pretargeting system}
NOTE - This subgroup covers the case wherein M and A in the definition ofA61K 47/48761 ・・・・{ADEPT, i.e. Antibody Directed Enzyme Prodrug Therapy}
NOTE - An enzyme being used as group A according to the definition inA61K 47/48769 ・・{the conjugate being characterized by a special physical or galenical form}
NOTE - The conjugates in the A61K 47/48769 subgroupes correspond (i) either to a pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent complexed/covalently linked to the special physical or galenical form, e.g. on the surface of a polymeric nanoparticle or liposome, or to polymeric chains in the matrix of a polymeric gel, (ii) or to a special physical or galenical form encapsulating the pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent and modified on its surface or matrix by a modifying agent. In case (i), classification being made according to the nature of the special physical or galenical form in the appropriate A61K 47/48769 subgroup and may be completed by the appropriate A61K 47/48 subgroup defining the compound to which the pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent being linked, e.g.A61K 47/48776 ・・・{forms of ingredients not provided for by groups A61K 47/48784 to A61K 47/48992, e.g. cells, cell fragments, viruses, ghosts, red blood cells, viral vectors having the pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent complexed or covalently linked to, or being themselves modified by complexation or covalent linkage by a modifying agent}
NOTE - Simple encapsulation in cells being isclassified in A61K 9/5068; simple encapsulation in a virus capsid is classified in A61K 9/5184A61K 47/48784 ・・・{the form being semi-solid, an ointment, a gel, a hydrogel, a solidifying gel}
A61K 47/48792 ・・・{the form being a colloid, emulsion, i.e. having at least a dispersed/continuous oil phase and a dispersed/continuous aqueous phase, dispersion or suspension}
A61K 47/488 ・・・・{the form being a micro-emulsion, nano-emulsion or micelle (Simple encapsulation of a drug in micelle: A61K 9/1075)}
NOTE - Micro-emulsion means that the dispersed phase being in the form of globules having a diameter above or equal to 1 micrometer.A61K 47/48807 ・・・・・{micelles formed by phospholipids}
A61K 47/48815 ・・・・{the form being a liposome, i.e. a bilayered vesicle, having its surface modified by covalent attachment or complexation of the pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent and/or modifying agent. (Simple encapsulation of a drug which being not functionalised on its surface by a modifying agent:
NOTE - Liposomes modified by a polymer because they incorporate a polymer-lipid conjugate are only additionally classified inA61K 47/48823 ・・・・・{the form being a liposome which being modified on its surface by an antibody}
NOTE - Classification being also made according to the nature of the antibody in the appropriate A61K 47/48515 subgroupA61K 47/4883 ・・・・・{the form being a polymersome, i.e. a liposome with polymerisable or polymerized bilayer-forming substances}{Note Liposomes comprising polymers grafted on their surface are not classified in A61K 47/4883, but in A61K 47/48815 if the polymer being unusual, or in A61K 9/1271}
A61K 47/48838 ・・・・{the form being a lipoprotein vesicle, e.g. HDL and LDL proteins}
A61K 47/48846 ・・・・{the form being a ribbon, tubule cochleate}
A61K 47/48853 ・・・{the form being a particulate, powder, adsorbate, bead, sphere}
A61K 47/48861 ・・・・{the form being an inorganic particle, e.g. a ceramic particle, silica particle, ferrite, synsorb}
NOTE - When the inorganic particle being a magnetic particle and being guided from outside the body with the means of a magnetic field, add theA61K 47/48869 ・・・・{the form being a micro- or nano-capsule or a micro/nano-bubble, i.e. a hollow or gas micro- or nano-particle or sphere, a gas-filled micro- or nano-particle for use in therapy (Micro- or nano-bubbles used only for ultrasound imaging are classified in A61K 49/223 or A61K 49/225 only)}
NOTE - Pharmacologically or therapeutically active agents released from a micro- or nano-capsule by acoustic/ultrasound activation are also classified in A61K 41/0028 and A61K 9/0009A61K 47/48876 ・・・・{the form being a solid microparticle having no hollow or gas-filled core}{Note Its size or diameter being higher or equal to 1 micrometer}
A61K 47/48884 ・・・・・{the form being a nanoparticle, e.g. an immuno-nanoparticle}{Note Its size or diameter being smaller than 1 micrometer. Classification being also made according to the nature of the antibody with the appropriate A61K 47/48515 subgroup}
A61K 47/48892 ・・・・・・{the material constituting the nanoparticle being a polymer}{Note The subgroups A61K 47/48169 are not additionally used}
A61K 47/489 ・・・・・・・{the material constituting the nanoparticle being a polymer obtained by reactions only involving carbon to carbon, e.g. poly(meth)acrylate, polystyrene, polyvinylpyrrolidone, polyvinylalcohol}
A61K 47/48907 ・・・・・・・{the material constituting the nanoparticle being a polymer obtained otherwise than by reactions involving carbon to carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyesters, polyamides, polyglycerol}
A61K 47/48915 ・・・・・・・・{the polymer being PLGA, PLA or polyglycolic acid}
A61K 47/48923 ・・・・・・・{the polymer being a polysaccharide, e.g. starch, chitosan, chitin, cellulose, pectin}
A61K 47/4893 ・・・・{the form being a granulate or an agglomerate}
A61K 47/48938 ・・・{the form being a pill, tablet, lozenge, capsule}
A61K 47/48946 ・・・{Microcapsules}
A61K 47/48953 ・・・・{Nanocapsules; Nanoparticles, e.g. immunonanoparticles}
A61K 47/48961 ・・・{the conjugate being in the form of a host-guest, i.e. being an inclusion complex, e.g. clathrate, cavitate, fullerene}
A61K 47/48969 ・・・・{inclusion being performed with a cyclodextrin (cyclodextrins used as simple excipients A61K 47/40)}
A61K 47/48976 ・・・{the form being a fibre, textile, slabb, sheet}
A61K 47/48984 ・・・{the form being a plaster, bandage, dressing, patch}
A61K 47/48992 ・・・{the form being a device, kit .e.g. stent, microdevice}
A61K 48/00 Medicinal preparations containing genetic material which is inserted into cells of the living body to treat genetic diseases; Gene therapy
NOTE - In this group the following expression is used with the meaning indicated:A61K 48/0008 ・{characterised by an aspect of the `non-active` part of the composition delivered, e.g. wherein such `non-active` part is not delivered simultaneously with the `active` part of the composition}
A61K 48/0016 ・・{wherein the nucleic acid is delivered as a `naked` nucleic acid, i.e. not combined with an entity such as a cationic lipid}
A61K 48/0025 ・・{wherein the non-active part clearly interacts with the delivered nuclic acid}
A61K 48/0033 ・・・{the non-active part being non-polymeric}
A61K 48/0041 ・・・{the non-active part being polymeric}
A61K 48/005 ・{characterised by an aspect of the `active` part of the composition delivered, i.e. the nucleic acid delivered}
A61K 48/0058 ・・{Nucleic acids adapted for tissue specific expression, e.g. having tissue specific promoters as part of a contruct}
A61K 48/0066 ・・{Manipulation of the nucleic acid to modify its expression pattern, e.g. enhance its duration of expression, achieved by the presence of particular introns in the delivered nucleic acid}
A61K 48/0075 ・{characterised by an aspect of the delivery route, e.g. oral, subcutaneous}
A61K 48/0083 ・{characterised by an aspect of the administration regime}
A61K 48/0091 ・{Purification or manufacturing processes for gene therapy compositions}
A61K 49/00 Preparations for testing in vivo
A61K 49/0002 ・{General or multifunctional contrast agents, e.g. chelated agents}
A61K 49/0004 ・{Screening or testing of compounds for diagnosis of disorders, assessment of conditions, e.g. renal clearance, gastric emptying, testing for diabetes, allergy, rheuma, pancreas functions}
A61K 49/0006 ・・{Skin tests, e.g. intradermal testing, test strips, delayed hypersensitivity}
A61K 49/0008 ・・{Screening agents using (non-human) animal models or transgenic animal models or chimeric hosts, e.g. Alzheimer disease animal model, transgenic model for heart failure}
A61K 49/001 ・{Preparation for luminescence or biological staining}
A61K 49/0013 ・・{Luminescence}
A61K 49/0015 ・・・{Phosphorescence}
A61K 49/0017 ・・・{Fluorescence in vivo}
A61K 49/0019 ・・・・{characterised by the fluorescent group}
A61K 49/0021 ・・・・・{the fluorescent group being a small organic molecule (oligomeric, polymeric, dendritic molecules: A61K 49/0019)}
NOTE - if this fluorescent group is complexed or covalently linked to a carrier, classification is also made according to the nature of the carrier in the appropriate A61K 49/005 subgroupA61K 49/0023 ・・・・・・{Di-or triarylmethane dye (xanthene dyes A61K 49/0041)}
A61K 49/0026 ・・・・・・{Acridine dyes}
A61K 49/0028 ・・・・・・{Oxazine dyes}
A61K 49/003 ・・・・・・{Thiazine dyes}
A61K 49/0032 ・・・・・・{Methine dyes, e.g. cyanine dyes}
A61K 49/0034 ・・・・・・・{Indocyanine green, i.e. ICG, cardiogreen} uC1206]
A61K 49/0036 ・・・・・・{Porphyrins (used in photodynamic therapy A61K 41/0071 or A61K 41/0076; used as targeting group or modifying agent for targeting a therapeutic compound A61K 47/48069)}
A61K 49/0039 ・・・・・・{Coumarin dyes}
A61K 49/0041 ・・・・・・{Xanthene dyes, used in vivo, e.g. administered to a mice, e.g. rhodamines, rose Bengal (in vivo G01N)}
A61K 49/0043 ・・・・・・・{Fluorescein, used in vivo}
A61K 49/0045 ・・・・・{the fluorescent agent being a peptide or protein used for imaging or diagnosis in vivo}
A61K 49/0047 ・・・・・・{Green fluorescent protein (GFP)}
A61K 49/005 ・・・・{characterised by the carrier molecule carrying the fluorescent agent}
NOTE - Classification is also made according to the nature of the fluorescent group in the appropriate subgroup of A61K 49/0019A61K 49/0052 ・・・・・{Small organic molecules (oligomers, polymers, dendrimers A61K 49/0054)}
A61K 49/0054 ・・・・・{Macromolecular compounds, i.e. oligomers, polymers, dendrimers}
A61K 49/0056 ・・・・・{Peptides, proteins, polyamino acids}
A61K 49/0058 ・・・・・{Antibodies}
A61K 49/006 ・・{Biological staining of tissues in vivo, e.g. methylene blue or toluidine blue O administered in the buccal area to detect epithelial cancer cells, dyes used for delineating tissues during surgery}
NOTE - If the dye used for staining is fluorescent, classification is also given for the appropriate subgroup of A61K 49/0019]A61K 49/0063 ・・{characterised by a special physical or galenical form, e.g. emulsions, microspheres}
NOTE - Note Classification is also made according to the nature of the luminescent or fluorescent agent and/or the carrier carrying the fluorescent agentA61K 49/0065 ・・・{the luminescent/fluorescent agent having itself a special physical form, e.g. gold nanoparticle}
A61K 49/0067 ・・・・{quantum dots, fluorescent nanocrystals}
NOTE - Quantum dots modified on their surface by an antibody are also classified in A61K 49/0058)A61K 49/0069 ・・・{the agent being in a particular physical galenical form}
NOTE - If the physical or galenical form containing a fluorescent agent is modified by a particular agent, classification is also made according to the nature of this agent in the appropriate A61K 49/005 subgroupA61K 49/0071 ・・・・{solution, solute}
A61K 49/0073 ・・・・{semi-solid, gel, hydrogel, ointment}
A61K 49/0076 ・・・・{dispersion, suspension, e.g. particles in a liquid, colloid, emulsion}
A61K 49/0078 ・・・・・{micro-emulsion, nano-emulsion}
NOTE - Micro-emulsion means that the dispersed phase is in the form of globules having a diameter above or equal to 1 micrometer.A61K 49/008 ・・・・・{lipoprotein vesicle, e.g. HDL or LDL proteins}
A61K 49/0082 ・・・・・{micelle, e.g. phospholipidic micelle and polymeric micelle}
NOTE - Micelles comprise a monolayer of surfactant molecules that are aggregated head-to-head and tail-to-tail, thus forming a small spherical particle; micelles can be normal, i.e., the surfactant heads are hydrophilic, or inverseA61K 49/0084 ・・・・・{liposome, i.e. bilayered vesicular structure}
NOTE - When the surface of the liposome encapsulating a fluorescent agent and used in vivo is functionalised by a modifying agent, classification is also made according to the nature of this modifying agent: e.g. a liposome modified on its surface by a peptide is classified in A61K 49/0084 and A61K 49/0056.Liposomes encapsulating a fluorescent agent, used in vivo and modified on their surface by a polymer because they incorporate a polymer-lipid conjugate, are only additionally classified in A61K 49/0054 if the polymer modifying the lipid is unusual. Liposomes encapsulating a fluorescent agent which are pegylated because they incorporate a pegylated lipid are only classified in A61K 49/0084, not in A61K 49/0054A61K 49/0086 ・・・・・・{Polymersome, i.e. liposome with polymerisable or polymerized bilayered-forming substances}
A61K 49/0089 ・・・・{Particulate, powder, adsorbate, bead, sphere}
A61K 49/0091 ・・・・・{Microparticle, microcapsule, microbubble, microsphere, microbead, i.e. having a size or diameter higher or equal to 1 micrometer}
NOTE - When the surface of the microparticle encapsulating a fluorescent agent and used in vivo is functionalised by a modifying agent, classification is also made according to the nature of this modifying agent, e.g. a microparticle modified on its surface by a peptide is classified in A61K 49/0091 and A61K 49/0056A61K 49/0093 ・・・・・・{Nanoparticle, nanocapsule, nanobubble, nanosphere, nanobead, i.e. having a size or diameter smaller than 1 micrometer, e.g. polymeric nanoparticle}
A61K 49/0095 ・・・・・・・{Nanotubes}
A61K 49/0097 ・・・・{Cells, viruses, ghosts, red blood cells, viral vectors, used for imaging or diagnosis in vivo}
A61K 49/04 ・X-ray contrast preparations
NOTE - In the preparation of new organic compounds and their use in X-ray contrast preparations, classification is only made in the relevant subclasses C07C toA61K 49/0404 ・・{containing barium sulfate}
A61K 49/0409 ・・{Physical forms of mixtures of two different X-ray contrast-enhancing agents, containing at least one X-ray contrast-enhancing agent which is not a halogenated organic compound}
A61K 49/0414 ・・・{Particles, beads, capsules or spheres}
A61K 49/0419 ・・・・{Microparticles, microbeads, microcapsules, microspheres, i.e. having a size or diameter higher or equal to 1 micrometer}
A61K 49/0423 ・・・・{Nanoparticles, nanobeads, nanospheres, nanocapsules, i.e. having a size or diameter smaller than 1 micrometer}
A61K 49/0428 ・・・・・{Surface-modified nanoparticles, e.g. immuno-nanoparticles}
A61K 49/0433 ・・{containing an organic halogenated X-ray contrast-enhancing agent}
A61K 49/0438 ・・・{Organic X-ray contrast-enhancing agent comprising an iodinated group or an iodine atom, e.g. iopamidol}
A61K 49/0442 ・・・{Polymeric X-ray contrast-enhancing agent comprising a halogenated group}
A61K 49/0447 ・・・{Physical forms of mixtures of two different X-ray contrast-enhancing agents, containing at least one X-ray contrast-enhancing agent which is a halogenated organic compound}
A61K 49/0452 ・・・・{Solutions, e.g. for injection}
A61K 49/0457 ・・・・{Semi-solid forms, ointments, gels, hydrogels}
A61K 49/0461 ・・・・{Dispersions, colloids, emulsions or suspensions}
A61K 49/0466 ・・・・・{Liposomes, lipoprotein vesicles, e.g. HDL or LDL lipoproteins, phospholipidic or polymeric micelles}
A61K 49/0471 ・・・・・{Perflubron, i.e. perfluoroctylbromide, C8F17Br emulsions}
A61K 49/0476 ・・・・{Particles, beads, capsules, spheres}
A61K 49/048 ・・・・・{Microparticles, microbeads, microcapsules, microspheres, i.e. having a size or diameter higher or equal to 1 micrometer}
A61K 49/0485 ・・・・・{Nanoparticles, nanobeads, nanospheres, nanocapsules, i.e. having a size or diameter smaller than 1 micrometer}
A61K 49/049 ・・・・・・{Surface-modified nanoparticles, e.g. immune-nanoparticles}
A61K 49/0495 ・・・・{intended for oral administration}
A61K 49/06 ・Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) contrast preparations; Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast preparations
NOTE - characterised only by the (inorganic) MRI-active nucleus, e.g. 129XeA61K 49/08 ・・characterised by the carrier
NOTE - characterised by the carrier carrying the MRI-active nucleus, e.g. inorganic carrier]A61K 49/085 ・・・{conjugated systems}
NOTE - The MRI-active nucleus being complexed to a complex-forming compound (e.g. chelating group) or being covalently linked to a molecule, which being further covalently linked or conjugated to a carrier, e.g. polymer.A61K 49/10 ・・・Organic compounds
NOTE - the carrier being an organic compound, e.g. 13C-labelled molecule or perfluorinated alkane, used as MRI in vivo probe, or a small organic molecule, e.g. a sugar, linked to a Gd-chelateA61K 49/101 ・・・・[N: the carrier being a complex-forming compound able to form MRI-active complexes with paramagnetic metals
NOTE - In the A61K 49/101 subgroups, the MRI-active nucleus being complexed to a complex-forming compound, e.g. chelating group.Classification being made according to the nature of this complex-forming agent, if it being either an uncommon or new complexing agent (not the usual DTPA, DOTA, DOTP, etc...groups) that forms the real contribution to the claimed MRI invention, or if it being not conjugated to any further molecule, e.g. which being not conjugated to a polymer, peptide, protein or antibody. In that latter case, the MRI probe being e.g. a paramagnetic metal chelate]A61K 49/103 ・・・・・{the complex-forming compound being acyclic, e.g. DTPA}
A61K 49/105 ・・・・・・{the metal complex being Gd-DTPA}
A61K 49/106 ・・・・・{the complex-forming compound being cyclic, e.g. DOTA}
A61K 49/108 ・・・・・・{the metal complex being Gd-DOTA}
A61K 49/12 ・・・・Macromolecular compounds
NOTE - the carrier being an organic macromolecular compound, i.e. an oligomeric, polymeric, dendrimeric molecule (not being a peptide, protein, polyamino acid (see A61K 49/00 or A61K 14/00) or an antibody (see A61K 49/00 or A61K 16/00)A61K 49/122 ・・・・・{dimers of complexes or complex-forming compounds}
A61K 49/124 ・・・・・{dendrimers, dendrons, hyperbranched compounds}
NOTE - Said compounds are either complexes or complex-forming compounds, or they form a backbone to which MRI active nuclei are complexed or covalently linked through chelating groups. In that latter case, the subgroup A61K 49/085 being also given.A61K 49/126 ・・・・・{Linear polymers, e.g. dextran, inulin, PEG}
A61K 49/128 ・・・・・・{comprising multiple complex or complex-forming groups, being either part of the linear polymeric backbone or being pending groups covalently linked to the linear polymeric backbone}
NOTE - In that latter case, classification is also made in A61K 49/085A61K 49/14 ・・・・Peptides, e.g. proteins
NOTE - the carrier being a peptide (polyamino acid, A61K 49/14T) or protein (not an antibody, see A61K 49/16). If the MRI-active nucleus being linked to the peptide or protein or polyamino acid via a complexing or chelating group, the subgroup A61K 49/085 should also be given. If the peptide or protein or polyamino acid being a dendrimer, a dendron, or hyperbranched, then the A61K 49/124 being also givenA61K 49/143 ・・・・・{the protein being an albumin, e.g. HSA, BSA, ovalbumin}
A61K 49/146 ・・・・・{the peptide being a polyamino acid, e.g. poly-lysine}
A61K 49/16 ・・・・・Antibodies; Immunoglobulins; Fragments thereof
NOTE - the protein being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof.If the MRI-active nucleus being linked to the antibody via a complexing or chelating group, the subgroup A61K 49/085 should also be givenA61K 49/18 ・・characterised by a special physical form, e.g. emulsions, microcapsules, liposomes
NOTE - Classification being also made according to the molecule complexing or bearing the MRI-active nucleusA61K 49/1803 ・・・{Semi-solid preparations, e.g. ointments, gels, hydrogels}
A61K 49/1806 ・・・{Suspensions, emulsions, colloids, dispersions}
A61K 49/1809 ・・・・{Micelles, e.g. phospholipidic or polymeric micelles}
A61K 49/1812 ・・・・{liposomes, polymersomes, e.g. immunoliposomes}
NOTE - If the paramagnetic metal complexes are covalently linked to the bilayered membrane, then the A61K 49/085 subgroup being also given.Liposomes modified on their external surface by a targeting agent, e.g. an antibody are classified in A61K 49/1812 without further indication for the targeting agentA61K 49/1815 ・・・・{compo-inhalant, e.g. breath tests}
A61K 49/1818 ・・・{particles, e.g. uncoated or non-functionalised microparticles or nanoparticles}
NOTE - For nanoparticles, i.e. having a size or diameter smaller than 1 micrometer, the subgroups B82Y 5/00 and B82Y 15/00 are also givenA61K 49/1821 ・・・・{coated or functionalised microparticles or nanoparticles}
A61K 49/1824 ・・・・・{coated or functionalised nanoparticles (liposomes A61K 49/1812; nano-emulsions A61K 49/1806; micelles A61K 49/1809)}
A61K 49/1827 ・・・・・・{having a (super)(para)magnetic core, being a solid MRI-active material, e.g. magnetite, or composed of a plurality of MRI-active, organic agents e.g. Gd-chelates, or nuclei, e.g. Eu3+, encapsulated or entrapped in the core of the coated or functionalised nanoparticle}
A61K 49/183 ・・・・・・・{having a (super)(para)magnetic core coated or functionalised with an inorganic material or being composed of an inorganic material entrapping the MRI-active nucleus, e.g. silica core doped with a
MRI-active nucleus}A61K 49/1833 ・・・・・・・{having a (super)(para)magnetic core coated or functionalised with a small organic molecule (oligomeric, polymeric, dendrimeric A61K 49/1851)}
A61K 49/1836 ・・・・・・・・{the small organic molecule being a carboxylic acid having less than 8 carbon atoms in the main chain}
A61K 49/1839 ・・・・・・・・{the small organic molecule being a lipid, a fatty acid having 8 or more carbon atoms in the main chain, or a phospholipid}
A61K 49/1842 ・・・・・・・・{the small organic molecule being a phosphate or a phosphonate, not being a phospholipid}
A61K 49/1845 ・・・・・・・・{the small organic molecule being a carbohydrate (monosaccharides, discacharides)}
A61K 49/1848 ・・・・・・・・{the small organic molecule being a silane}
A61K 49/1851 ・・・・・・・{having a (super)(para)magnetic core coated or functionalised with an organic macromolecular compound, i.e. oligomeric, polymeric, dendrimeric organic molecule (peptide or protein A61K 49/1866; polyamino acid A61K 49/1872; antibody A61K 49/1875)}
NOTE - In case of block copolymers, the different (large) blocks are classified in the appropriate A61K 47/48169 or A61K 47/48238 subgroupsA61K 49/1854 ・・・・・・・・{the organic macromolecular compound being obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. poly(meth)acrylate, polyacrylamide, polyvinylpyrrolidone, polyvinylalcohol}
A61K 49/1857 ・・・・・・・・{the organic macromolecular compound being obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. PLGA}
A61K 49/186 ・・・・・・・・・{the organic macromolecular compound being polyethyleneglycol (PEG)}
A61K 49/1863 ・・・・・・・・{the organic macromolecular compound being a polysaccharide or derivative thereof, e.g. chitosan, chitin, cellulose, pectin, starch}
A61K 49/1866 ・・・・・・・{the nanoparticle having a (super)(para)magnetic core coated or functionalised with a peptide, e.g. protein, polyamino acid}
A61K 49/1869 ・・・・・・・・{coated or functionalised with a protein being an albumin, e.g. HSA, BSA, ovalbumin}
A61K 49/1872 ・・・・・・・・{coated or functionalised with a polyamino acid, e.g. polylysine, polyglutamic acid}
A61K 49/1875 ・・・・・・・{coated or functionalised with an antibody}
A61K 49/1878 ・・・・・・{the nanoparticle having a magnetically inert core and a (super)(para)magnetic coating}
A61K 49/1881 ・・・・・・・{wherein the coating consists of chelates, i.e. chelating group complexing a (super)(para)magnetic ion, bound to the surface}
A61K 49/1884 ・・・・{Nanotubes, nanorods or nanowires}
A61K 49/1887 ・・・・{Agglomerates, clusters, i.e. more than one (super)(para)magnetic microparticle or nanoparticle are aggregated or entrapped in the same maxtrix}
A61K 49/189 ・・・{Host-guest complexes, e.g. cyclodextrins}
A61K 49/1893 ・・・・{Molecular sieves}
A61K 49/1896 ・・・{not provided for elsewhere, e.g. cells, viruses, ghosts, red blood cells, virus capsides}
A61K 49/20 ・・containing free radicals {e.g. trityl radical for overhauser}
A61K 49/22 ・Echographic preparations; Ultrasound imaging preparation {Optoacoustic imaging preparations}
A61K 49/221 ・・{characterised by the targeting agent or modifying agent linked to the acoustically-active agent}
A61K 49/222 ・・{characterised by a special physical form, e.g. emulsions, liposomes}
A61K 49/223 ・・・{Micro-bubbles, hollow microspheres, free gas bubbles, gas microspheres}
A61K 49/225 ・・・{Microparticles, microcapsules (gas-filled to be classified in A61K 49/223)}
A61K 49/226 ・・・{Solutes, emulsions, suspensions, dispersions, semi-solid forms, e.g. hydrogels}
A61K 49/227 ・・・{Liposomes, lipoprotein vesicles, e.g. LDL or HDL lipoproteins, micelles, e.g. phospholipidic or polymeric}
A61K 49/228 ・・・{Host-guest complexes, clathrates, chelates}
A61K 51/00 Preparations containing radioactive substances for use in therapy or testing in vivo
A61K 51/02 ・characterised by the carrier, {i.e. characterised by the agent or material covalently linked or complexing the radioactive nucleus}
A61K 51/025 ・・{inorganic Tc complexes or compounds}
A61K 51/04 ・・organic compounds
NOTE - Organic compounds used as carriersA61K 51/0402 ・・・{carboxylic acid carriers, fatty acids (amino acids A61K 51/0406)}
A61K 51/0404 ・・・{Lipids, e.g. triglycerides; Polycationic carriers (fatty acids A61K 51/0402; cholesterol A61K 51/0493; polycationic carriers being oligomers, polymers, dendrimers A61K 47/48169)}
A61K 51/0406 ・・・・{Amines, polyamines, e.g. spermine, spermidine, amino acids, (bis)guanidines}
A61K 51/0408 ・・・・{Phospholipids (liposomes encapsulating the radioactive probe or having no radiolabelled phospholipids A61K 51/1231)}
A61K 51/041 ・・・{Heterocyclic compounds.}
NOTE - Under this group, the last place rule is followedA61K 51/0412 ・・・・{having oxygen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. fungichromin}
A61K 51/0414 ・・・・・{having three-membered rings, e.g. oxirane, fumagillin}
A61K 51/0417 ・・・・・{having four-membered rings, e.g. taxol}
A61K 51/0419 ・・・・・{having five-membered rings with one oxygen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. isosorbide}
A61K 51/0421 ・・・・・{having six-membered rings with one oxygen as the only ring hetero atom}
A61K 51/0423 ・・・・・{having two or more oxygen atoms in the same ring, e.g. crown ethers, guanadrel}
A61K 51/0425 ・・・・・{compounds containing methylenedioxyphenol groups, e.g. sesamin}
A61K 51/0427 ・・・・・{Lactones}
A61K 51/0429 ・・・・{having sulfur as a ring hetero atom}
A61K 51/0431 ・・・・・{having five-membered rings}
A61K 51/0434 ・・・・・{having six-membered rings, e.g. thioxanthenes (thiotixene A61K 51/0459)}
A61K 51/0436 ・・・・・{having two or more sulfur atoms in the same ring}
A61K 51/0438 ・・・・・{having oxygen in the same ring}
A61K 51/044 ・・・・{having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine, rifamycins (rifampin A61K 51/0459)}
A61K 51/0442 ・・・・・{having three-membered rings, e.g. aziridine}
A61K 51/0444 ・・・・・{having four-membered rings, e.g. azetidine}
A61K 51/0446 ・・・・・{having five-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. sulpiride, succinimide, tolmetin, buflomedil}
A61K 51/0448 ・・・・・・{tropane or nortropane groups, e.g. cocaine}
A61K 51/0451 ・・・・・・{having four such rings, e.g. phorphine derivatives, bilirubin, biliverdine (hemin, hematin A61K 51/0472)}
NOTE - Porphyrins or texaphyrins used as complex-forming compounds, i.e. wherein the nitrogen atoms forming the central ring system complex the radioactive metal, are classified in A61K 51/0485A61K 51/0453 ・・・・・{having five-membered rings with two or more ring hetero atoms, at least one of which being nitrogen, e.g. tetrazole}
A61K 51/0455 ・・・・・{having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom}
A61K 51/0457 ・・・・・・{Vesamicol}
A61K 51/0459 ・・・・・{having six-membered rings with two nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, e.g. piperazine}
A61K 51/0461 ・・・・・{having six-membered rings with three nitrogens as the only ring hetero atoms, e.g. chlorazanil, melamine (melarsoprol A61K 51/0472)}
A61K 51/0463 ・・・・・{having six-membered rings with at least one nitrogen and one oxygen as the ring hetero atoms, e.g. 1,2-oxazines}
A61K 51/0465 ・・・・・{having six-membered rings with at least one nitrogen and one sulfur as the ring hetero atoms, e.g. sulthiame}
A61K 51/0468 ・・・・・{having seven-membered rings, e.g. azelastine, pentylenetetrazole}
A61K 51/047 ・・・・・・{Benzodiazepines}
A61K 51/0472 ・・・・{containing heavy metals, e.g. hemin, hematin, melarsoprol}
A61K 51/0474 ・・・{complexes or complex-forming compounds, i.e. wherein a radioactive metal (e.g. 111In3+) is complexed or chelated by e.g. a N2S2, N3S, NS3, N4 chelating group}
NOTE - Classification is made according to the nature of this complex-forming agent, if it is either an uncommon or new complexing agent (not the usualA61K 51/0476 ・・・・{complexes from monodendate ligands, e.g. sestamibi}
A61K 51/0478 ・・・・{complexes from non-cyclic ligands, e.g. EDTA, MAG3}
A61K 51/048 ・・・・・{DTPA (diethylenetriamine tetraacetic acid)}
A61K 51/0482 ・・・・{chelates from cyclic ligands, e.g. DOTA}
A61K 51/0485 ・・・・{Porphyrins, texaphyrins wherein the nitrogen atoms forming the central ring system complex the radioactive metal}
NOTE - Porphyrins used as simple heterocyclic carriers containing a radioactive nucleus (e.g. 11C) or substituted with a radioactive nucleus (e.g. 18F), are classified in A61K 51/0451A61K 51/0487 ・・・・{Metallocenes, i.e. complexes based on a radioactive metal complexed by two cyclopentadienyl anions}
A61K 51/0489 ・・・{Phosphates or phosphonates, e.g. bone-seeking phosphonates; (phospholipids: A61K 51/0408; nucleotides or nucleic acids: A61K 51/0491)}
A61K 51/0491 ・・・{Sugars, nucleosides, nucleotides, oligonucleotides, nucleic acids, e.g. DNA, RNA, nucleic acid aptamers}
A61K 51/0493 ・・・{Steroids, e.g. cholesterol, testosterone}
A61K 51/0495 ・・・{Pretargeting}
NOTE - Pretargeting is the administration of an agent X bearing the radioisotope or radioactive nucleus and of an agent Y capable of binding X and a cell Y in several steps, e.g. the radiolabelled agent is a radiolabelled biotin and the agent Y is a (strept)avidin molecule targeting specific cells. Classification is also made according to the nature of the carrier bearing/linked to the radioactive nucleus, e.g. an antibodyA61K 51/0497 ・・・{conjugates with a carrier being an organic compounds}
NOTE - The compound which bears, complexes or chelates the radioactive nucleus, is covalently linked or complexed to the carrier being another (small) organic molecule, i.e. not oligomeric, polymeric, dendrimeric.A61K 51/06 ・・・Macromolecular compounds, {carriers being organic macromolecular compounds, i.e. organic oligomeric, polymeric, dendrimeric molecules (peptides, proteins, polyamino acids A61K 51/08; antibodies A61K 51/10)}
A61K 51/065 ・・・・{conjugates with carriers being macromolecules}
NOTE - The compound which bears, complexes or chelates the radioactive nucleus, is covalently linked or complexed to the carrier being a macromolecule (not being a peptide, polyamino acid, protein, antibody). In case of a conjugate comprising a complex-forming compound (chelating group) complexing a radioactive metal linked to the carrier (organic macromolecular compound in A61K 49/06Z), the nature of this complex-forming compound is not classified except if it is the real contribution of the claimed invention and it is an uncommon complexing/chelating group, e.g. 111In-DTPA-PEG is classified inA61K 51/08 ・・・Peptides, e.g. proteins, {carriers being peptides, polyamino acids, proteins}
A61K 51/081 ・・・・{the protein being an albumin, e.g. human serum albumin (HSA), bovine serum albumin (BSA), ovalbumin}
A61K 51/082 ・・・・{the peptide being a RGD-containing peptide}
A61K 51/083 ・・・・{the peptide being octreotide or a somatostatin-receptor-binding peptide}
A61K 51/084 ・・・・{the peptide being oxytocin}
A61K 51/085 ・・・・{the peptide being neurotensin}
A61K 51/086 ・・・・{the peptide being alphaMSH, alpha melanocyte stimulating hormone}
A61K 51/087 ・・・・{the peptide being an annexin, e.g. annexin V}
A61K 51/088 ・・・・{conjugates with carriers being peptides, polyamino acids, proteins (antibodies A61K 51/10)}
NOTE - The compound which bears, complexes or chelates the radioactive nucleus, is covalently linked/complexed to the carrier being a peptide, polyamino acid, protein (not being an antibody). Classification is also made according to the nature of the peptide or protein (e.g. if it is BSA, then A61K 51/081 is also indicated). In case of a conjugate comprising a complex-forming compound (chelating group) complexing a radioactive metal linked to the carrier (peptide, protein, polyamino acid in A61K 51/088), the nature of this complex-forming compound is not classified except if it is the real contribution of the claimed invention and it is an uncommon complexing or chelating group, e.g.A61K 51/10 ・・・・Antibodies or immunoglobulins; Fragments thereof, {the carrier being an antibody or an immunoglobulin, or a fragment thereof, e.g. a camelised human single domain antibody, or the Fc fragment of an antibody}
A61K 51/1003 ・・・・・{not used, see subgroups}
A61K 51/1006 ・・・・・・{the antibody being against or targeting material from viruses}
A61K 51/1009 ・・・・・・{against material from bacteria}
A61K 51/1012 ・・・・・・{against material from fungi, lichens, algae}
A61K 51/1015 ・・・・・・{against material from plants}
A61K 51/1018 ・・・・・・{against material from animals or humans}
A61K 51/1021 ・・・・・・{against cytokines, e.g. growth factors, VEGF, TNF, lymphokines, interferons}
A61K 51/1024 ・・・・・・{against hormones, hormone-releasing or hormone-inhibiting factors}
A61K 51/1027 ・・・・・・{against receptors, cell-surface antigens, cell-surface determinants}
A61K 51/103 ・・・・・・・{against receptors for growth factors or receptors for growth regulators}
A61K 51/1033 ・・・・・・・{against receptors for cytokines, lymphokines, interferons}
A61K 51/1036 ・・・・・・・{against hormone receptors}
A61K 51/1039 ・・・・・・・{against T-cell receptors}
A61K 51/1042 ・・・・・・・・{against Tcell receptor (TcR)-CD3 complex}
A61K 51/1045 ・・・・・・{against animal or human tumor cells or tumor cell determinants}
A61K 51/1048 ・・・・・・・{the tumor cell determinant being a carcino embryonic antigen}
A61K 51/1051 ・・・・・・・{the tumor cell being from breast, e.g. the antibody being herceptin}
A61K 51/1054 ・・・・・・・{the tumor cell being from lung}
A61K 51/1057 ・・・・・・・{the tumour cell being from liver or pancreas}
A61K 51/106 ・・・・・・・{the tumor cell being from kidney, bladder}
A61K 51/1063 ・・・・・・・{the tumor cell being from stomach or intestines}
A61K 51/1066 ・・・・・・・{the tumor cell being from skin}
A61K 51/1069 ・・・・・・・{the tumor cell being from blood cells, e.g. the cancer being a myeloma}
A61K 51/1072 ・・・・・・・{the tumor cell being from the reproductive system, e.g. ovaria, uterus, testes, prostate}
A61K 51/1075 ・・・・・・{the antibody being against an enzyme}
A61K 51/1078 ・・・・・・{the antibody being against an immunoglobulin, i.e. being an (anti)-anti-idiotypic antibody}
A61K 51/1081 ・・・・・・{the antibody being against a material not provided elsewhere}
A61K 51/1084 ・・・・・・{the antibody being a hybrid immunoglobulin}
A61K 51/1087 ・・・・・・・{the immunoglobulin comprises domains from different animal species, e.g. chimeric immunoglobulins}
A61K 51/109 ・・・・・・・{immunoglobulins having two or more different antigen-binding sites, multifunctional antibodies}
A61K 51/1093 ・・・・・{conjugates with carriers being antibodies}
NOTE - The compound which bears, complexes or chelates the radioactive nucleus, being covalently linked or complexed to the carrier being an antibody Classification being also made according to the appropriate A61K 51/1003 subclass.In case of a conjugate comprising a complex-forming compound (chelating group) complexing a radioactive metal linked to the carrier (antibody in A61K 51/1093), the nature of this complex-forming compound being not classified except if it being the real contribution of the claimed invention and it being an uncommon complexing/chelating group, e.g. 111In-DTPA-herceptin being classified in A61K 51/1093 and A61K 51/1051, new DTPA-like derivatives conjugated to herceptin and complexing 111In for use in vivo being classified inA61K 51/1096 ・・・・・・{radioimmunotoxins, i.e. conjugates being structurally as defined in A61K 51/1093, and including a radioactive nucleus for use in radiotherapeutic applications}
A61K 51/12 ・characterised by a special physical form, e.g. emulsion, microcapsules, liposomes, {characterized by a special physical form, e.g. emulsions, dispersions, microcapsules (liposomes A61K 51/1234)}
A61K 51/1203 ・・{in a form not provided for by groups A61K 51/1206 to A61K 51/1296, e.g. cells, cell fragments, viruses, virus capsides, ghosts, red blood cells, viral vectors}
A61K 51/1206 ・・{Administration of radioactive gases, aerosols or breath tests}
A61K 51/121 ・・{Solutions, i.e. homogeneous liquid formulation}
A61K 51/1213 ・・{Semi-solid forms, gels, hydrogels, ointments, fats and waxes that are solid at room temperature}
A61K 51/1217 ・・{Dispersions, suspensions, colloids, emulsions, e.g. perfluorinated emulsion, sols}
A61K 51/122 ・・・{Micro-emulsions, nano-emulsions}
A61K 51/1224 ・・・{Lipoprotein vesicles, e.g. HDL and LDL proteins}
A61K 51/1227 ・・・{Micelles, e.g. phospholipidic or polymeric micelles}
A61K 51/1231 ・・・{Aerosols or breath tests, e.g. administration of gasses, emanators}
A61K 51/1234 ・・・{Liposomes}{Note Liposomes modified on their external surface by a targeting agent, e.g. an antibody, are not additionally classified with the symbol of the targeting agent}
NOTE - Note Liposomes modified on their external surface by a targeting agent, e.g. an antibody, are not additionally classified with the symbol of the targeting agentA61K 51/1237 ・・・・{Polymersomes, i.e. liposomes with polymerisable or polymerized bilayer-forming substances}
A61K 51/1241 ・・{particles, powders, lyophilizates, adsorbates, e.g. polymers or resins for adsorption or ion-exchange resins}
A61K 51/1244 ・・・{micro- particles or nano-particles, e.g. polymeric nanoparticles}
A61K 51/1248 ・・・・{nanotubes}
A61K 51/1251 ・・・・{micro- or nano-spheres, micro- or nano-beads, micro- or nano-capsules}
A61K 51/1255 ・・・{Granulates, agglomerates, microspheres}
A61K 51/1258 ・・{Pills, tablets, lozenges}
A61K 51/1262 ・・{Capsules}
A61K 51/1265 ・・・{Microcapsules}
A61K 51/1268 ・・{host-guest, closed hollow molecules, inclusion complexes, e.g. with cyclodextrins, clathrates, cavitates, fullerenes}
A61K 51/1272 ・・{Sponges}
A61K 51/1275 ・・{Fibers, textiles, slabbs, or sheets}
A61K 51/1279 ・・{Plasters, bandages, dressings, patches or adhesives}
A61K 51/1282 ・・{Devices used in vivo and carrying the radioactive therapeutic or diagnostic agent, therapeutic or in vivo diagnostic kits, stents}
A61K 51/1286 ・・・{Ampoules, glass carriers carrying the therapeutic or in vivo diagnostic agent}
A61K 51/1289 ・・・{Devices or containers for impregnation, for emanation, e.g. bottles or jars for radioactive water for use in radiotherapy}
A61K 51/1293 ・・{Radioactive cosmetics, e.g. radioactive bathsalts, soaps}
A61K 51/1296 ・・{Radioactive food, e.g. chocolates, drinks}
A61K 2008/00 Cosmetic or similar toilet preparations (casings or accessories for storing or handling of solid or pasty toilet or cosmetic substances A45D 40/00)
NOTE - Use of cosmetics or similar toilet preparations is further classified in subclass A61Q.A61K 2008/02 ・characterised by special physical form
A61K 2008/04 ・・Dispersions; Emulsions
A61K 2008/048 ・・・{Microbeadlets; Microspheres; Granules; Microgranules}
A61K 2008/11 ・・Encapsulated compositions
A61K 2008/115 ・・・{Microcapsules}
A61K 2035/00 Medicinal preparations containing materials or reaction products thereof with undetermined constitution
NOTE - When classifying in this group, the last place rule (applied throughout A61K) does not apply. Namely, classification is made for each active component or material.A61K 2035/11 ・Medicinal preparations comprising living procariotic cells
A61K 2035/115 ・・Probiotics
A61K 2035/12 ・Materials from mammals; {compositions comprising non-specified tissues or cells; Compositions comprising non-embryonic stem cells (uncharacterized stem cells A61K 35/545); Genetically modified cells (gene therapy C12N 5/10; vaccines or medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies A61K 39/00)}{Note: If the cells are characterized, classify under the corresponding tissue or tissue of origin}
NOTE - When the cells are characterized, classification is given under the corresponding tissue or tissue of originA61K 2035/122 ・・for inducing tolerance or supression of immune responses
A61K 2035/124 ・・the cells being hematopoietic, bone marrow derived or blood cells
A61K 2035/126 ・・Immunoprotecting barriers, e.g. jackets, diffusion chambers
A61K 2035/128 ・・・capsules, e.g. microcapsules
A61K 2039/00 Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies (materials for immunoassay G01N 33/53)
NOTE - Groups A61K 39/002 to A61K 39/295 cover preparations containing protozoa, bacteria, viruses, or subunits thereof, e.g. membrane parts.A61K 2039/02 ・Bacterial antigens
A61K 2039/10 ・・Brucella; Bordetella, e.g. Bordetella pertussis {Not used, see subgroups}
A61K 2039/106 ・・Vibrio; Campylobacter {Not used, see subgroups}
A61K 2039/505 ・comprising antibodies
A61K 2039/507 ・・Comprising a combination of two or more separate antibodies
A61K 2039/51 ・comprising whole cells, viruses or DNA/RNA
A61K 2039/515 ・・Animal cells
A61K 2039/5152 ・・・Tumor cells
A61K 2039/5154 ・・・Antigen presenting cells [APCs], e.g. dendritic cells, macrophages
A61K 2039/5156 ・・・expressing foreign proteins
A61K 2039/5158 ・・・Antigen-pulsed cells e.g. T-cells
A61K 2039/517 ・・Plant cells
A61K 2039/52 ・・Bacterial cells; Fungal cells; Protozoal cells
A61K 2039/521 ・・・inactivated (killed)
A61K 2039/522 ・・・avirulent or attenuated
A61K 2039/523 ・・・expressing foreign proteins
A61K 2039/525 ・・Virus
A61K 2039/5252 ・・・inactivated (killed)
A61K 2039/5254 ・・・avirulent or attenuated
A61K 2039/5256 ・・・expressing foreign proteins
A61K 2039/5258 ・・・Virus-like particles
A61K 2039/53 ・・DNA (RNA) vaccination
A61K 2039/54 ・characterised by the route of administration
A61K 2039/541 ・・Mucosal route
A61K 2039/542 ・・・oral/gastrointestinal
A61K 2039/543 ・・・intranasal
A61K 2039/544 ・・・to the airways (intranasal A61K 2039/543)
A61K 2039/545 ・characterised by the dose, timing or administration schedule
A61K 2039/55 ・characterised by the host/recipient, e.g. newborn with maternal antibodies
A61K 2039/552 ・・Veterinary vaccine
A61K 2039/555 ・characterised by a specific combination antigen/adjuvant
A61K 2039/55505 ・・Inorganic adjuvants
A61K 2039/55511 ・・Organic adjuvants
A61K 2039/55516 ・・・Proteins; Peptides
A61K 2039/55522 ・・・Cytokines; Lymphokines; Interferons
A61K 2039/55527 ・・・・Interleukins
A61K 2039/55533 ・・・・・IL-2
A61K 2039/55538 ・・・・・IL-12
A61K 2039/55544 ・・・Bacterial toxins
A61K 2039/5555 ・・・Muramyl dipeptides
A61K 2039/55555 ・・・Liposomes; Vesicles, e.g. nanoparticles; Spheres, e.g. nanospheres; Polymers
A61K 2039/55561 ・・・CpG containing adjuvants; Oligonucleotide containing adjuvants
A61K 2039/55566 ・・・Emulsions, e.g. Freund's adjuvant, MF59
A61K 2039/55572 ・・・Lipopolysaccharides; Lipid A; Monophosphoryl lipid A
A61K 2039/55577 ・・・Saponins; Quil A; QS21; ISCOMS
A61K 2039/55583 ・・・Polysaccharides
A61K 2039/55588 ・・Adjuvants of undefined constitution
A61K 2039/55594 ・・・from bacteria
A61K 2039/57 ・characterised by the type of response, e.g. Th1, Th2
A61K 2039/572 ・・cytotoxic response
A61K 2039/575 ・・humoral response
A61K 2039/577 ・・tolerising response
A61K 2039/58 ・raising an immune response against a target which is not the antigen used for immunisation
A61K 2039/585 ・・wherein the target is cancer
A61K 2039/60 ・characteristics by the carrier linked to the antigen
A61K 2039/6006 ・・Cells (recombinantly expressing antigens A61K 2039/5156, A61K 2039/523)
A61K 2039/6012 ・・Haptens, e.g. di- or trinitrophenyl (DNP, TNP)
A61K 2039/6018 ・・Lipids, e.g. in lipopeptides
A61K 2039/6025 ・・Nucleotides
A61K 2039/6031 ・・Proteins
A61K 2039/6037 ・・・Bacterial toxins, e.g. diphteria toxoid (DT), tetanus toxoid (TT)
A61K 2039/6043 ・・・Heat shock proteins
A61K 2039/605 ・・・MHC molecules or ligands thereof
A61K 2039/6056 ・・・Antibodies
A61K 2039/6062 ・・・Muramyl peptides
A61K 2039/6068 ・・・Other bacterial proteins, e.g. OMP
A61K 2039/6075 ・・・Viral proteins
A61K 2039/6081 ・・・Albumin; Keyhole limpet haemocyanin (KLH)
A61K 2039/6087 ・・Polysaccharides; Lipopolysaccharides (LPS)
A61K 2039/6093 ・・Synthetic polymers, e.g. polyethyleneglycol (PEG), Polymers or copolymers of (D) glutamate and (D) lysine
A61K 2039/62 ・characterised by the link between antigen and carrier
A61K 2039/622 ・・non-covalent binding
A61K 2039/625 ・・binding through the biotin-streptavidin system or similar
A61K 2039/627 ・・characterised by the linker
A61K 2039/64 ・characterised by the architecture of the carrier-antigen complex, e.g. repetition of carrier-antigen units
A61K 2039/645 ・・Dendrimers; Multiple antigen peptides
A61K 2039/70 ・Multivalent vaccine
A61K 2121/00 Preparations for use in therapy
A61K 2123/00 Preparations for testing in vivo
A61K 2201/00 Compositions or compounds characterised by specific properties
A61K 2201/01 ・Optical properties
A61K 2201/012 ・・Transparent compositions; Translucent compositions
A61K 2201/02 ・Colour properties
A61K 2201/021 ・・Pigments; Dyes
A61K 2201/022 ・・Direct dyes
A61K 2201/0223 ・・・in preparations for temporarily colouring the hair further containing an oxidising agent
A61K 2201/0225 ・・・in preparations for permanently dyeing the hair
A61K 2201/023 ・・Luminescent, fluorescent; Optical brighteners; Photosensitizers
A61K 2201/025 ・・Interference pigments, e.g. iridescent, pearlescent
A61K 2201/027 ・・pH- or Redox indicators
A61K 2201/029 ・・Chromophoric; photochromic; phototropic
A61K 2201/03 ・Electromagnetic properties
A61K 2201/032 ・・Electrophoresis; Electrodes; electrolytic phenomena
A61K 2201/034 ・・Magnetic materials
A61K 2201/036 ・・Cosmetics treated by (ir)radiation
A61K 2201/038 ・・Radiochemicals
A61K 2201/04 ・Gas releasing compositions
A61K 2201/045 ・・Effervescent compositions
A61K 2201/05 ・Thermal properties
A61K 2201/052 ・・Exothermic; Self-heating
A61K 2201/054 ・・Endothermic; Cooling
A61K 2201/056 ・・Frozen or deep-frozen cosmetics
A61K 2201/06 ・Stabilizers
A61K 2201/062 ・・Antioxidants
A61K 2201/064 ・・Corrosion inhibitors
A61K 2201/066 ・・Chelating agents
A61K 2201/068 ・・Preservatives
A61K 2201/07 ・Homeopathic compositions
A61K 2201/08 ・Rubbing or scrubbing compositions; Peeling or abrasive compositions; Exfoliants
A61K 2201/09 ・Biological properties
A61K 2201/093 ・・Enzyme modulators
A61K 2201/094 ・・Enzyme inhibitors; Enzyme antagonists
A61K 2201/10 ・Compositions or compounds characterised by the form
A61K 2201/101 ・・Microsized, i.e. compounds having particle sizes between 0.1 and 100 micrometers, e.g. micronised compounds
A61K 2201/103 ・・Nanosized, i.e. compounds having particle sizes below 100 nanometers, e.g. nanoparticles, nanopigments
A61K 2201/105 ・・Fibres; Fibrils; Micro- or nanofibres
A61K 2201/107 ・・Tablets; Lozenges; Dragees
A61K 2201/109 ・・Sticks
A61K 2201/111 ・・Pencils; Crayons; Felt-tip pens
A61K 2201/113 ・・Brushes
A61K 2201/115 ・・Dental appliances
A61K 2201/117 ・・Dental floss
A61K 2201/119 ・・Chewing gum
A61K 2201/123 ・・Tattoos; Stencils
A61K 2201/125 ・・Tattoo removal
A61K 2201/131 ・・Artificial nails
A61K 2201/142 ・・Containers; Packaging
A61K 2201/144 ・・・Two- or multipart kits
A61K 2201/145 ・・・Roll-on
A61K 2201/15 ・・Striped compositions; Core/shell compositions
A61K 2201/19 ・・Anhydrous compositions
A61K 2201/20 ・Mixtures
A61K 2201/21 ・・Mixtures of polymers
A61K 2201/24 ・・Mixtures of surface active compounds
A61K 2201/30 ・Polymers characterised by specific properties
A61K 2201/32 ・・characterised by the charge
A61K 2201/322 ・・・nonionic
A61K 2201/324 ・・・anionic
A61K 2201/326 ・・・cationic
A61K 2201/328 ・・・amphoteric
A61K 2201/35 ・・Ion-exchangers
A61K 2201/40 ・Compounds, e.g. perfumes absorbed onto or entrapped into a solid carrier, e.g. inclusion compounds
A61K 2201/50 ・Compounds, e.g. perfumes covalently linked to a carrier molecule, e.g. conjugates, pro-fragrances
A61K 2201/60 ・Perfumes having both deodorant and antibacterial properties
A61K 2201/70 ・Fermentation products, e.g. yoghurt
A61K 2201/702 ・・Alcohol-containing, e.g. beer, wine
A61K 2201/80 ・Products obtained by genetic engineering
A61K 2201/90 ・Compositions based essentially on surface active compounds
A61K 2201/92 ・・characterised by the charge
A61K 2201/922 ・・・nonionic
A61K 2201/924 ・・・anionic
A61K 2201/926 ・・・cationic
A61K 2201/928 ・・・amphoteric or zwitterionic
A61K 2236/00 Isolation or extraction methods of medicinal preparations of undetermined constitution containing material from algae, lichens, fungi or plants, or derivatives thereof, e.g. traditional herbal medicine
NOTE - If the isolation or extraction method is considered relevant, at least one symbol ofA61K 2236/10 ・Preparation or pretreatment of starting material
A61K 2236/11 ・・involving culturing conditions, e.g. cultivation in the dark or under defined water stress
A61K 2236/13 ・・involving cleaning, e.g. washing or peeling
A61K 2236/15 ・・involving mechanical treatment, e.g. chopping up, cutting or grinding
A61K 2236/17 ・・involving drying, e.g. sun-drying or wilting
A61K 2236/19 ・・involving fermentation using yeast, bacteria or both; enzymatic treatment (fermentation or enzyme-using processes in general C12P)
A61K 2236/30 ・Extraction of the material
A61K 2236/31 ・・involving untreated material, e.g. fruit juice or sap obtained from fresh plants
A61K 2236/33 ・・involving extraction with hydrophilic solvents, e.g. lower alcohols, esters or ketones
A61K 2236/331 ・・・using water, e.g. cold water, infusion, tea, steam distillation, decoction (subcritical water extraction A61K 2236/37)
A61K 2236/333 ・・・using mixed solvents, e.g. 70% EtOH
A61K 2236/35 ・・Extraction with lipophilic solvents, e.g. Hexane or petrol ether
A61K 2236/37 ・・Extraction at elevated pressure or temperature, e.g. pressurized solvent extraction [PSE], supercritical carbon dioxide extraction or subcritical water extraction
A61K 2236/39 ・・Complex extraction schemes, e.g. fractionation or repeated extraction steps
A61K 2236/50 ・Methods involving additional extraction steps
A61K 2236/51 ・・Concentration or drying of the extract, e.g. Lyophilisation, freeze-drying or spray-drying
A61K 2236/53 ・・Liquid-solid separation, e.g. centrifugation, sedimentation or crystallization
A61K 2236/55 ・・Liquid-liquid separation; Phase separation
A61K 2300/00 Mixtures or combinations of active ingredients, wherein at least one active ingredient is fully defined in groups A61K 31/00 to A61K 41/00.
NOTE -A61K 2800/00 Properties of cosmetic compositions or active ingredients thereof or formulation aids used therein and process related aspects [Note:This subclass is a secondary classification, e.g. obligatory supplementary classification when already classified in group A61K 8/00 or subclass A61Q]
A61K 2800/10 ・General cosmetic use
A61K 2800/20 ・Chemical, physico-chemical or functional or structural properties of the composition as a whole
A61K 2800/21 ・・Emulsions characterized by droplet sizes below 1 micron
A61K 2800/22 ・・Gas releasing
A61K 2800/222 ・・・Effervescent
A61K 2800/24 ・・Thermal properties
A61K 2800/242 ・・・Exothermic; Self-heating; Heating sensation
A61K 2800/244 ・・・Endothermic; Cooling; Cooling sensation
A61K 2800/26 ・・Optical properties
A61K 2800/262 ・・・Transparent; Translucent
A61K 2800/28 ・・Rubbing or scrubbing compositions; Peeling or abrasive compositions; Containing exfoliants
A61K 2800/30 ・・Characterized by the absence of a particular group of ingredients
A61K 2800/31 ・・・Anhydrous
A61K 2800/33 ・・・Free of surfactant
A61K 2800/34 ・・・Free of silicones
A61K 2800/40 ・Chemical, physico-chemical or functional or structural properties of particular ingredients
A61K 2800/41 ・・Particular ingredients further characterized by their size
A61K 2800/412 ・・・Micro-sized, i.e. having sizes between 0.1 and 100 microns
A61K 2800/413 ・・・Nano-sized, i.e. having sizes below 100 nm
A61K 2800/42 ・・Colour properties
A61K 2800/43 ・・・Pigments; Dyes
A61K 2800/432 ・・・・Direct dyes
A61K 2800/4322 ・・・・・in preparations for temporarily coloring the hair further containing an oxidizing agent
A61K 2800/4324 ・・・・・in preparations for permanently dyeing the hair
A61K 2800/434 ・・・・Luminescent, Fluorescent; Optical brighteners; Photosensitizers
A61K 2800/436 ・・・・Interference pigments, e.g. Iridescent, Pearlescent
A61K 2800/437 ・・・・Diffractive phenomena; Photonic arrays
A61K 2800/438 ・・・・Thermochromatic; Photochromic; Phototropic
A61K 2800/45 ・・・Colour indicators, e.g. pH- or Redox indicators
A61K 2800/47 ・・Magnetic materials; Paramagnetic compounds
A61K 2800/48 ・・Thickener, Thickening system
A61K 2800/49 ・・Solubiliser, Solubilising system
A61K 2800/51 ・・Chelating agents
A61K 2800/52 ・・Stabilizers
A61K 2800/522 ・・・Antioxidants; Radical scavengers
A61K 2800/524 ・・・Preservatives
A61K 2800/526 ・・・Corrosion inhibitors
A61K 2800/54 ・・Polymers characterized by specific structures/properties
A61K 2800/542 ・・・characterized by the charge
A61K 2800/5422 ・・・・nonionic
A61K 2800/5424 ・・・・anionic
A61K 2800/5426 ・・・・cationic
A61K 2800/5428 ・・・・amphoteric or zwitterionic
A61K 2800/544 ・・・Dendrimers, Hyperbranched polymers
A61K 2800/546 ・・・Swellable particulate polymers
A61K 2800/548 ・・・Associative polymers
A61K 2800/56 ・・Compounds, absorbed onto or entrapped into a solid carrier, e.g. encapsulated perfumes, inclusion compounds, sustained release forms
A61K 2800/57 ・・Compounds covalently linked to a(n inert) carrier molecule, e.g. conjugates, pro-fragrances
A61K 2800/58 ・・Metal complex; Coordination compounds
A61K 2800/59 ・・Mixtures
A61K 2800/591 ・・・Mixtures of compounds not provided for by any of the codes A61K 2800/592 to A61K 2800/596
A61K 2800/592 ・・・Mixtures of compounds complementing their respective functions
A61K 2800/5922 ・・・・At least two compounds being classified in the same subclass of A61K 8/18
A61K 2800/594 ・・・Mixtures of polymers
A61K 2800/596 ・・・Mixtures of surface active compounds
A61K 2800/60 ・・Particulates further characterized by their structure or composition
A61K 2800/61 ・・・Surface treated
A61K 2800/612 ・・・・By organic compounds
A61K 2800/614 ・・・・By macromolecular compounds
A61K 2800/62 ・・・・Coated
A61K 2800/621 ・・・・・by inorganic compounds
A61K 2800/622 ・・・・・by organic compounds
A61K 2800/623 ・・・・・Coating mediated by organosilicone compounds
A61K 2800/624 ・・・・・by macromolecular compounds
A61K 2800/63 ・・・・・More than one coating
A61K 2800/65 ・・・Characterized by the composition of the particulate/core
A61K 2800/651 ・・・・The particulate/core comprising inorganic material
A61K 2800/652 ・・・・The particulate/core comprising organic material
A61K 2800/654 ・・・・The particulate/core comprising macromolecular material
A61K 2800/70 ・Biological properties of the composition as a whole
A61K 2800/72 ・・Hypo-allergenic
A61K 2800/74 ・Biological properties of particular ingredients
A61K 2800/75 ・・Anti-irritant
A61K 2800/77 ・・Perfumes having both deodorant and antibacterial properties
A61K 2800/78 ・・Enzyme modulators, e.g. Enzyme agonists
A61K 2800/782 ・・・Enzyme inhibitors; Enzyme antagonists
A61K 2800/80 ・Process related aspects concerning the preparation of the cosmetic composition or the storage or application thereof
A61K 2800/805 ・・Corresponding aspects not provided for by any of codes A61K 2800/81 to A61K 2800/95
A61K 2800/81 ・・Preparation or application process involves irradiation
A61K 2800/82 ・・Preparation or application process involves sonication or ultrasonication
A61K 2800/83 ・・Electrophoresis; Electrodes; Electrolytic phenomena
A61K 2800/84 ・・Products or compounds obtained by lyophilisation, freeze-drying
A61K 2800/85 ・・Products or compounds obtained by fermentation, e.g. yoghurt, beer, wine
A61K 2800/86 ・・Products or compounds obtained by genetic engineering
A61K 2800/87 ・・Application Devices; Containers; Packaging
A61K 2800/872 ・・・Pencils; Crayons; Felt-tip pens
A61K 2800/874 ・・・Roll-on
A61K 2800/88 ・・Two- or multipart kits
A61K 2800/882 ・・・Mixing prior to application
A61K 2800/884 ・・・Sequential application
A61K 2800/91 ・・Injection
A61K 2800/92 ・・Oral administration
A61K 2800/94 ・・Involves covalent bonding to the substrate
A61K 2800/95 ・・Involves in-situ formation or cross-linking of polymers
--- Edited by Muguruma Professional Engineer Office(C), 2013 ---